Input interpretation

L-lysine | molecular mass
Result

Find the molecular mass, m, for L-lysine: m = sum _iN_im_i Plan: • Write the chemical formula and gather atomic masses from the periodic table. • Determine values for N_i and m_i using these items. • Finally, compute the mass. Write the chemical formula: H_2N(CH_2)_4CH(NH_2)CO_2H Use the chemical formula to count the number of atoms, N_i, for each element: | N_i C (carbon) | 6 H (hydrogen) | 14 N (nitrogen) | 2 O (oxygen) | 2 Look up the atomic mass, m_i, in unified atomic mass units, u, for each element in the periodic table: | N_i | m_i/u C (carbon) | 6 | 12.011 H (hydrogen) | 14 | 1.008 N (nitrogen) | 2 | 14.007 O (oxygen) | 2 | 15.999 Multiply N_i by m_i to compute the mass for each element. Then sum those values to compute the molecular mass, m: Answer: | | | N_i | m_i/u | mass/u C (carbon) | 6 | 12.011 | 6 × 12.011 = 72.066 H (hydrogen) | 14 | 1.008 | 14 × 1.008 = 14.112 N (nitrogen) | 2 | 14.007 | 2 × 14.007 = 28.014 O (oxygen) | 2 | 15.999 | 2 × 15.999 = 31.998 m = 72.066 u + 14.112 u + 28.014 u + 31.998 u = 146.190 u
Unit conversions
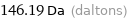
146.19 Da (daltons)
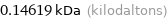
0.14619 kDa (kilodaltons)
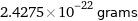
2.4275×10^-22 grams
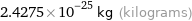
2.4275×10^-25 kg (kilograms)
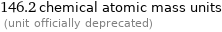
146.2 chemical atomic mass units (unit officially deprecated)
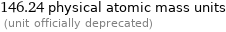
146.24 physical atomic mass units (unit officially deprecated)
Comparisons as mass of molecule
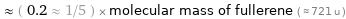
≈ ( 0.2 ≈ 1/5 ) × molecular mass of fullerene ( ≈ 721 u )
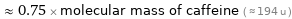
≈ 0.75 × molecular mass of caffeine ( ≈ 194 u )
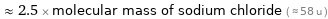
≈ 2.5 × molecular mass of sodium chloride ( ≈ 58 u )
Corresponding quantities
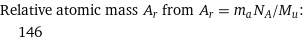
Relative atomic mass A_r from A_r = m_aN_A/M_u: | 146
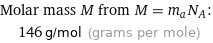
Molar mass M from M = m_aN_A: | 146 g/mol (grams per mole)
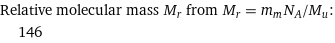
Relative molecular mass M_r from M_r = m_mN_A/M_u: | 146
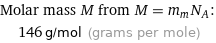
Molar mass M from M = m_mN_A: | 146 g/mol (grams per mole)