Input interpretation
ozone
Chemical names and formulas
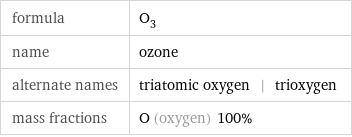
formula | O_3 name | ozone alternate names | triatomic oxygen | trioxygen mass fractions | O (oxygen) 100%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of ozone. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 3 n_O, val = 18 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 3 n_O, full = 24 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 24 - 18 = 6 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 2 bonds already present in the diagram add 1 bond. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 1 bond by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding the central oxygen to the other highlighted oxygen atom would result in an equivalent molecule: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
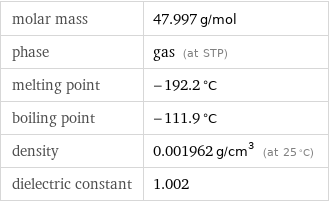
molar mass | 47.997 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -192.2 °C boiling point | -111.9 °C density | 0.001962 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) dielectric constant | 1.002
Gas properties (at STP)
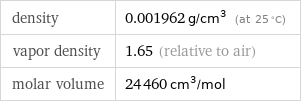
density | 0.001962 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) vapor density | 1.65 (relative to air) molar volume | 24460 cm^3/mol
Units

Thermodynamic properties

specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 0.8167 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 39.2 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 3.4 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 163.2 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 2.973 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 142.7 kJ/mol specific entropy S° | gas | 4.979 J/(g K) molar entropy S° | gas | 239 J/(mol K) critical temperature | 261 K | critical pressure | 5.45 MPa | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
![CAS number | 10028-15-6 PubChem CID number | 24823 SMILES identifier | [O-][O+]=O InChI identifier | InChI=1/O3/c1-3-2 EU number | 233-069-2 Gmelin number | 1101 RTECS number | RS8225000](../image_source/fa36a1afbb1e9eea7e3e4c52dc7c99b4.png)
CAS number | 10028-15-6 PubChem CID number | 24823 SMILES identifier | [O-][O+]=O InChI identifier | InChI=1/O3/c1-3-2 EU number | 233-069-2 Gmelin number | 1101 RTECS number | RS8225000
Toxicity properties

short-term exposure limit | 0.6 mg/m^3

long-term exposure limit | 0.2 mg/m^3 (over 8 hours) RTECS classes | tumorigen | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data | primary irritant