Input interpretation
halogenated compounds | element types
Summary
bromine | carbon | chlorine | copper | fluorine | hydrogen | iodine | potassium | lithium | nitrogen | sodium | oxygen | rubidium | zinc
Periodic table location
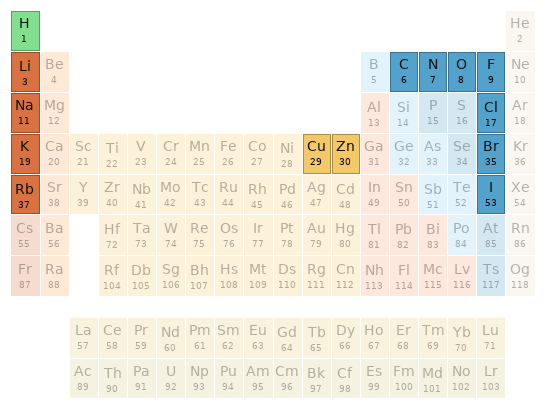
Periodic table location
Images

Images
Basic elemental properties
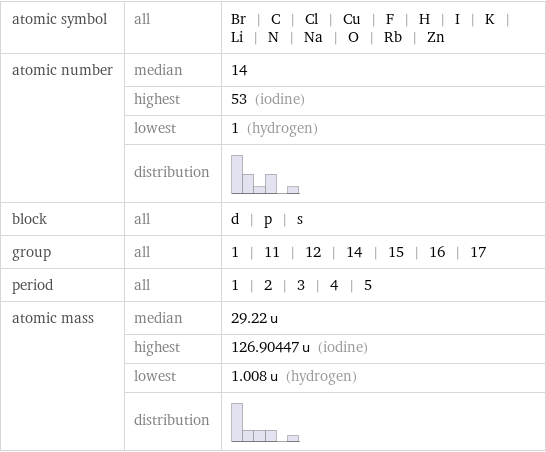
atomic symbol | all | Br | C | Cl | Cu | F | H | I | K | Li | N | Na | O | Rb | Zn atomic number | median | 14 | highest | 53 (iodine) | lowest | 1 (hydrogen) | distribution | block | all | d | p | s group | all | 1 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 period | all | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 atomic mass | median | 29.22 u | highest | 126.90447 u (iodine) | lowest | 1.008 u (hydrogen) | distribution |
Table
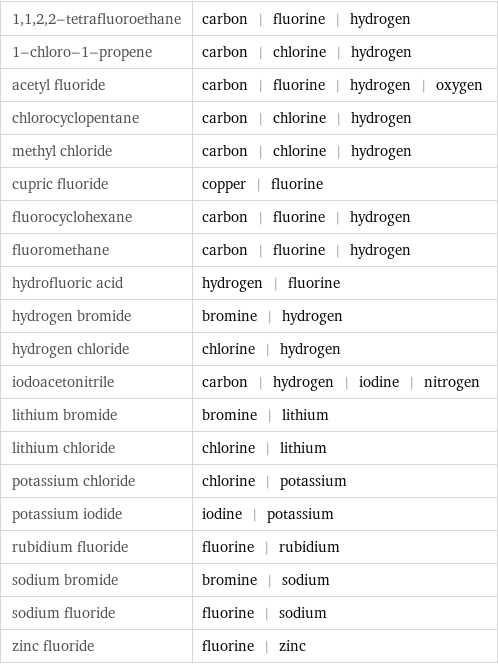
1, 1, 2, 2-tetrafluoroethane | carbon | fluorine | hydrogen 1-chloro-1-propene | carbon | chlorine | hydrogen acetyl fluoride | carbon | fluorine | hydrogen | oxygen chlorocyclopentane | carbon | chlorine | hydrogen methyl chloride | carbon | chlorine | hydrogen cupric fluoride | copper | fluorine fluorocyclohexane | carbon | fluorine | hydrogen fluoromethane | carbon | fluorine | hydrogen hydrofluoric acid | hydrogen | fluorine hydrogen bromide | bromine | hydrogen hydrogen chloride | chlorine | hydrogen iodoacetonitrile | carbon | hydrogen | iodine | nitrogen lithium bromide | bromine | lithium lithium chloride | chlorine | lithium potassium chloride | chlorine | potassium potassium iodide | iodine | potassium rubidium fluoride | fluorine | rubidium sodium bromide | bromine | sodium sodium fluoride | fluorine | sodium zinc fluoride | fluorine | zinc
Thermodynamic properties
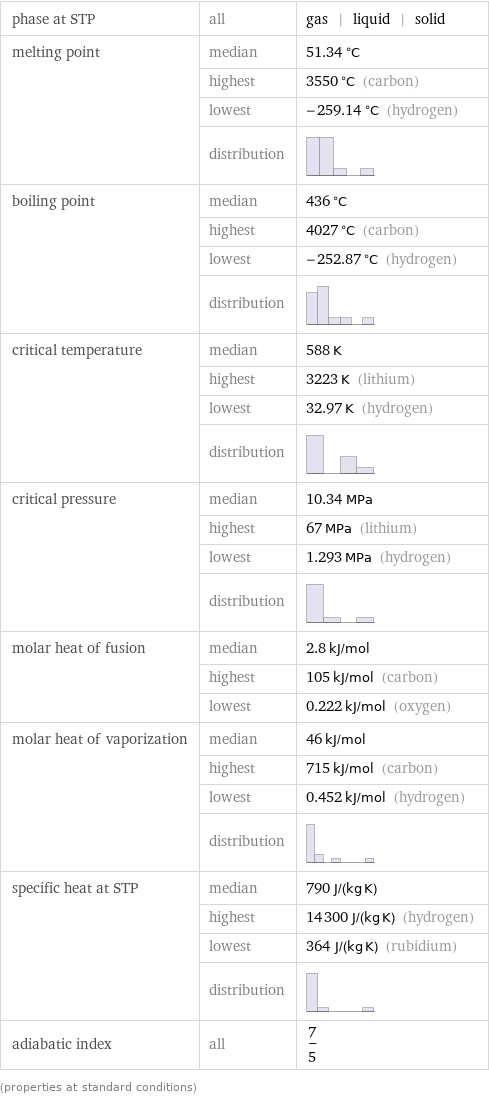
phase at STP | all | gas | liquid | solid melting point | median | 51.34 °C | highest | 3550 °C (carbon) | lowest | -259.14 °C (hydrogen) | distribution | boiling point | median | 436 °C | highest | 4027 °C (carbon) | lowest | -252.87 °C (hydrogen) | distribution | critical temperature | median | 588 K | highest | 3223 K (lithium) | lowest | 32.97 K (hydrogen) | distribution | critical pressure | median | 10.34 MPa | highest | 67 MPa (lithium) | lowest | 1.293 MPa (hydrogen) | distribution | molar heat of fusion | median | 2.8 kJ/mol | highest | 105 kJ/mol (carbon) | lowest | 0.222 kJ/mol (oxygen) molar heat of vaporization | median | 46 kJ/mol | highest | 715 kJ/mol (carbon) | lowest | 0.452 kJ/mol (hydrogen) | distribution | specific heat at STP | median | 790 J/(kg K) | highest | 14300 J/(kg K) (hydrogen) | lowest | 364 J/(kg K) (rubidium) | distribution | adiabatic index | all | 7/5 (properties at standard conditions)
Material properties
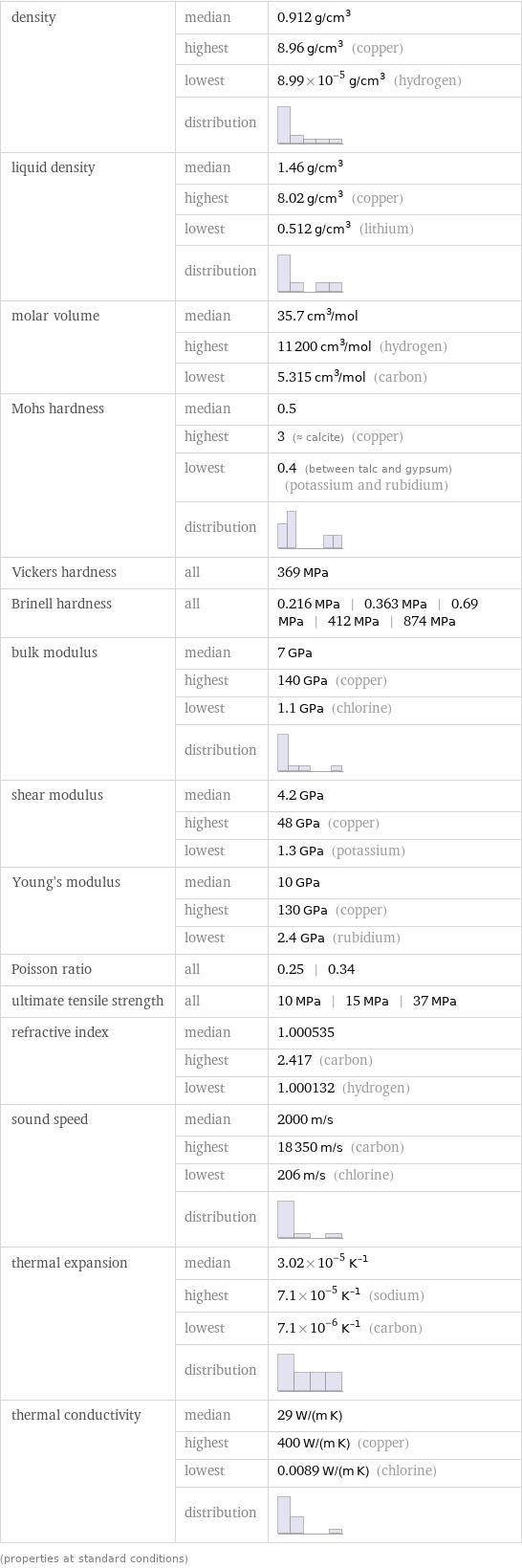
density | median | 0.912 g/cm^3 | highest | 8.96 g/cm^3 (copper) | lowest | 8.99×10^-5 g/cm^3 (hydrogen) | distribution | liquid density | median | 1.46 g/cm^3 | highest | 8.02 g/cm^3 (copper) | lowest | 0.512 g/cm^3 (lithium) | distribution | molar volume | median | 35.7 cm^3/mol | highest | 11200 cm^3/mol (hydrogen) | lowest | 5.315 cm^3/mol (carbon) Mohs hardness | median | 0.5 | highest | 3 (≈ calcite) (copper) | lowest | 0.4 (between talc and gypsum) (potassium and rubidium) | distribution | Vickers hardness | all | 369 MPa Brinell hardness | all | 0.216 MPa | 0.363 MPa | 0.69 MPa | 412 MPa | 874 MPa bulk modulus | median | 