Input interpretation
copper(II) sulfate | elemental oxidation states
Result
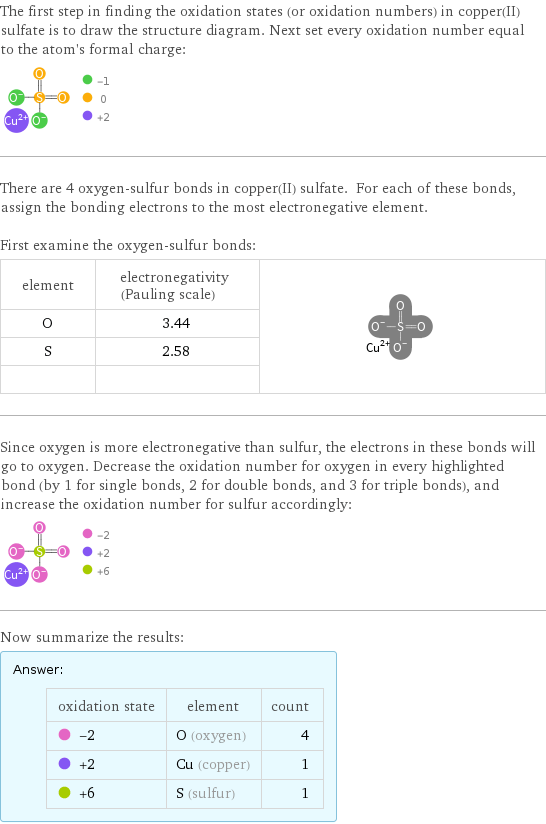
The first step in finding the oxidation states (or oxidation numbers) in copper(II) sulfate is to draw the structure diagram. Next set every oxidation number equal to the atom's formal charge: There are 4 oxygen-sulfur bonds in copper(II) sulfate. For each of these bonds, assign the bonding electrons to the most electronegative element. First examine the oxygen-sulfur bonds: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | O | 3.44 | S | 2.58 | | | Since oxygen is more electronegative than sulfur, the electrons in these bonds will go to oxygen. Decrease the oxidation number for oxygen in every highlighted bond (by 1 for single bonds, 2 for double bonds, and 3 for triple bonds), and increase the oxidation number for sulfur accordingly: Now summarize the results: Answer: | | oxidation state | element | count -2 | O (oxygen) | 4 +2 | Cu (copper) | 1 +6 | S (sulfur) | 1
Chemical names and formulas

formula | CuSO_4 Hill formula | CuO_4S name | copper(II) sulfate IUPAC name | copper sulfate alternate names | cupric sulfate mass fractions | Cu (copper) 39.8% | O (oxygen) 40.1% | S (sulfur) 20.1%
Ion equivalents

Cu^(2+) (copper(II) cation) | 1 (SO_4)^(2-) (sulfate anion) | 1