Input interpretation

caffeine
Chemical names and formulas
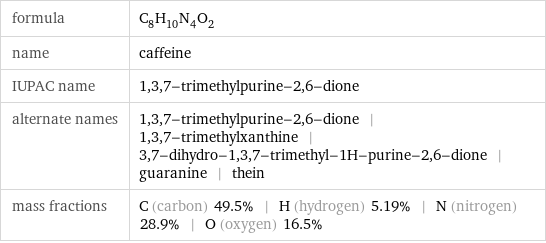
formula | C_8H_10N_4O_2 name | caffeine IUPAC name | 1, 3, 7-trimethylpurine-2, 6-dione alternate names | 1, 3, 7-trimethylpurine-2, 6-dione | 1, 3, 7-trimethylxanthine | 3, 7-dihydro-1, 3, 7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2, 6-dione | guaranine | thein mass fractions | C (carbon) 49.5% | H (hydrogen) 5.19% | N (nitrogen) 28.9% | O (oxygen) 16.5%
Lewis structure
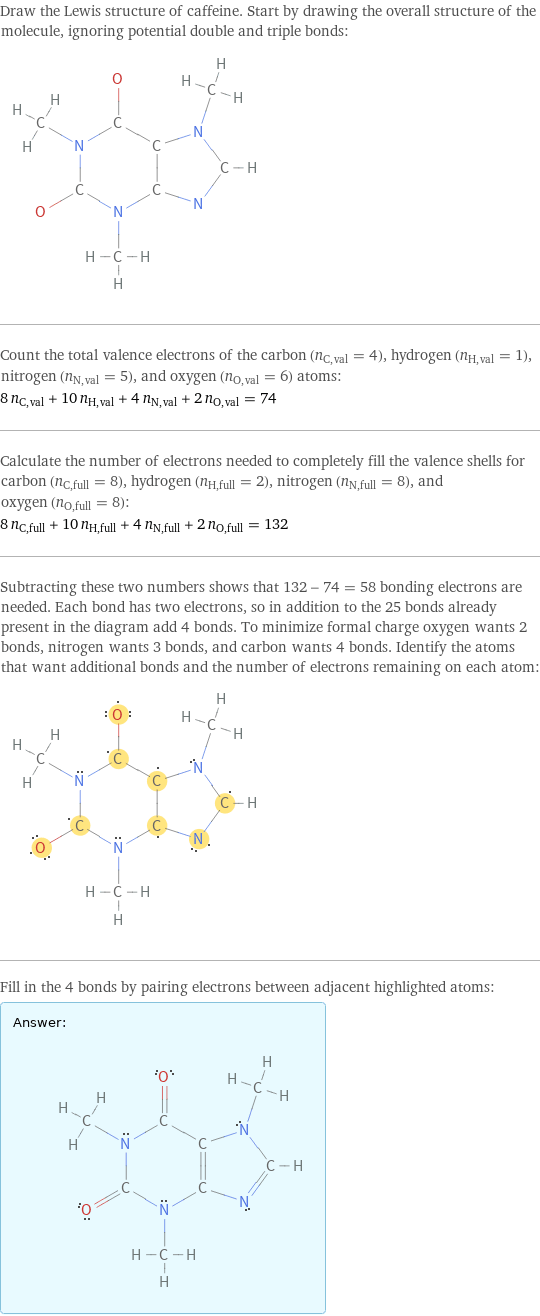
Draw the Lewis structure of caffeine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 8 n_C, val + 10 n_H, val + 4 n_N, val + 2 n_O, val = 74 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 8 n_C, full + 10 n_H, full + 4 n_N, full + 2 n_O, full = 132 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 132 - 74 = 58 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 25 bonds already present in the diagram add 4 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds, nitrogen wants 3 bonds, and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 4 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
3D structure
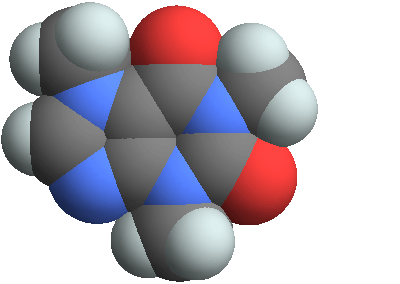
3D structure
Basic properties
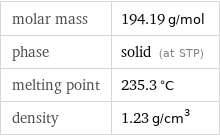
molar mass | 194.19 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 235.3 °C density | 1.23 g/cm^3
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | -0.5 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | -0.23 experimental LogS | -0.97 predicted LogS | -1.25 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -4.41
Basic drug properties
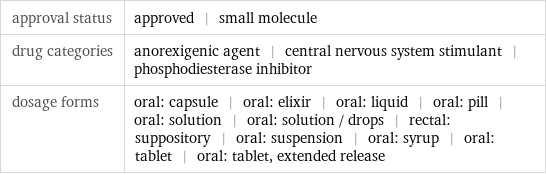
approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | anorexigenic agent | central nervous system stimulant | phosphodiesterase inhibitor dosage forms | oral: capsule | oral: elixir | oral: liquid | oral: pill | oral: solution | oral: solution / drops | rectal: suppository | oral: suspension | oral: syrup | oral: tablet | oral: tablet, extended release
