Input interpretation

group 18 elements | melting point
Summary

median | -157.36 °C highest | -71 °C (radon) lowest | -248.59 °C (neon) distribution | | (based on 5 values; 2 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
helium | oganesson (total: 2)
Plot
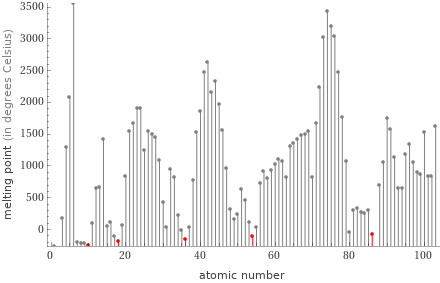
Plot
Melting point rankings
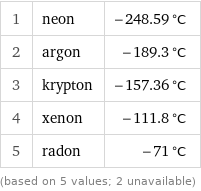
1 | neon | -248.59 °C 2 | argon | -189.3 °C 3 | krypton | -157.36 °C 4 | xenon | -111.8 °C 5 | radon | -71 °C (based on 5 values; 2 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median melting point -157.36 °C
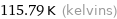
115.79 K (kelvins)
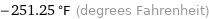
-251.25 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
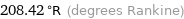
208.42 °R (degrees Rankine)

-125.89 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-75.114 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point -157.36 °C
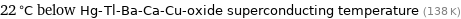
22 °C below Hg-Tl-Ba-Ca-Cu-oxide superconducting temperature (138 K)
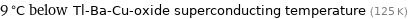
9 °C below Tl-Ba-Cu-oxide superconducting temperature (125 K)
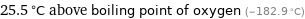
25.5 °C above boiling point of oxygen (-182.9 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 10 meV (millielectronvolts)
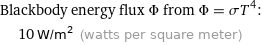
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 10 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 5.1×10^-65 lx (lux)
Thermodynamic properties
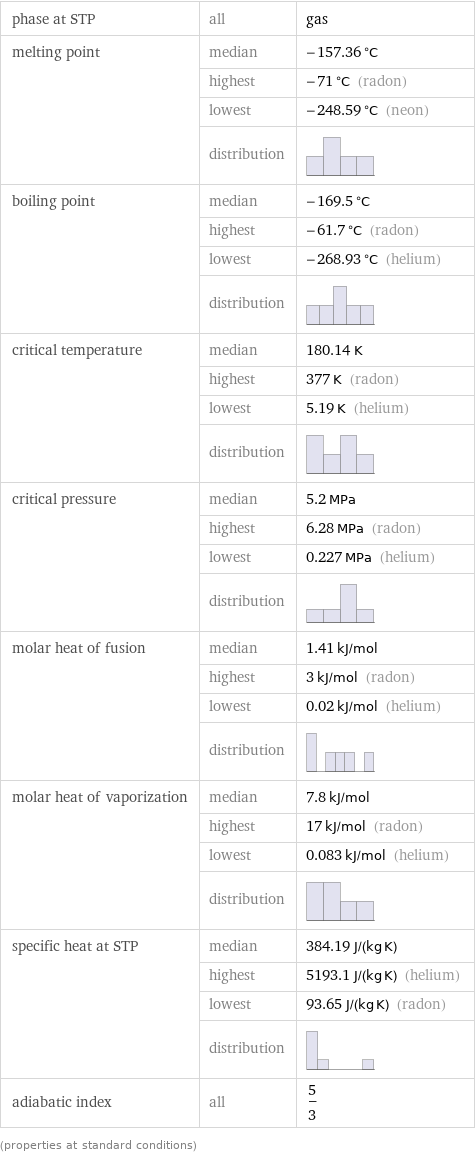
phase at STP | all | gas melting point | median | -157.36 °C | highest | -71 °C (radon) | lowest | -248.59 °C (neon) | distribution | boiling point | median | -169.5 °C | highest | -61.7 °C (radon) | lowest | -268.93 °C (helium) | distribution | critical temperature | median | 180.14 K | highest | 377 K (radon) | lowest | 5.19 K (helium) | distribution | critical pressure | median | 5.2 MPa | highest | 6.28 MPa (radon) | lowest | 0.227 MPa (helium) | distribution | molar heat of fusion | median | 1.41 kJ/mol | highest | 3 kJ/mol (radon) | lowest | 0.02 kJ/mol (helium) | distribution | molar heat of vaporization | median | 7.8 kJ/mol | highest | 17 kJ/mol (radon) | lowest | 0.083 kJ/mol (helium) | distribution | specific heat at STP | median | 384.19 J/(kg K) | highest | 5193.1 J/(kg K) (helium) | lowest | 93.65 J/(kg K) (radon) | distribution | adiabatic index | all | 5/3 (properties at standard conditions)