Input interpretation

scopolamine | aromatic atom count
Result

6 atoms
Aromatic atoms in place
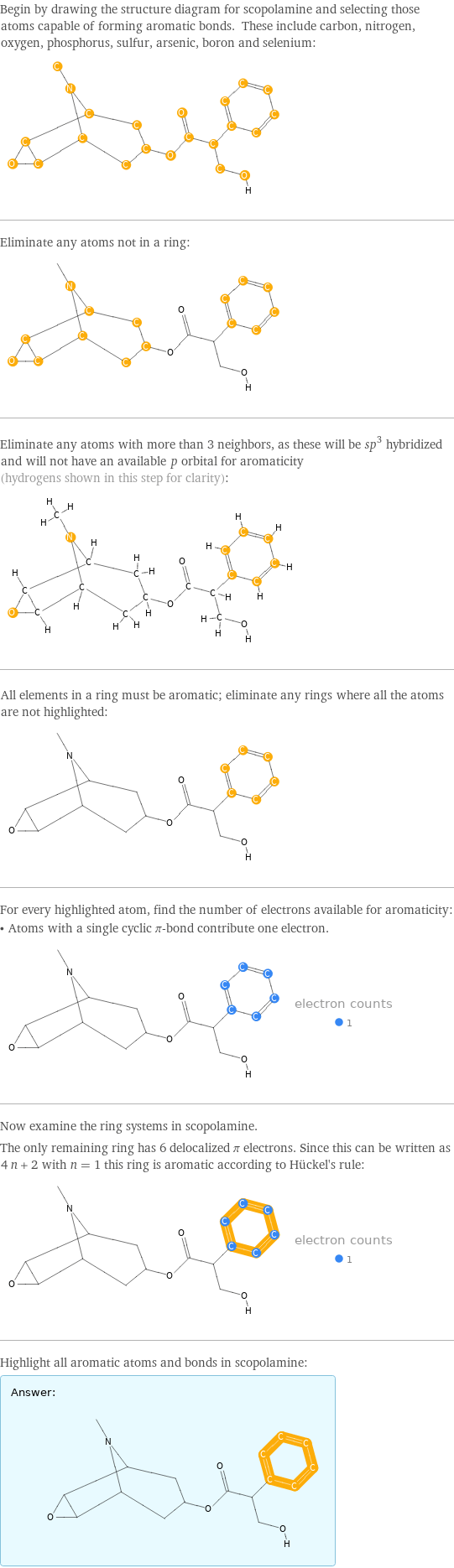 "Italic"]\) orbital for aromaticity (hydrogens shown in this step for clarity): All elements in a ring must be aromatic; eliminate any rings where all the atoms are not highlighted: For every highlighted atom, find the number of electrons available for aromaticity: • Atoms with a single cyclic π-bond contribute one electron. Now examine the ring systems in scopolamine. The only remaining ring has 6 delocalized π electrons. Since this can be written as 4 n + 2 with n = 1 this ring is aromatic according to Hückel's rule: Highlight all aromatic atoms and bonds in scopolamine: Answer: | | " />
"Italic"]\) orbital for aromaticity (hydrogens shown in this step for clarity): All elements in a ring must be aromatic; eliminate any rings where all the atoms are not highlighted: For every highlighted atom, find the number of electrons available for aromaticity: • Atoms with a single cyclic π-bond contribute one electron. Now examine the ring systems in scopolamine. The only remaining ring has 6 delocalized π electrons. Since this can be written as 4 n + 2 with n = 1 this ring is aromatic according to Hückel's rule: Highlight all aromatic atoms and bonds in scopolamine: Answer: | | " />
Begin by drawing the structure diagram for scopolamine and selecting those atoms capable of forming aromatic bonds. These include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, arsenic, boron and selenium: Eliminate any atoms not in a ring: Eliminate any atoms with more than 3 neighbors, as these will be sp^3 hybridized and will not have an available \!\(\*StyleBox["p", FontSlant->"Italic"]\) orbital for aromaticity (hydrogens shown in this step for clarity): All elements in a ring must be aromatic; eliminate any rings where all the atoms are not highlighted: For every highlighted atom, find the number of electrons available for aromaticity: • Atoms with a single cyclic π-bond contribute one electron. Now examine the ring systems in scopolamine. The only remaining ring has 6 delocalized π electrons. Since this can be written as 4 n + 2 with n = 1 this ring is aromatic according to Hückel's rule: Highlight all aromatic atoms and bonds in scopolamine: Answer: | |
Aromatic atoms elemental composition
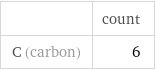
| count C (carbon) | 6
Quantitative molecular descriptors
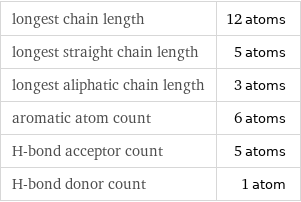
longest chain length | 12 atoms longest straight chain length | 5 atoms longest aliphatic chain length | 3 atoms aromatic atom count | 6 atoms H-bond acceptor count | 5 atoms H-bond donor count | 1 atom
Corresponding quantity
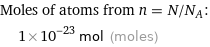
Moles of atoms from n = N/N_A: | 1×10^-23 mol (moles)