Input interpretation
chlorine pentafluoride
Chemical names and formulas
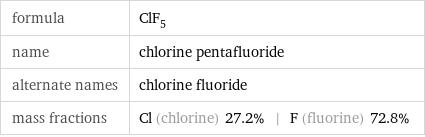
formula | ClF_5 name | chlorine pentafluoride alternate names | chlorine fluoride mass fractions | Cl (chlorine) 27.2% | F (fluorine) 72.8%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of chlorine pentafluoride. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the chlorine (n_Cl, val = 7) and fluorine (n_F, val = 7) atoms: n_Cl, val + 5 n_F, val = 42 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for chlorine (n_Cl, full = 8) and fluorine (n_F, full = 8): n_Cl, full + 5 n_F, full = 48 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 48 - 42 = 6 bonding electrons are needed, which are already accounted for in the structure. Note that the valence shell of chlorine has been expanded to 5 bonds. After accounting for the expanded valence, there are 5 bonds and hence 10 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 42 - 10 = 32 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
Basic properties

molar mass | 130.44 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -90 °C boiling point | -13.1 °C density | 0.005332 g/cm^3 (at 20 °C)
Units

Gas properties (at STP)
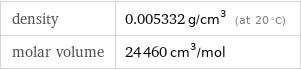
density | 0.005332 g/cm^3 (at 20 °C) molar volume | 24460 cm^3/mol
Units

Thermodynamic properties
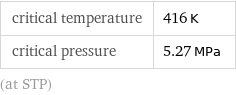
critical temperature | 416 K critical pressure | 5.27 MPa (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
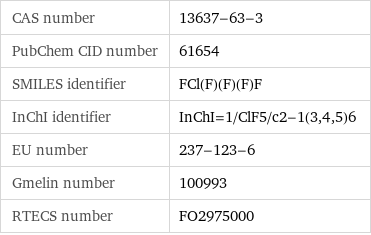
CAS number | 13637-63-3 PubChem CID number | 61654 SMILES identifier | FCl(F)(F)(F)F InChI identifier | InChI=1/ClF5/c2-1(3, 4, 5)6 EU number | 237-123-6 Gmelin number | 100993 RTECS number | FO2975000
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | other