Input interpretation
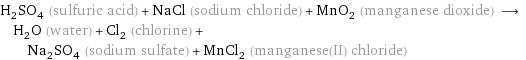
H_2SO_4 (sulfuric acid) + NaCl (sodium chloride) + MnO_2 (manganese dioxide) ⟶ H_2O (water) + Cl_2 (chlorine) + Na_2SO_4 (sodium sulfate) + MnCl_2 (manganese(II) chloride)
Balanced equation

Balance the chemical equation algebraically: H_2SO_4 + NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ H_2O + Cl_2 + Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Add stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, to the reactants and products: c_1 H_2SO_4 + c_2 NaCl + c_3 MnO_2 ⟶ c_4 H_2O + c_5 Cl_2 + c_6 Na_2SO_4 + c_7 MnCl_2 Set the number of atoms in the reactants equal to the number of atoms in the products for H, O, S, Cl, Na and Mn: H: | 2 c_1 = 2 c_4 O: | 4 c_1 + 2 c_3 = c_4 + 4 c_6 S: | c_1 = c_6 Cl: | c_2 = 2 c_5 + 2 c_7 Na: | c_2 = 2 c_6 Mn: | c_3 = c_7 Since the coefficients are relative quantities and underdetermined, choose a coefficient to set arbitrarily. To keep the coefficients small, the arbitrary value is ordinarily one. For instance, set c_3 = 1 and solve the system of equations for the remaining coefficients: c_1 = 2 c_2 = 4 c_3 = 1 c_4 = 2 c_5 = 1 c_6 = 2 c_7 = 1 Substitute the coefficients into the chemical reaction to obtain the balanced equation: Answer: | | 2 H_2SO_4 + 4 NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ 2 H_2O + Cl_2 + 2 Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2
Structures
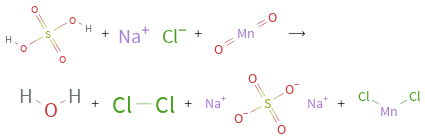
+ + ⟶ + + +
Names
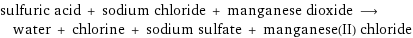
sulfuric acid + sodium chloride + manganese dioxide ⟶ water + chlorine + sodium sulfate + manganese(II) chloride
Reaction thermodynamics
Enthalpy
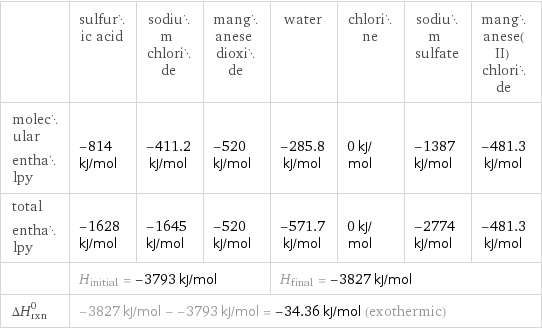
| sulfuric acid | sodium chloride | manganese dioxide | water | chlorine | sodium sulfate | manganese(II) chloride molecular enthalpy | -814 kJ/mol | -411.2 kJ/mol | -520 kJ/mol | -285.8 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -1387 kJ/mol | -481.3 kJ/mol total enthalpy | -1628 kJ/mol | -1645 kJ/mol | -520 kJ/mol | -571.7 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -2774 kJ/mol | -481.3 kJ/mol | H_initial = -3793 kJ/mol | | | H_final = -3827 kJ/mol | | | ΔH_rxn^0 | -3827 kJ/mol - -3793 kJ/mol = -34.36 kJ/mol (exothermic) | | | | | |
Gibbs free energy
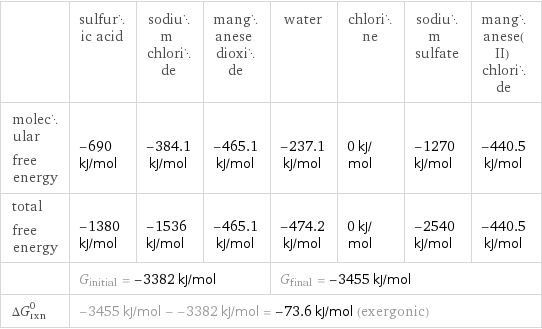
| sulfuric acid | sodium chloride | manganese dioxide | water | chlorine | sodium sulfate | manganese(II) chloride molecular free energy | -690 kJ/mol | -384.1 kJ/mol | -465.1 kJ/mol | -237.1 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -1270 kJ/mol | -440.5 kJ/mol total free energy | -1380 kJ/mol | -1536 kJ/mol | -465.1 kJ/mol | -474.2 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -2540 kJ/mol | -440.5 kJ/mol | G_initial = -3382 kJ/mol | | | G_final = -3455 kJ/mol | | | ΔG_rxn^0 | -3455 kJ/mol - -3382 kJ/mol = -73.6 kJ/mol (exergonic) | | | | | |
Equilibrium constant
