Input interpretation

Snell's law
Equation

n_1 sin(θ_1) = n_2 sin(θ_2) | θ_2 | angle of refraction n_1 | index of refraction (first medium) n_2 | index of refraction (second medium) θ_1 | angle of incidence
Input values

index of refraction (first medium) | 1 index of refraction (second medium) | 1.3 angle of incidence | 45° (degrees)
Results

angle of refraction | 32.95° (degrees) = 575.1 mrad (milliradians) = 0.5751 radians = 32 degrees 57 arc minutes 5.246 arc seconds
Possible intermediate steps

Calculate the angle of refraction using the following information: known variables | | n_1 | index of refraction (first medium) | 1 n_2 | index of refraction (second medium) | 1.3 θ_1 | angle of incidence | 45° The relevant equation that relates angle of refraction (θ_2), index of refraction (first medium) (n_1), index of refraction (second medium) (n_2), and angle of incidence (θ_1) is: n_1 sin(θ_1) = n_2 sin(θ_2) n_1 sin(θ_1) = n_2 sin(θ_2) is equivalent to n_2 sin(θ_2) = n_1 sin(θ_1): n_2 sin(θ_2) = n_1 sin(θ_1) Divide both sides by n_2: sin(θ_2) = (n_1 sin(θ_1))/n_2 Take the inverse sine of both sides: θ_2 = sin^(-1)((n_1 sin(θ_1))/n_2) Substitute known variables into the equation: known variables | | n_1 | index of refraction (first medium) | 1 n_2 | index of refraction (second medium) | 1.3 θ_1 | angle of incidence | 45° | : θ_2 = sin^(-1)((1 sin(45°))/1.3) Evaluate sin(45°): θ_2 = sin^(-1)(0.7071 1/1.3) Add the unit rad for angles to the answer: θ_2 = sin^(-1)((1×0.7071)/1.3) rad Evaluate sin^(-1)((1×0.7071)/1.3): θ_2 = 0.57511 rad Convert 0.57511 rad into degrees using the following: 1 rad = 57.296°: Answer: | | θ_2 = 32.95°
Ray plot
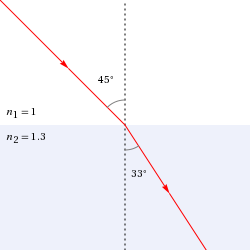
Ray plot