Input interpretation
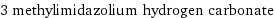
3 methylimidazolium hydrogen carbonate
Basic properties
![molar mass | 144.1 g/mol formula | C_5H_8N_2O_3 empirical formula | C_5O_3N_2H_8 SMILES identifier | CN1C=C[NH+]=C1.C(=O)(O)[O-] InChI identifier | InChI=1/C4H6N2.CH2O3/c1-6-3-2-5-4-6;2-1(3)4/h2-4H, 1H3;(H2, 2, 3, 4)/fC4H7N2.CHO3/h5H;2H/q+1;-1 InChI key | BOHWBTQSJFPMFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N](../image_source/0be024ea9661d5c788d2282e70d59d25.png)
molar mass | 144.1 g/mol formula | C_5H_8N_2O_3 empirical formula | C_5O_3N_2H_8 SMILES identifier | CN1C=C[NH+]=C1.C(=O)(O)[O-] InChI identifier | InChI=1/C4H6N2.CH2O3/c1-6-3-2-5-4-6;2-1(3)4/h2-4H, 1H3;(H2, 2, 3, 4)/fC4H7N2.CHO3/h5H;2H/q+1;-1 InChI key | BOHWBTQSJFPMFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Structure diagram
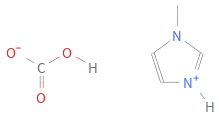
Structure diagram
Quantitative molecular descriptors
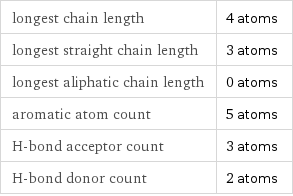
longest chain length | 4 atoms longest straight chain length | 3 atoms longest aliphatic chain length | 0 atoms aromatic atom count | 5 atoms H-bond acceptor count | 3 atoms H-bond donor count | 2 atoms
Elemental composition
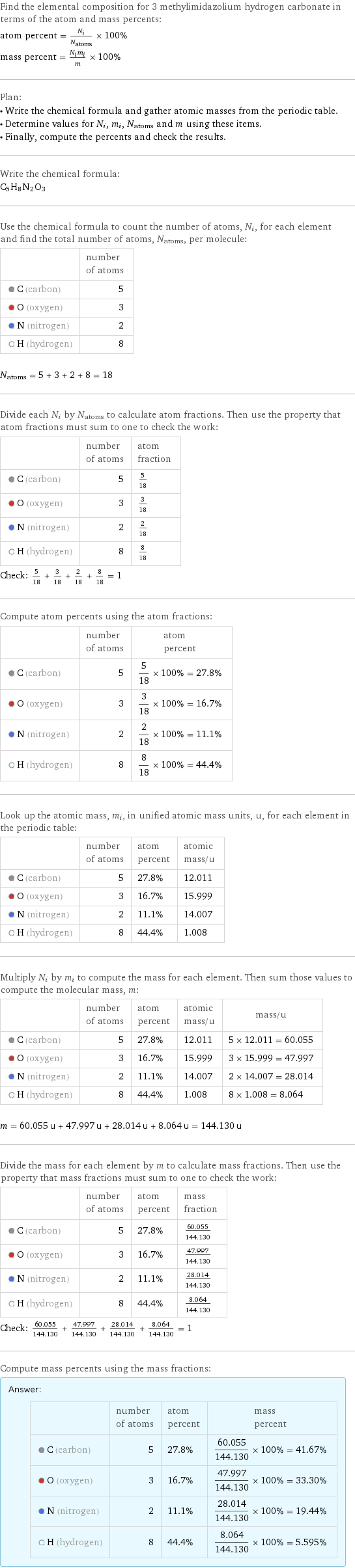
Find the elemental composition for 3 methylimidazolium hydrogen carbonate in terms of the atom and mass percents: atom percent = N_i/N_atoms × 100% mass percent = (N_im_i)/m × 100% Plan: • Write the chemical formula and gather atomic masses from the periodic table. • Determine values for N_i, m_i, N_atoms and m using these items. • Finally, compute the percents and check the results. Write the chemical formula: C_5H_8N_2O_3 Use the chemical formula to count the number of atoms, N_i, for each element and find the total number of atoms, N_atoms, per molecule: | number of atoms C (carbon) | 5 O (oxygen) | 3 N (nitrogen) | 2 H (hydrogen) | 8 N_atoms = 5 + 3 + 2 + 8 = 18 Divide each N_i by N_atoms to calculate atom fractions. Then use the property that atom fractions must sum to one to check the work: | number of atoms | atom fraction C (carbon) | 5 | 5/18 O (oxygen) | 3 | 3/18 N (nitrogen) | 2 | 2/18 H (hydrogen) | 8 | 8/18 Check: 5/18 + 3/18 + 2/18 + 8/18 = 1 Compute atom percents using the atom fractions: | number of atoms | atom percent C (carbon) | 5 | 5/18 × 100% = 27.8% O (oxygen) | 3 | 3/18 × 100% = 16.7% N (nitrogen) | 2 | 2/18 × 100% = 11.1% H (hydrogen) | 8 | 8/18 × 100% = 44.4% Look up the atomic mass, m_i, in unified atomic mass units, u, for each element in the periodic table: | number of atoms | atom percent | atomic mass/u C (carbon) | 5 | 27.8% | 12.011 O (oxygen) | 3 | 16.7% | 15.999 N (nitrogen) | 2 | 11.1% | 14.007 H (hydrogen) | 8 | 44.4% | 1.008 Multiply N_i by m_i to compute the mass for each element. Then sum those values to compute the molecular mass, m: | number of atoms | atom percent | atomic mass/u | mass/u C (carbon) | 5 | 27.8% | 12.011 | 5 × 12.011 = 60.055 O (oxygen) | 3 | 16.7% | 15.999 | 3 × 15.999 = 47.997 N (nitrogen) | 2 | 11.1% | 14.007 | 2 × 14.007 = 28.014 H (hydrogen) | 8 | 44.4% | 1.008 | 8 × 1.008 = 