Input interpretation
fluoxetine
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | C_17H_18F_3NO name | fluoxetine IUPAC name | N-methyl-3-phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propan-1-amine alternate names | deprex | fluval | prozac mass fractions | C (carbon) 66% | F (fluorine) 18.4% | H (hydrogen) 5.87% | N (nitrogen) 4.53% | O (oxygen) 5.17%](../image_source/5feed2297a53f6a8d695238845fad327.png)
formula | C_17H_18F_3NO name | fluoxetine IUPAC name | N-methyl-3-phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propan-1-amine alternate names | deprex | fluval | prozac mass fractions | C (carbon) 66% | F (fluorine) 18.4% | H (hydrogen) 5.87% | N (nitrogen) 4.53% | O (oxygen) 5.17%
Lewis structure
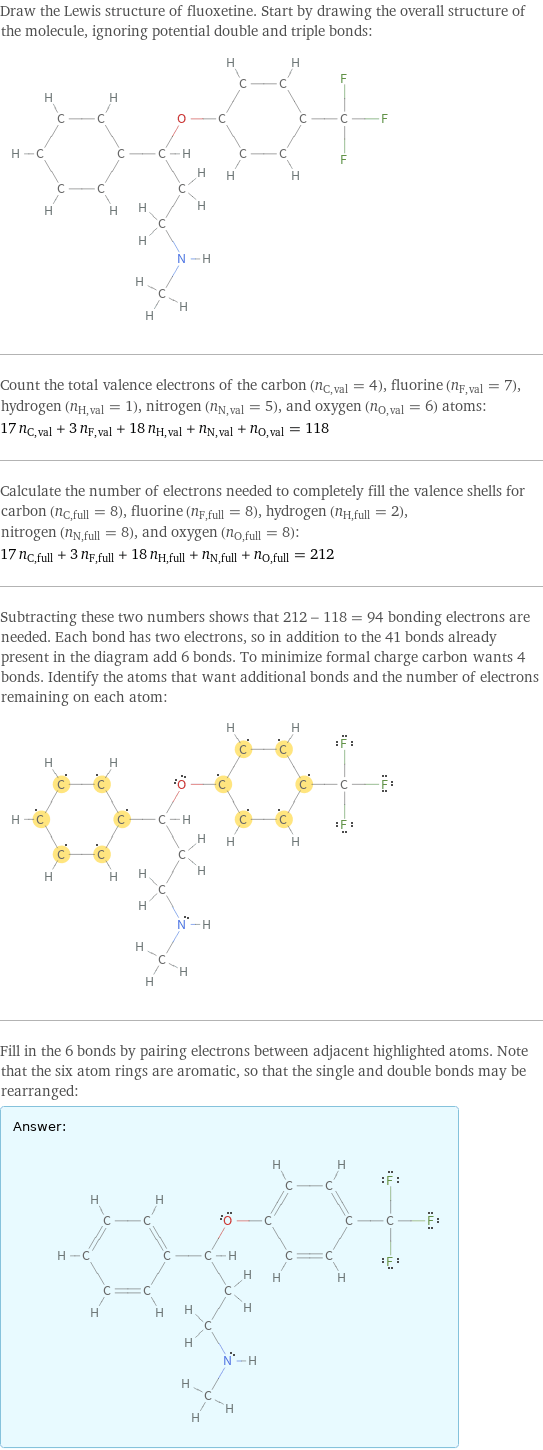
Draw the Lewis structure of fluoxetine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), fluorine (n_F, val = 7), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 17 n_C, val + 3 n_F, val + 18 n_H, val + n_N, val + n_O, val = 118 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), fluorine (n_F, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 17 n_C, full + 3 n_F, full + 18 n_H, full + n_N, full + n_O, full = 212 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 212 - 118 = 94 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 41 bonds already present in the diagram add 6 bonds. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 6 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom rings are aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
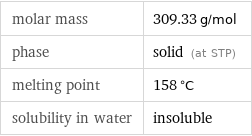
molar mass | 309.33 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 158 °C solubility in water | insoluble
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 4.6 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 4.1 predicted LogS | -5.26
Drug interactions

acenocoumarol | almotriptan | amitriptyline | amoxapine | amphetamine | anisindione | astemizole | atomoxetine | benzphetamine | carbamazepine | carvedilol | cilostazol | clarithromycin | clomipramine | clozapine | cyclosporin A | cyproheptadine | desipramine | dexfenfluramine | dextroamphetamine | ... (total: 71)
Basic drug properties
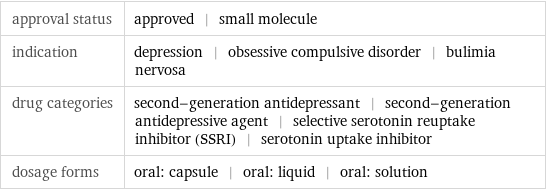
approval status | approved | small molecule indication | depression | obsessive compulsive disorder | bulimia nervosa drug categories | second-generation antidepressant | second-generation antidepressive agent | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) | serotonin uptake inhibitor dosage forms | oral: capsule | oral: liquid | oral: solution
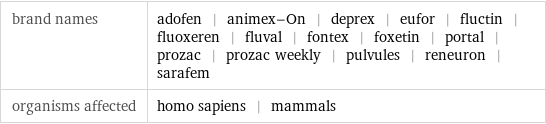
brand names | adofen | animex-On | deprex | eufor | fluctin | fluoxeren | fluval | fontex | foxetin | portal | prozac | prozac weekly | pulvules | reneuron | sarafem organisms affected | homo sapiens | mammals
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
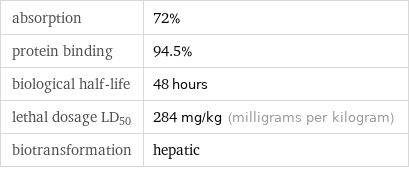
absorption | 72% protein binding | 94.5% biological half-life | 48 hours lethal dosage LD_50 | 284 mg/kg (milligrams per kilogram) biotransformation | hepatic
Chemical identifiers
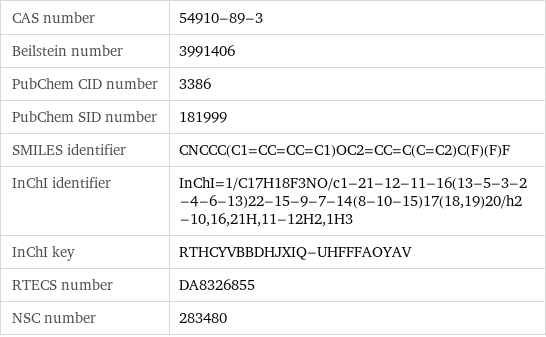
CAS number | 54910-89-3 Beilstein number | 3991406 PubChem CID number | 3386 PubChem SID number | 181999 SMILES identifier | CNCCC(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC2=CC=C(C=C2)C(F)(F)F InChI identifier | InChI=1/C17H18F3NO/c1-21-12-11-16(13-5-3-2-4-6-13)22-15-9-7-14(8-10-15)17(18, 19)20/h2-10, 16, 21H, 11-12H2, 1H3 InChI key | RTHCYVBBDHJXIQ-UHFFFAOYAV RTECS number | DA8326855 NSC number | 283480
Toxicity properties

lethal dosage LD_50 | 284 mg/kg (oral dose for mice)

RTECS classes | drug | reproductive effector | human data