Input interpretation
methylene chloride
Chemical names and formulas
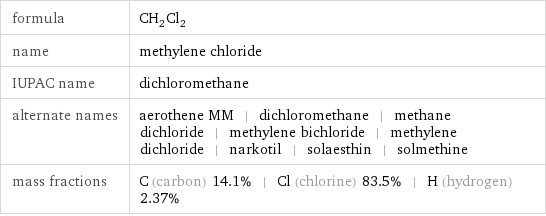
formula | CH_2Cl_2 name | methylene chloride IUPAC name | dichloromethane alternate names | aerothene MM | dichloromethane | methane dichloride | methylene bichloride | methylene dichloride | narkotil | solaesthin | solmethine mass fractions | C (carbon) 14.1% | Cl (chlorine) 83.5% | H (hydrogen) 2.37%
Lewis structure
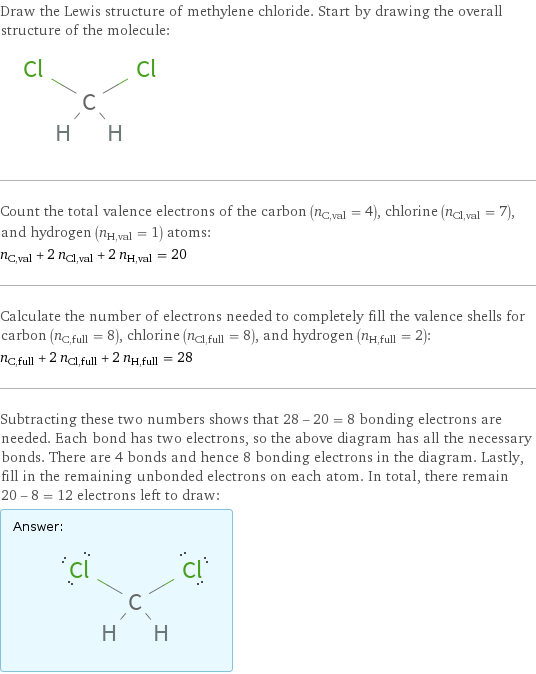
Draw the Lewis structure of methylene chloride. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), chlorine (n_Cl, val = 7), and hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: n_C, val + 2 n_Cl, val + 2 n_H, val = 20 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), chlorine (n_Cl, full = 8), and hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): n_C, full + 2 n_Cl, full + 2 n_H, full = 28 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 28 - 20 = 8 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 4 bonds and hence 8 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 20 - 8 = 12 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
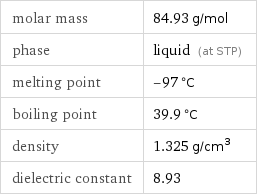
molar mass | 84.93 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | -97 °C boiling point | 39.9 °C density | 1.325 g/cm^3 dielectric constant | 8.93
Liquid properties (at STP)
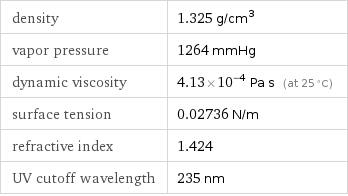
density | 1.325 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 1264 mmHg dynamic viscosity | 4.13×10^-4 Pa s (at 25 °C) surface tension | 0.02736 N/m refractive index | 1.424 UV cutoff wavelength | 235 nm
Units
Thermodynamic properties
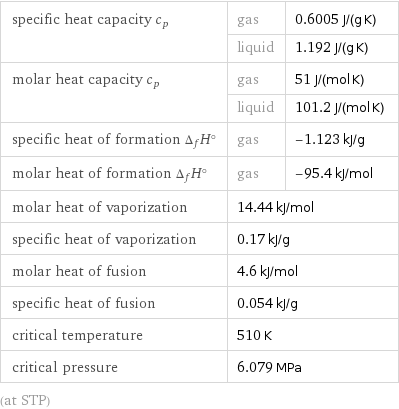
specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 0.6005 J/(g K) | liquid | 1.192 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 51 J/(mol K) | liquid | 101.2 J/(mol K) specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -1.123 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -95.4 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 14.44 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.17 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 4.6 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.054 kJ/g | critical temperature | 510 K | critical pressure | 6.079 MPa | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
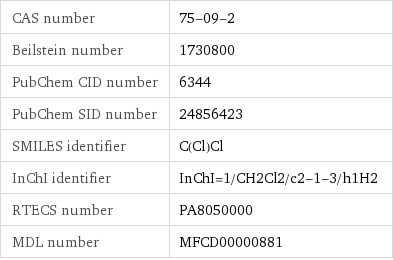
CAS number | 75-09-2 Beilstein number | 1730800 PubChem CID number | 6344 PubChem SID number | 24856423 SMILES identifier | C(Cl)Cl InChI identifier | InChI=1/CH2Cl2/c2-1-3/h1H2 RTECS number | PA8050000 MDL number | MFCD00000881
NFPA label

NFPA label
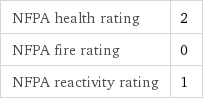
NFPA health rating | 2 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 1
Safety properties
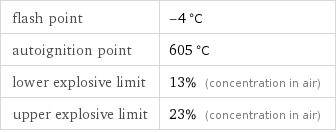
flash point | -4 °C autoignition point | 605 °C lower explosive limit | 13% (concentration in air) upper explosive limit | 23% (concentration in air)
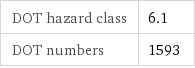
DOT hazard class | 6.1 DOT numbers | 1593
Toxicity properties
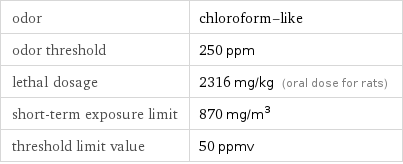
odor | chloroform-like odor threshold | 250 ppm lethal dosage | 2316 mg/kg (oral dose for rats) short-term exposure limit | 870 mg/m^3 threshold limit value | 50 ppmv
probable lethal dose for man | 600 mL (milliliters) long-term exposure limit | 350 mg/m^3 (over 8 hours) RTECS classes | agricultural chemical and pesticide | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data | primary irritant