![Construct the equilibrium constant, K, expression for: H_2SO_4 + NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ H_2O + Cl_2 + Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the activity expression for each chemical species. • Use the activity expressions to build the equilibrium constant expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 2 H_2SO_4 + 4 NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ 2 H_2O + Cl_2 + 2 Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | -4 MnO_2 | 1 | -1 H_2O | 2 | 2 Cl_2 | 1 | 1 Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 Assemble the activity expressions accounting for the state of matter and ν_i: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | activity expression H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 | ([H2SO4])^(-2) NaCl | 4 | -4 | ([NaCl])^(-4) MnO_2 | 1 | -1 | ([MnO2])^(-1) H_2O | 2 | 2 | ([H2O])^2 Cl_2 | 1 | 1 | [Cl2] Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 | ([Na2SO4])^2 MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 | [MnCl2] The equilibrium constant symbol in the concentration basis is: K_c Mulitply the activity expressions to arrive at the K_c expression: Answer: | | K_c = ([H2SO4])^(-2) ([NaCl])^(-4) ([MnO2])^(-1) ([H2O])^2 [Cl2] ([Na2SO4])^2 [MnCl2] = (([H2O])^2 [Cl2] ([Na2SO4])^2 [MnCl2])/(([H2SO4])^2 ([NaCl])^4 [MnO2])](../image_source/e3733c798ea14d6bb2aa175c3d495d21.png)
Construct the equilibrium constant, K, expression for: H_2SO_4 + NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ H_2O + Cl_2 + Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the activity expression for each chemical species. • Use the activity expressions to build the equilibrium constant expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 2 H_2SO_4 + 4 NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ 2 H_2O + Cl_2 + 2 Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | -4 MnO_2 | 1 | -1 H_2O | 2 | 2 Cl_2 | 1 | 1 Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 Assemble the activity expressions accounting for the state of matter and ν_i: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | activity expression H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 | ([H2SO4])^(-2) NaCl | 4 | -4 | ([NaCl])^(-4) MnO_2 | 1 | -1 | ([MnO2])^(-1) H_2O | 2 | 2 | ([H2O])^2 Cl_2 | 1 | 1 | [Cl2] Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 | ([Na2SO4])^2 MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 | [MnCl2] The equilibrium constant symbol in the concentration basis is: K_c Mulitply the activity expressions to arrive at the K_c expression: Answer: | | K_c = ([H2SO4])^(-2) ([NaCl])^(-4) ([MnO2])^(-1) ([H2O])^2 [Cl2] ([Na2SO4])^2 [MnCl2] = (([H2O])^2 [Cl2] ([Na2SO4])^2 [MnCl2])/(([H2SO4])^2 ([NaCl])^4 [MnO2])
Rate of reaction
![Construct the rate of reaction expression for: H_2SO_4 + NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ H_2O + Cl_2 + Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the rate term for each chemical species. • Write the rate of reaction expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 2 H_2SO_4 + 4 NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ 2 H_2O + Cl_2 + 2 Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | -4 MnO_2 | 1 | -1 H_2O | 2 | 2 Cl_2 | 1 | 1 Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 The rate