Input interpretation
ascorbic acid
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | H_2C_6H_6O_6 Hill formula | C_6H_8O_6 name | ascorbic acid alternate names | (2R)-2-[(1S)-1, 2-dihydroxyethyl]-4, 5-dihydroxy-furan-3-one | (2R)-2-[(1S)-1, 2-dihydroxyethyl]-4, 5-dihydroxyfuran-3-one | antiscorbutic factor | L-3-ketothreohexuronic acid lactone | L-(+)-ascorbic acid | L-threoascorbic acid | vitamin C mass fractions | C (carbon) 40.9% | H (hydrogen) 4.58% | O (oxygen) 54.5%](../image_source/3de544de011cb8dc5bdf394685169814.png)
formula | H_2C_6H_6O_6 Hill formula | C_6H_8O_6 name | ascorbic acid alternate names | (2R)-2-[(1S)-1, 2-dihydroxyethyl]-4, 5-dihydroxy-furan-3-one | (2R)-2-[(1S)-1, 2-dihydroxyethyl]-4, 5-dihydroxyfuran-3-one | antiscorbutic factor | L-3-ketothreohexuronic acid lactone | L-(+)-ascorbic acid | L-threoascorbic acid | vitamin C mass fractions | C (carbon) 40.9% | H (hydrogen) 4.58% | O (oxygen) 54.5%
Lewis structure
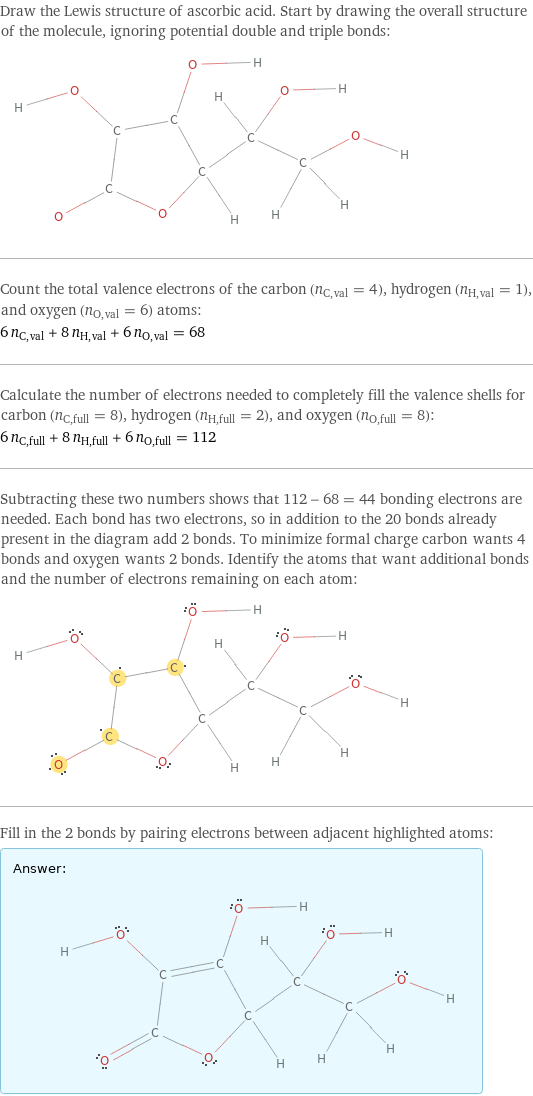
Draw the Lewis structure of ascorbic acid. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 6 n_C, val + 8 n_H, val + 6 n_O, val = 68 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 6 n_C, full + 8 n_H, full + 6 n_O, full = 112 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 112 - 68 = 44 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 20 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds and oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
Basic properties
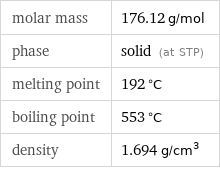
molar mass | 176.12 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 192 °C boiling point | 553 °C density | 1.694 g/cm^3
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | -0.5 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | -1.86 predicted LogS | 0.16
Basic drug properties
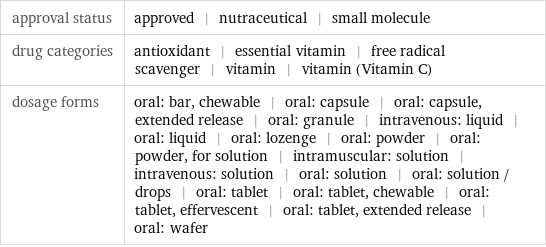
approval status | approved | nutraceutical | small molecule drug categories | antioxidant | essential vitamin | free radical scavenger | vitamin | vitamin (Vitamin C) dosage forms | oral: bar, chewable | oral: capsule | oral: capsule, extended release | oral: granule | intravenous: liquid | oral: liquid | oral: lozenge | oral: powder | oral: powder, for solution | intramuscular: solution | intravenous: solution | oral: solution | oral: solution / drops | oral: tablet | oral: tablet, chewable | oral: tablet, effervescent | oral: tablet, extended release | oral: wafer
