Input interpretation
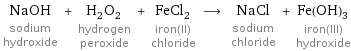
NaOH sodium hydroxide + H_2O_2 hydrogen peroxide + FeCl_2 iron(II) chloride ⟶ NaCl sodium chloride + Fe(OH)_3 iron(III) hydroxide
Balanced equation

Balance the chemical equation algebraically: NaOH + H_2O_2 + FeCl_2 ⟶ NaCl + Fe(OH)_3 Add stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, to the reactants and products: c_1 NaOH + c_2 H_2O_2 + c_3 FeCl_2 ⟶ c_4 NaCl + c_5 Fe(OH)_3 Set the number of atoms in the reactants equal to the number of atoms in the products for H, Na, O, Cl and Fe: H: | c_1 + 2 c_2 = 3 c_5 Na: | c_1 = c_4 O: | c_1 + 2 c_2 = 3 c_5 Cl: | 2 c_3 = c_4 Fe: | c_3 = c_5 Since the coefficients are relative quantities and underdetermined, choose a coefficient to set arbitrarily. To keep the coefficients small, the arbitrary value is ordinarily one. For instance, set c_2 = 1 and solve the system of equations for the remaining coefficients: c_1 = 4 c_2 = 1 c_3 = 2 c_4 = 4 c_5 = 2 Substitute the coefficients into the chemical reaction to obtain the balanced equation: Answer: | | 4 NaOH + H_2O_2 + 2 FeCl_2 ⟶ 4 NaCl + 2 Fe(OH)_3
Structures
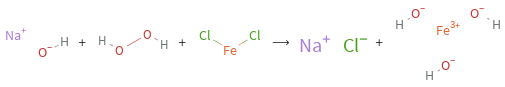
+ + ⟶ +
Names
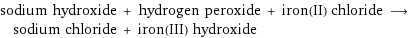
sodium hydroxide + hydrogen peroxide + iron(II) chloride ⟶ sodium chloride + iron(III) hydroxide
Equilibrium constant
![Construct the equilibrium constant, K, expression for: NaOH + H_2O_2 + FeCl_2 ⟶ NaCl + Fe(OH)_3 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the activity expression for each chemical species. • Use the activity expressions to build the equilibrium constant expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 4 NaOH + H_2O_2 + 2 FeCl_2 ⟶ 4 NaCl + 2 Fe(OH)_3 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i NaOH | 4 | -4 H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | 4 Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 Assemble the activity expressions accounting for the state of matter and ν_i: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | activity expression NaOH | 4 | -4 | ([NaOH])^(-4) H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 | ([H2O2])^(-1) FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 | ([FeCl2])^(-2) NaCl | 4 | 4 | ([NaCl])^4 Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 | ([Fe(OH)3])^2 The equilibrium constant symbol in the concentration basis is: K_c Mulitply the activity expressions to arrive at the K_c expression: Answer: | | K_c = ([NaOH])^(-4) ([H2O2])^(-1) ([FeCl2])^(-2) ([NaCl])^4 ([Fe(OH)3])^2 = (([NaCl])^4 ([Fe(OH)3])^2)/(([NaOH])^4 [H2O2] ([FeCl2])^2)](../image_source/0c59f545bdb0e83ecbfcea44cf6da10d.png)
Construct the equilibrium constant, K, expression for: NaOH + H_2O_2 + FeCl_2 ⟶ NaCl + Fe(OH)_3 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the activity expression for each chemical species. • Use the activity expressions to build the equilibrium constant expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 4 NaOH + H_2O_2 + 2 FeCl_2 ⟶ 4 NaCl + 2 Fe(OH)_3 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i NaOH | 4 | -4 H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | 4 Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 Assemble the activity expressions accounting for the state of matter and ν_i: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | activity expression NaOH | 4 | -4 | ([NaOH])^(-4) H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 | ([H2O2])^(-1) FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 | ([FeCl2])^(-2) NaCl | 4 | 4 | ([NaCl])^4 Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 | ([Fe(OH)3])^2 The equilibrium constant symbol in the concentration basis is: K_c Mulitply the activity expressions to arrive at the K_c expression: Answer: | | K_c = ([NaOH])^(-4) ([H2O2])^(-1) ([FeCl2])^(-2) ([NaCl])^4 ([Fe(OH)3])^2 = (([NaCl])^4 ([Fe(OH)3])^2)/(([NaOH])^4 [H2O2] ([FeCl2])^2)
Rate of reaction