7 GPa | highest | 140 GPa (copper) | lowest | 1.1 GPa (chlorine) | distribution | shear modulus | median | 4.2 GPa | highest | 48 GPa (copper) | lowest | 1.3 GPa (potassium) Young's modulus | median | 10 GPa | highest | 130 GPa (copper) | lowest | 2.4 GPa (rubidium) Poisson ratio | all | 0.25 | 0.34 ultimate tensile strength | all | 10 MPa | 15 MPa | 37 MPa refractive index | median | 1.000535 | highest | 2.417 (carbon) | lowest | 1.000132 (hydrogen) sound speed | median | 2000 m/s | highest | 18350 m/s (carbon) | lowest | 206 m/s (chlorine) | distribution | thermal expansion | median | 3.02×10^-5 K^(-1) | highest | 7.1×10^-5 K^(-1) (sodium) | lowest | 7.1×10^-6 K^(-1) (carbon) | distribution | thermal conductivity | median | 29 W/(m K) | highest | 400 W/(m K) (copper) | lowest | 0.0089 W/(m K) (chlorine) | distribution | (properties at standard conditions)
Electromagnetic properties
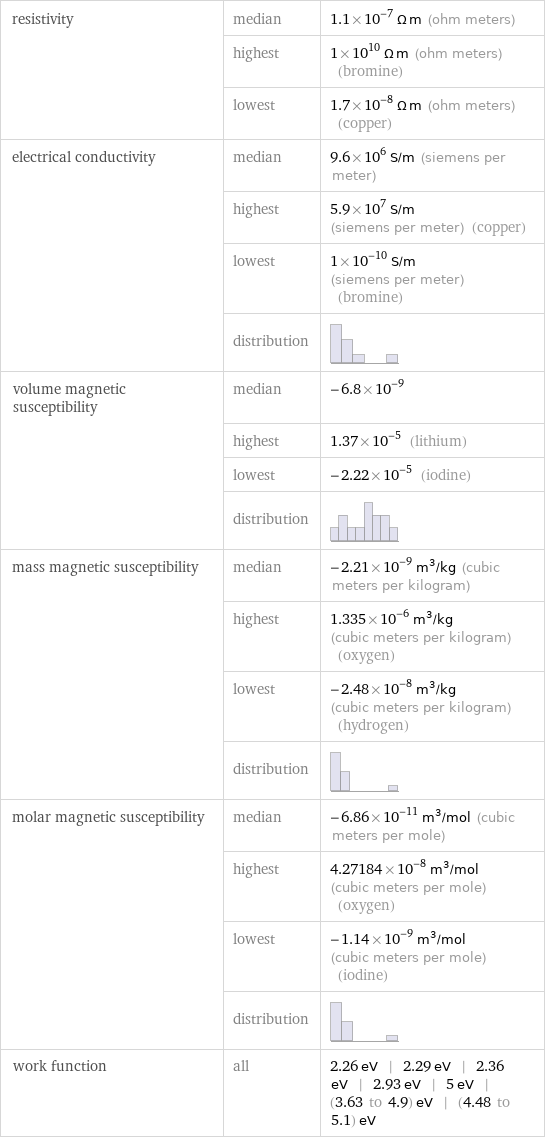
resistivity | median | 1.1×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) | highest | 1×10^10 Ω m (ohm meters) (bromine) | lowest | 1.7×10^-8 Ω m (ohm meters) (copper) electrical conductivity | median | 9.6×10^6 S/m (siemens per meter) | highest | 5.9×10^7 S/m (siemens per meter) (copper) | lowest | 1×10^-10 S/m (siemens per meter) (bromine) | distribution | volume magnetic susceptibility | median | -6.8×10^-9 | highest | 1.37×10^-5 (lithium) | lowest | -2.22×10^-5 (iodine) | distribution | mass magnetic susceptibility | median | -2.21×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | highest | 1.335×10^-6 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) (oxygen) | lowest | -2.48×10^-8 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) (hydrogen) | distribution | molar magnetic susceptibility | median | -6.86×10^-11 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | highest | 4.27184×10^-8 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) (oxygen) | lowest | -1.14×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) (iodine) | distribution | work function | all | 2.26 eV | 2.29 eV | 2.36 eV | 2.93 eV | 5 eV | (3.63 to 4.9) eV | (4.48 to 5.1) eV
Reactivity
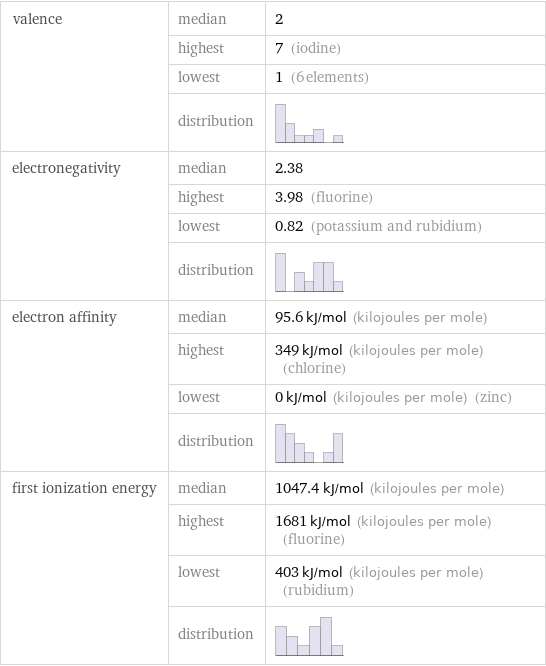
valence | median | 2 | highest | 7 (iodine) | lowest | 1 (6 elements) | distribution | electronegativity | median | 2.38 | highest | 3.98 (fluorine) | lowest | 0.82 (potassium and rubidium) | distribution | electron affinity | median | 95.6 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | highest | 349 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) (chlorine) | lowest | 0 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) (zinc) | distribution | first ionization energy | median | 1047.4 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | highest | 1681 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) (fluorine) | lowest | 403 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) (rubidium) | distribution |
Atomic properties
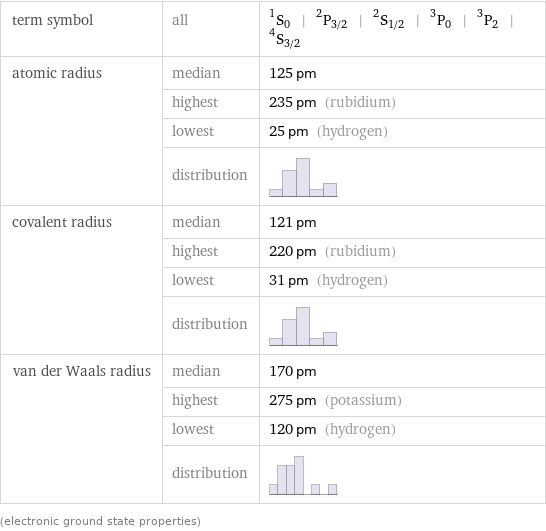
term symbol | all | ^1S_0 | ^2P_(3/2) | ^2S_(1/2) | ^3P_0 | ^3P_2 | ^4S_(3/2) atomic radius | median | 125 pm | highest | 235 pm (rubidium) | lowest | 25 pm (hydrogen) | distribution | covalent radius | median | 121 pm | highest | 220 pm (rubidium) | lowest | 31 pm (hydrogen) | distribution | van der Waals radius | median | 170 pm | highest | 275 pm (potassium) | lowest | 120 pm (hydrogen) | distribution | (electronic ground state properties)