Input interpretation
hydroxide anion
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of hydroxide anion. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms, including the net charge: n_H, val + n_O, val - n_charge = 8 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2) and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): n_H, full + n_O, full = 10 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 10 - 8 = 2 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There is 1 bond and hence 2 bonding electrons in the diagram. Fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 8 - 2 = 6 electrons left to draw. Lastly, fill in the formal charges: Answer: | |
General properties
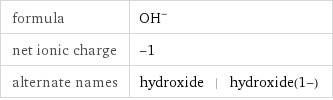
formula | (OH)^- net ionic charge | -1 alternate names | hydroxide | hydroxide(1-)
Ionic radii

4-coordinate | 135 pm 6-coordinate | 137 pm thermochemical radius | 133 pm
Units

Other properties

ion class | anions | biomolecule ions | oxoanions | polyatomic ions | ionic strong bases common sources of ion | strontium lanthanum aluminate (2 eq) | strontium hydroxide octahydrate (2 eq) | strontium hydroxide (2 eq) | sodium phosphomolybdate hydrate (1 eq) | rubidium hydroxide hydrate (1 eq) | potassium hexahydroxyantimonate (6 eq) | magnesium hydroxide (2 eq)
Thermodynamic properties
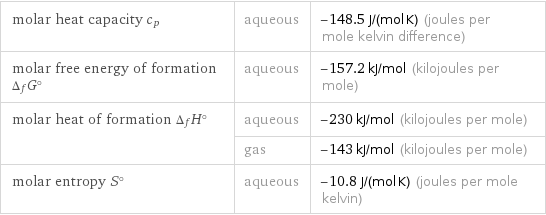
molar heat capacity c_p | aqueous | -148.5 J/(mol K) (joules per mole kelvin difference) molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | aqueous | -157.2 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | aqueous | -230 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | gas | -143 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) molar entropy S° | aqueous | -10.8 J/(mol K) (joules per mole kelvin)