Input interpretation
phenytoin
Chemical names and formulas

formula | C_15H_12N_2O_2 name | phenytoin IUPAC name | 5, 5-di(phenyl)imidazolidine-2, 4-dione alternate names | 5, 5-diphenyl-2, 4-imidazolidinedione | 5, 5-di(phenyl)imidazolidine-2, 4-dione | aleviatin | causoin mass fractions | C (carbon) 71.4% | H (hydrogen) 4.79% | N (nitrogen) 11.1% | O (oxygen) 12.7%
Lewis structure
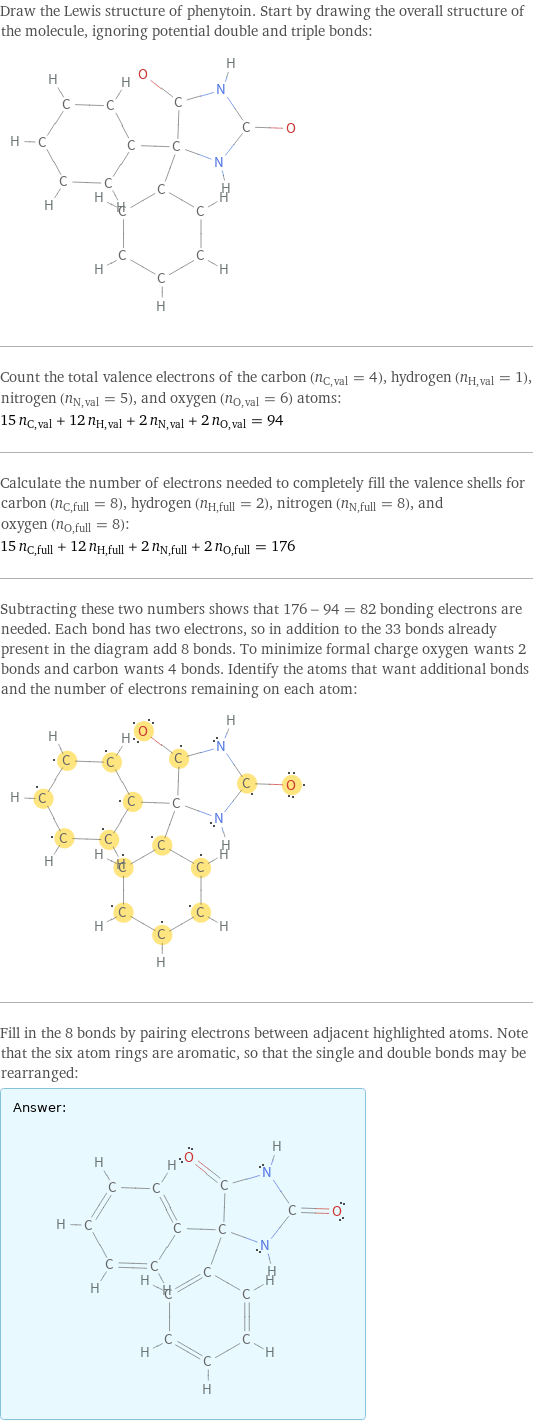
Draw the Lewis structure of phenytoin. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 15 n_C, val + 12 n_H, val + 2 n_N, val + 2 n_O, val = 94 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 15 n_C, full + 12 n_H, full + 2 n_N, full + 2 n_O, full = 176 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 176 - 94 = 82 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 33 bonds already present in the diagram add 8 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 8 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom rings are aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
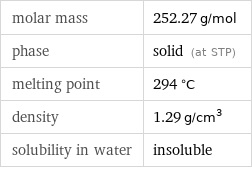
molar mass | 252.27 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 294 °C density | 1.29 g/cm^3 solubility in water | insoluble
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties
experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 2.2 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 2.26 predicted LogS | -3.55 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -4.57
Drug interactions

acenocoumarol | alprazolam | aminophylline | amiodarone | anisindione | aprepitant | atracurium besilate | betamethasone | bleomycin | capecitabine | carboplatin | carmustine | chloramphenicol | chlordiazepoxide | chlorotrianisene | chlorpheniramine | cimetidine | 3-quinolinecarboxylic acid | cis-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II) | clarithromycin | ... (total: 124)
Basic drug properties

approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | anticonvulsant dosage forms | oral: capsule | intramuscular: liquid | intravenous: liquid | intramuscular: solution | oral: suspension | oral: tablet

brand names | aleviatin | antisacer | auranile | causoin | citrullamon | citrulliamon | comital | comitoina | convul | danten | dantinal | dantoinal | dantoinal klinos | dantoine | denyl | Di-hydan | Di-lan | Di-phetine | didan TDC 250 | difenilhidantoina | difenin | difetoin | difhydan | dihycon | dilabid | dilantin | dilantin acid | dilantin-125 | dilantine | dillantin | dintoin | dintoina | diphantoin | diphedal | diphedan | diphenat | diphenin | diphenine | diphentoin | diphentyn | diphenylan | ditoinate | ekko | elepsindon | enkelfel | epamin | epanutin | epasmir 5 | epdantoin simple | epdantoine simple | epelin | epifenyl | epihydan | epilan | epilan D | epilan-D | epilantin | epinat | epised | eptal | eptoin | fenantoin | fenidantoin s | fentoin | fenylepsin | fenytoin dak | fenytoine | gerot-epilan-D | hidan | hidantal | hidantilo | hidantina | hidantina senosian | hidantina vitoria | hidantomin | hindatal | hydantal | hydantin | hydantoin | hydantoinal | hydantol | ictalis simple | idantoil | idantoin | iphenylhydantoin | kessodanten | labopal | lehydan | lepitoin | lepsin | mesantoin | minetoin | neos-hidantoina | neosidantoina | novantoina | novophenytoin | Om hidantoina simple | Om-hydantoine | oxylan | phanantin | phanatine | phenatine | phenatoine | phenhydan | phenhydanin | phenitoin | phentoin | phentytoin | phenytex | phenytoin AWD | phenytoin-gerot | prompt phenytoin sodium | ritmenal | saceril | sanepil | silantin | sinergina | sodanthon | sodantoin | sodanton | solantin | solantoin | solantyl | sylantoic | TOIN | tacosal | thilophenyl | toin unicelles | zentronal | zentropil
Solid properties (at STP)

density | 1.29 g/cm^3
Units

Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 57-41-0 Beilstein number | 384532 PubChem CID number | 1775 PubChem SID number | 148821 SMILES identifier | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2(C(=O)NC(=O)N2)C3=CC=CC=C3 InChI identifier | InChI=1/C15H12N2O2/c18-13-15(17-14(19)16-13, 11-7-3-1-4-8-11)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10H, (H2, 16, 17, 18, 19)/f/h16-17H InChI key | CXOFVDLJLONNDW-XQMQJMAZCS RTECS number | MU1050000 MDL number | MFCD00005264
NFPA label
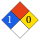
NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 1 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties

autoignition point | 600 °C

DOT numbers | 2811
Toxicity properties

odor | odorless

RTECS classes | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data