![Construct the rate of reaction expression for: NaOH + H_2O_2 + FeCl_2 ⟶ NaCl + Fe(OH)_3 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the rate term for each chemical species. • Write the rate of reaction expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 4 NaOH + H_2O_2 + 2 FeCl_2 ⟶ 4 NaCl + 2 Fe(OH)_3 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i NaOH | 4 | -4 H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | 4 Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 The rate term for each chemical species, B_i, is 1/ν_i(Δ[B_i])/(Δt) where [B_i] is the amount concentration and t is time: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | rate term NaOH | 4 | -4 | -1/4 (Δ[NaOH])/(Δt) H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 | -(Δ[H2O2])/(Δt) FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 | -1/2 (Δ[FeCl2])/(Δt) NaCl | 4 | 4 | 1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 | 1/2 (Δ[Fe(OH)3])/(Δt) (for infinitesimal rate of change, replace Δ with d) Set the rate terms equal to each other to arrive at the rate expression: Answer: | | rate = -1/4 (Δ[NaOH])/(Δt) = -(Δ[H2O2])/(Δt) = -1/2 (Δ[FeCl2])/(Δt) = 1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[Fe(OH)3])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)](../image_source/c7d86f4e4d9d87261ed04c5ea40a5ba1.png)
Construct the rate of reaction expression for: NaOH + H_2O_2 + FeCl_2 ⟶ NaCl + Fe(OH)_3 Plan: • Balance the chemical equation. • Determine the stoichiometric numbers. • Assemble the rate term for each chemical species. • Write the rate of reaction expression. Write the balanced chemical equation: 4 NaOH + H_2O_2 + 2 FeCl_2 ⟶ 4 NaCl + 2 Fe(OH)_3 Assign stoichiometric numbers, ν_i, using the stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, from the balanced chemical equation in the following manner: ν_i = -c_i for reactants and ν_i = c_i for products: chemical species | c_i | ν_i NaOH | 4 | -4 H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 NaCl | 4 | 4 Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 The rate term for each chemical species, B_i, is 1/ν_i(Δ[B_i])/(Δt) where [B_i] is the amount concentration and t is time: chemical species | c_i | ν_i | rate term NaOH | 4 | -4 | -1/4 (Δ[NaOH])/(Δt) H_2O_2 | 1 | -1 | -(Δ[H2O2])/(Δt) FeCl_2 | 2 | -2 | -1/2 (Δ[FeCl2])/(Δt) NaCl | 4 | 4 | 1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) Fe(OH)_3 | 2 | 2 | 1/2 (Δ[Fe(OH)3])/(Δt) (for infinitesimal rate of change, replace Δ with d) Set the rate terms equal to each other to arrive at the rate expression: Answer: | | rate = -1/4 (Δ[NaOH])/(Δt) = -(Δ[H2O2])/(Δt) = -1/2 (Δ[FeCl2])/(Δt) = 1/4 (Δ[NaCl])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[Fe(OH)3])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)
Chemical names and formulas
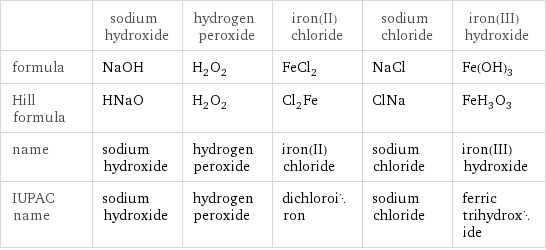
| sodium hydroxide | hydrogen peroxide | iron(II) chloride | sodium chloride | iron(III) hydroxide formula | NaOH | H_2O_2 | FeCl_2 | NaCl | Fe(OH)_3 Hill formula | HNaO | H_2O_2 | Cl_2Fe | ClNa | FeH_3O_3 name | sodium hydroxide | hydrogen peroxide | iron(II) chloride | sodium chloride | iron(III) hydroxide IUPAC name | sodium hydroxide | hydrogen peroxide | dichloroiron | sodium chloride | ferric trihydroxide
Substance properties
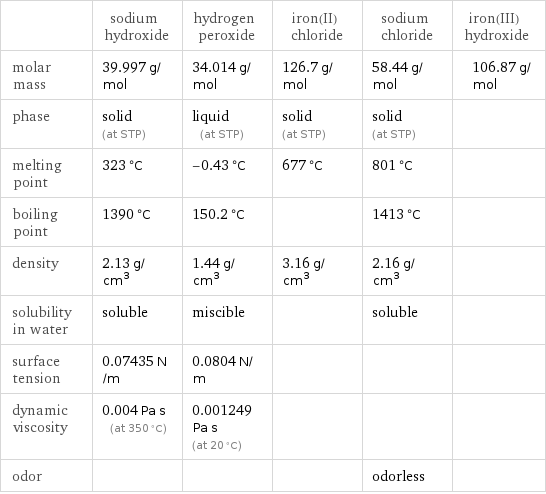
| sodium hydroxide | hydrogen peroxide | iron(II) chloride | sodium chloride | iron(III) hydroxide molar mass | 39.997 g/mol | 34.014 g/mol | 126.7 g/mol | 58.44 g/mol | 106.87 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) | liquid (at STP) | solid (at STP) | solid (at STP) | melting point | 323 °C | -0.43 °C | 677 °C | 801 °C | boiling point | 1390 °C | 150.2 °C | | 1413 °C | density | 2.13 g/cm^3 | 1.44 g/cm^3 | 3.16 g/cm^3 | 2.16 g/cm^3 | solubility in water | soluble | miscible | | soluble | surface tension | 0.07435 N/m | 0.0804 N/m | | | dynamic viscosity | 0.004 Pa s (at 350 °C) | 0.001249 Pa s (at 20 °C) | | | odor | | | | odorless |
Units
