Input interpretation

strong electrolytes | electron count
Summary

median | 48 e highest | 146 e (magic acid) lowest | 12 e (lithium hydroxide and sodium hydride) distribution |
Units

Distribution plots
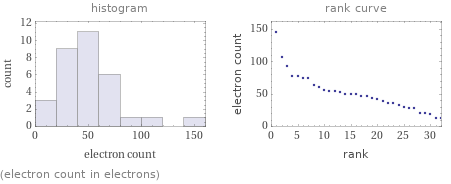
(electron count in electrons)
Electron count rankings
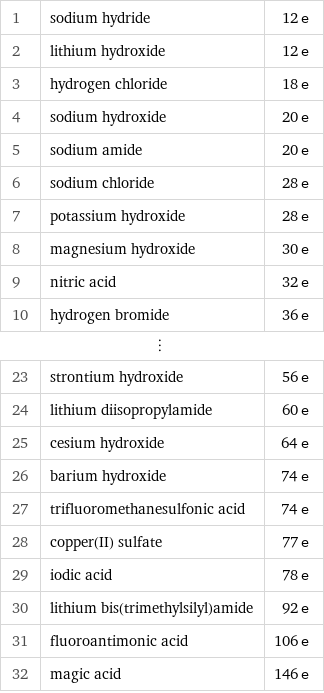
1 | sodium hydride | 12 e 2 | lithium hydroxide | 12 e 3 | hydrogen chloride | 18 e 4 | sodium hydroxide | 20 e 5 | sodium amide | 20 e 6 | sodium chloride | 28 e 7 | potassium hydroxide | 28 e 8 | magnesium hydroxide | 30 e 9 | nitric acid | 32 e 10 | hydrogen bromide | 36 e ⋮ | | 23 | strontium hydroxide | 56 e 24 | lithium diisopropylamide | 60 e 25 | cesium hydroxide | 64 e 26 | barium hydroxide | 74 e 27 | trifluoromethanesulfonic acid | 74 e 28 | copper(II) sulfate | 77 e 29 | iodic acid | 78 e 30 | lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide | 92 e 31 | fluoroantimonic acid | 106 e 32 | magic acid | 146 e
Corresponding quantity
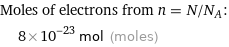
Moles of electrons from n = N/N_A: | 8×10^-23 mol (moles)