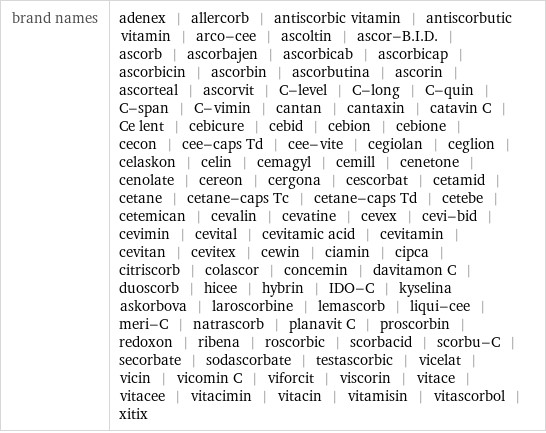
brand names | adenex | allercorb | antiscorbic vitamin | antiscorbutic vitamin | arco-cee | ascoltin | ascor-B.I.D. | ascorb | ascorbajen | ascorbicab | ascorbicap | ascorbicin | ascorbin | ascorbutina | ascorin | ascorteal | ascorvit | C-level | C-long | C-quin | C-span | C-vimin | cantan | cantaxin | catavin C | Ce lent | cebicure | cebid | cebion | cebione | cecon | cee-caps Td | cee-vite | cegiolan | ceglion | celaskon | celin | cemagyl | cemill | cenetone | cenolate | cereon | cergona | cescorbat | cetamid | cetane | cetane-caps Tc | cetane-caps Td | cetebe | cetemican | cevalin | cevatine | cevex | cevi-bid | cevimin | cevital | cevitamic acid | cevitamin | cevitan | cevitex | cewin | ciamin | cipca | citriscorb | colascor | concemin | davitamon C | duoscorb | hicee | hybrin | IDO-C | kyselina askorbova | laroscorbine | lemascorb | liqui-cee | meri-C | natrascorb | planavit C | proscorbin | redoxon | ribena | roscorbic | scorbacid | scorbu-C | secorbate | sodascorbate | testascorbic | vicelat | vicin | vicomin C | viforcit | viscorin | vitace | vitacee | vitacimin | vitacin | vitamisin | vitascorbol | xitix
Solid properties (at STP)

density | 1.694 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 2×10^-14 mmHg (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties
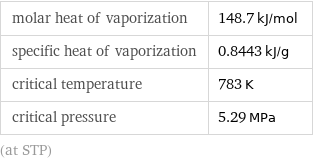
molar heat of vaporization | 148.7 kJ/mol specific heat of vaporization | 0.8443 kJ/g critical temperature | 783 K critical pressure | 5.29 MPa (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
O1)O)O)O)O InChI key | TYQCGQRIZGCHNB-JLAZNSOCBA RTECS number | CI7650000 MDL number | MFCD00064328](../image_source/c5a2bd8b756ad5ba37be97b3f3335941.png)
CAS number | 50-81-7 Beilstein number | 84272 SMILES identifier | C([C@@H]([C@@H]1C(=C(C(=O)O1)O)O)O)O InChI key | TYQCGQRIZGCHNB-JLAZNSOCBA RTECS number | CI7650000 MDL number | MFCD00064328
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 1 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties
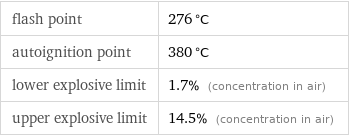
flash point | 276 °C autoignition point | 380 °C lower explosive limit | 1.7% (concentration in air) upper explosive limit | 14.5% (concentration in air)
Toxicity properties
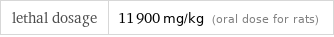
lethal dosage | 11900 mg/kg (oral dose for rats)

probable lethal dose for man | 1 L (liter) RTECS classes | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data