term for each chemical species, B_i, is 1/ν_i(Δ[B_i])/(Δt) where [B_i] is the amount concentration and t is time: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | rate term H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 | -1/2 (Δ[H2SO4])/(Δt) NaCl | 4 | -4 | -1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) MnO_2 | 1 | -1 | -(Δ[MnO2])/(Δt) H_2O | 2 | 2 | 1/2 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) Cl_2 | 1 | 1 | (Δ[Cl2])/(Δt) Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 | 1/2 (Δ[Na2SO4])/(Δt) MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 | (Δ[MnCl2])/(Δt) (for infinitesimal rate of change, replace Δ with d) Set the rate terms equal to each other to arrive at the rate expression: Answer: | | rate = -1/2 (Δ[H2SO4])/(Δt) = -1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) = -(Δ[MnO2])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = (Δ[Cl2])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[Na2SO4])/(Δt) = (Δ[MnCl2])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)](../image_source/d0a8c0726019a3f625fef13a37360c48.png)
Construct the rate of reaction expression for: H_2SO_4 + NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ H_2O + Cl_2 + Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the rate term for each chemical species. • Write the rate of reaction expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 2 H_2SO_4 + 4 NaCl + MnO_2 ⟶ 2 H_2O + Cl_2 + 2 Na_2SO_4 + MnCl_2 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | -4 MnO_2 | 1 | -1 H_2O | 2 | 2 Cl_2 | 1 | 1 Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 The rate term for each chemical species, B_i, is 1/ν_i(Δ[B_i])/(Δt) where [B_i] is the amount concentration and t is time: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | rate term H_2SO_4 | 2 | -2 | -1/2 (Δ[H2SO4])/(Δt) NaCl | 4 | -4 | -1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) MnO_2 | 1 | -1 | -(Δ[MnO2])/(Δt) H_2O | 2 | 2 | 1/2 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) Cl_2 | 1 | 1 | (Δ[Cl2])/(Δt) Na_2SO_4 | 2 | 2 | 1/2 (Δ[Na2SO4])/(Δt) MnCl_2 | 1 | 1 | (Δ[MnCl2])/(Δt) (for infinitesimal rate of change, replace Δ with d) Set the rate terms equal to each other to arrive at the rate expression: Answer: | | rate = -1/2 (Δ[H2SO4])/(Δt) = -1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) = -(Δ[MnO2])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = (Δ[Cl2])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[Na2SO4])/(Δt) = (Δ[MnCl2])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)
Chemical names and formulas
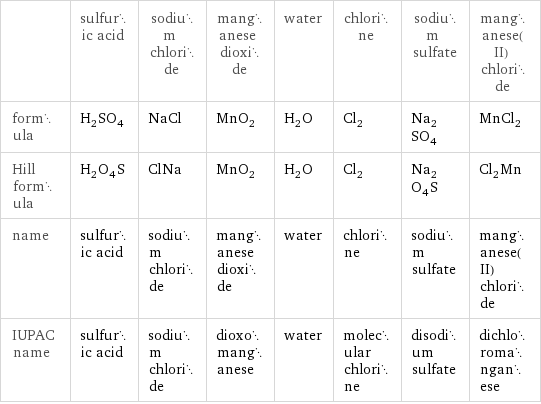
| sulfuric acid | sodium chloride | manganese dioxide | water | chlorine | sodium sulfate | manganese(II) chloride formula | H_2SO_4 | NaCl | MnO_2 | H_2O | Cl_2 | Na_2SO_4 | MnCl_2 Hill formula | H_2O_4S | ClNa | MnO_2 | H_2O | Cl_2 | Na_2O_4S | Cl_2Mn name | sulfuric acid | sodium chloride | manganese dioxide | water | chlorine | sodium sulfate | manganese(II) chloride IUPAC name | sulfuric acid | sodium chloride | dioxomanganese | water | molecular chlorine | disodium sulfate | dichloromanganese