Input interpretation

strong bases | freezing point
Summary

median | 338.85 °C highest | 800 °C (sodium hydride) lowest | -34 °C (butyllithium) distribution | | (based on 11 values; 4 unavailable)
Entities with missing values

lithium diethylamide | lithium diisopropylamide | strontium hydroxide | lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (total: 4)
Distribution plots
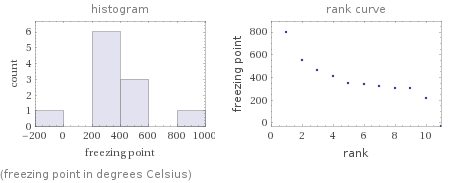
(freezing point in degrees Celsius)
Freezing point rankings
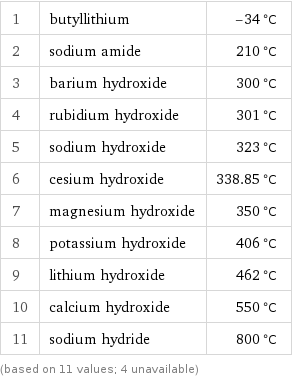
1 | butyllithium | -34 °C 2 | sodium amide | 210 °C 3 | barium hydroxide | 300 °C 4 | rubidium hydroxide | 301 °C 5 | sodium hydroxide | 323 °C 6 | cesium hydroxide | 338.85 °C 7 | magnesium hydroxide | 350 °C 8 | potassium hydroxide | 406 °C 9 | lithium hydroxide | 462 °C 10 | calcium hydroxide | 550 °C 11 | sodium hydride | 800 °C (based on 11 values; 4 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median freezing point 338.85 °C
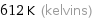
612 K (kelvins)

641.93 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

1101.6 °R (degrees Rankine)

271.08 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
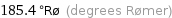
185.4 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median freezing point 338.85 °C
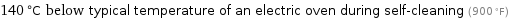
140 °C below typical temperature of an electric oven during self-cleaning (900 °F)
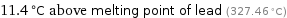
11.4 °C above melting point of lead (327.46 °C)
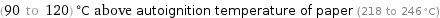
(90 to 120) °C above autoignition temperature of paper (218 to 246 °C)
Corresponding quantities
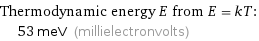
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 53 meV (millielectronvolts)
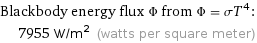
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 7955 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 4.3×10^-6 lx (lux)