Input interpretation

cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate | melting point
Result

56 °C (degrees Celsius)
Unit conversions
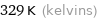
329 K (kelvins)
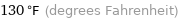
130 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

590 °R (degrees Rankine)

45 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
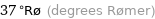
37 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature
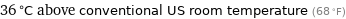
36 °C above conventional US room temperature (68 °F)

36 °C above temperature at STP (standard temperature and pressure), using the National Institute of Standards and Technology convention (20 °C)

40 °C above temperature at STP (standard temperature and pressure), using the US customary convention (60 °F)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 28 meV (millielectronvolts)
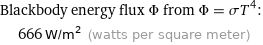
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 666 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 6.5×10^-19 lx (lux)
Nearest corresponding gas marks

| temperature | usage thermostat 2 | 60 °C | France (actual measurements may vary)