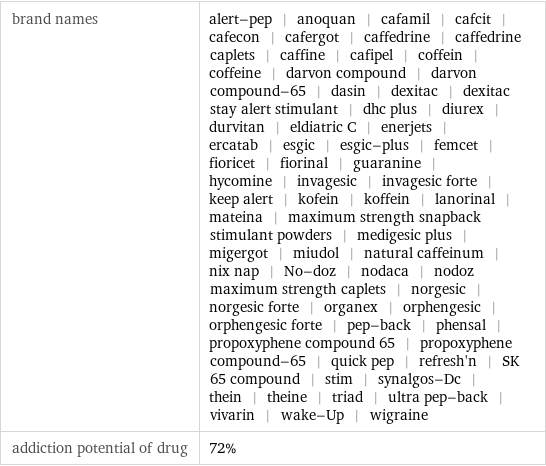
brand names | alert-pep | anoquan | cafamil | cafcit | cafecon | cafergot | caffedrine | caffedrine caplets | caffine | cafipel | coffein | coffeine | darvon compound | darvon compound-65 | dasin | dexitac | dexitac stay alert stimulant | dhc plus | diurex | durvitan | eldiatric C | enerjets | ercatab | esgic | esgic-plus | femcet | fioricet | fiorinal | guaranine | hycomine | invagesic | invagesic forte | keep alert | kofein | koffein | lanorinal | mateina | maximum strength snapback stimulant powders | medigesic plus | migergot | miudol | natural caffeinum | nix nap | No-doz | nodaca | nodoz maximum strength caplets | norgesic | norgesic forte | organex | orphengesic | orphengesic forte | pep-back | phensal | propoxyphene compound 65 | propoxyphene compound-65 | quick pep | refresh'n | SK 65 compound | stim | synalgos-Dc | thein | theine | triad | ultra pep-back | vivarin | wake-Up | wigraine addiction potential of drug | 72%
Solid properties (at STP)
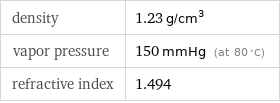
density | 1.23 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 150 mmHg (at 80 °C) refractive index | 1.494
Units

Thermodynamic properties

molar heat of fusion | 22 kJ/mol specific heat of fusion | 0.11 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 58-08-2 Beilstein number | 17705 PubChem CID number | 2519 PubChem SID number | 148854 SMILES identifier | CN1C=NC2=C1C(=O)N(C(=O)N2C)C InChI identifier | InChI=1/C8H10N4O2/c1-10-4-9-6-5(10)7(13)12(3)8(14)11(6)2/h4H, 1-3H3 InChI key | RYYVLZVUVIJVGH-UHFFFAOYAW RTECS number | EV6475000 MDL number | MFCD00005758
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 2 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties

autoignition point | 600 °C

DOT hazard class | 6.1 DOT numbers | 1544
Toxicity properties
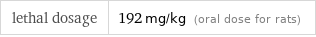
lethal dosage | 192 mg/kg (oral dose for rats)

probable lethal dose for man | 30 mL (milliliters) RTECS classes | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data | natural product