Input interpretation
nitric acid
Physical properties

vapor pressure | 1.935 kPa (kilopascals)
Solution properties
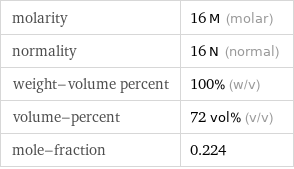
molarity | 16 M (molar) normality | 16 N (normal) weight-volume percent | 100% (w/v) volume-percent | 72 vol% (v/v) mole-fraction | 0.224
Solute properties per 100 mL
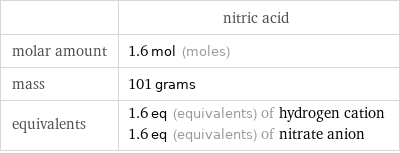
| nitric acid molar amount | 1.6 mol (moles) mass | 101 grams equivalents | 1.6 eq (equivalents) of hydrogen cation 1.6 eq (equivalents) of nitrate anion
Acid-base information
![K_a | 100. pK_a | -2.00 pH | -1.20 [H_3O^+] | 16 mol/L (moles per liter) pOH | 15.2 [OH^-] | 6.25×10^-16 mol/L (moles per liter) % ionization | 100%](../image_source/ba7a5b16c223b071d2435abe740a9e7a.png)
K_a | 100. pK_a | -2.00 pH | -1.20 [H_3O^+] | 16 mol/L (moles per liter) pOH | 15.2 [OH^-] | 6.25×10^-16 mol/L (moles per liter) % ionization | 100%
Lewis structure
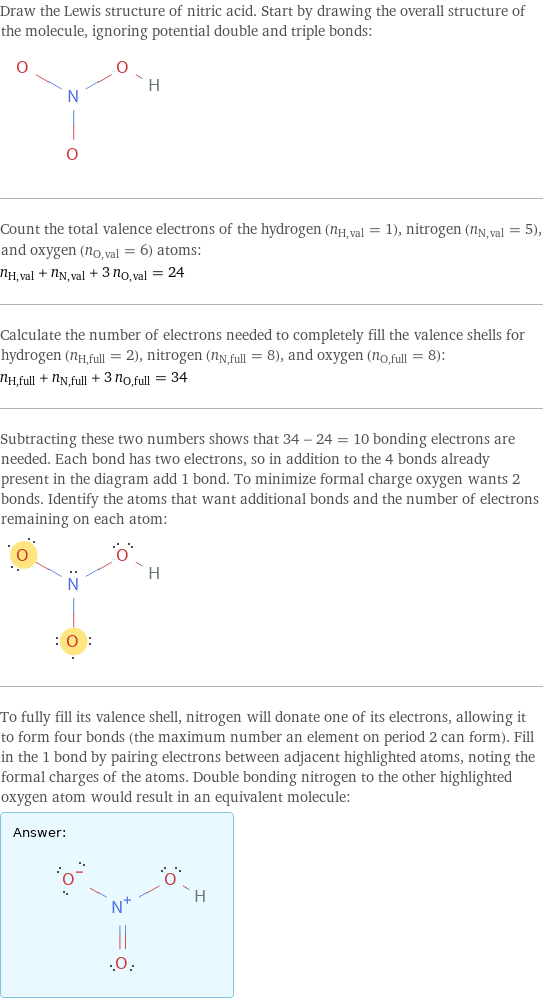
Draw the Lewis structure of nitric acid. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: n_H, val + n_N, val + 3 n_O, val = 24 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): n_H, full + n_N, full + 3 n_O, full = 34 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 34 - 24 = 10 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 4 bonds already present in the diagram add 1 bond. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: To fully fill its valence shell, nitrogen will donate one of its electrons, allowing it to form four bonds (the maximum number an element on period 2 can form). Fill in the 1 bond by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding nitrogen to the other highlighted oxygen atom would result in an equivalent molecule: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
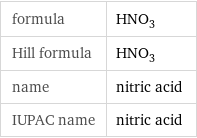
formula | HNO_3 Hill formula | HNO_3 name | nitric acid IUPAC name | nitric acid
Substance properties
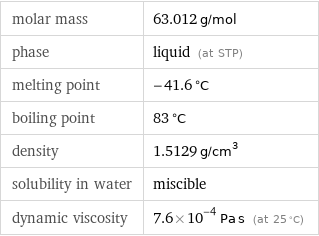
molar mass | 63.012 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | -41.6 °C boiling point | 83 °C density | 1.5129 g/cm^3 solubility in water | miscible dynamic viscosity | 7.6×10^-4 Pa s (at 25 °C)
Units