8.064 m = 60.055 u + 47.997 u + 28.014 u + 8.064 u = 144.130 u Divide the mass for each element by m to calculate mass fractions. Then use the property that mass fractions must sum to one to check the work: | number of atoms | atom percent | mass fraction C (carbon) | 5 | 27.8% | 60.055/144.130 O (oxygen) | 3 | 16.7% | 47.997/144.130 N (nitrogen) | 2 | 11.1% | 28.014/144.130 H (hydrogen) | 8 | 44.4% | 8.064/144.130 Check: 60.055/144.130 + 47.997/144.130 + 28.014/144.130 + 8.064/144.130 = 1 Compute mass percents using the mass fractions: Answer: | | | number of atoms | atom percent | mass percent C (carbon) | 5 | 27.8% | 60.055/144.130 × 100% = 41.67% O (oxygen) | 3 | 16.7% | 47.997/144.130 × 100% = 33.30% N (nitrogen) | 2 | 11.1% | 28.014/144.130 × 100% = 19.44% H (hydrogen) | 8 | 44.4% | 8.064/144.130 × 100% = 5.595%
Elemental oxidation states
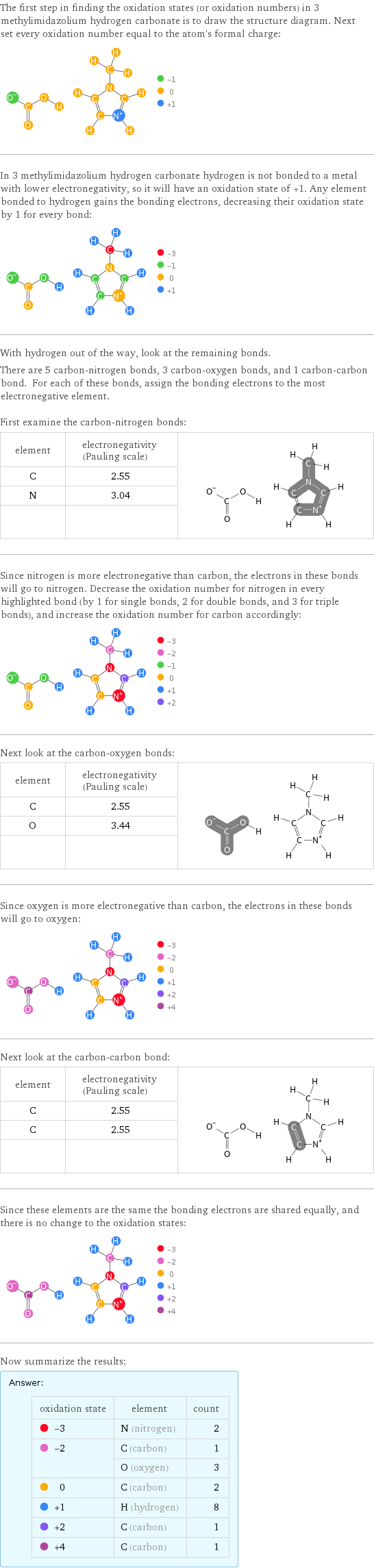
The first step in finding the oxidation states (or oxidation numbers) in 3 methylimidazolium hydrogen carbonate is to draw the structure diagram. Next set every oxidation number equal to the atom's formal charge: In 3 methylimidazolium hydrogen carbonate hydrogen is not bonded to a metal with lower electronegativity, so it will have an oxidation state of +1. Any element bonded to hydrogen gains the bonding electrons, decreasing their oxidation state by 1 for every bond: With hydrogen out of the way, look at the remaining bonds. There are 5 carbon-nitrogen bonds, 3 carbon-oxygen bonds, and 1 carbon-carbon bond. For each of these bonds, assign the bonding electrons to the most electronegative element. First examine the carbon-nitrogen bonds: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | C | 2.55 | N | 3.04 | | | Since nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon, the electrons in these bonds will go to nitrogen. Decrease the oxidation number for nitrogen in every highlighted bond (by 1 for single bonds, 2 for double bonds, and 3 for triple bonds), and increase the oxidation number for carbon accordingly: Next look at the carbon-oxygen bonds: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | C | 2.55 | O | 3.44 | | | Since oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, the electrons in these bonds will go to oxygen: Next look at the carbon-carbon bond: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | C | 2.55 | C | 2.55 | | | Since these elements are the same the bonding electrons are shared equally, and there is no change to the oxidation states: Now summarize the results: Answer: | | oxidation state | element | count -3 | N (nitrogen) | 2 -2 | C (carbon) | 1 | O (oxygen) | 3 0 | C (carbon) | 2 +1 | H (hydrogen) | 8 +2 | C (carbon) | 1 +4 | C (carbon) | 1
Orbital hybridization
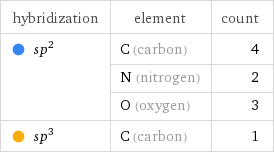
hybridization | element | count sp^2 | C (carbon) | 4 | N (nitrogen) | 2 | O (oxygen) | 3 sp^3 | C (carbon) | 1
Structure diagram
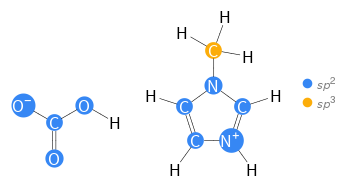
Orbital hybridization Structure diagram
Topological indices
vertex count | 18 edge count | 17 Schultz index | Wiener index | Hosoya index | Balaban index |