Input interpretation

f-block elements | thermal conductivity
Summary

median | 13 W/(m K) highest | 54 W/(m K) (thorium) lowest | 6 W/(m K) (neptunium and plutonium) distribution | | (based on 22 values; 6 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
curium | californium | einsteinium | fermium | mendelevium | nobelium (total: 6)
Distribution plots
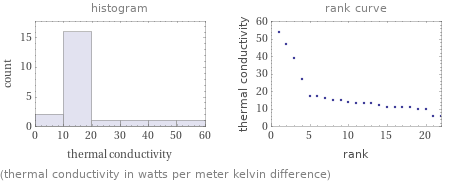
(thermal conductivity in watts per meter kelvin difference)
Thermal conductivity rankings
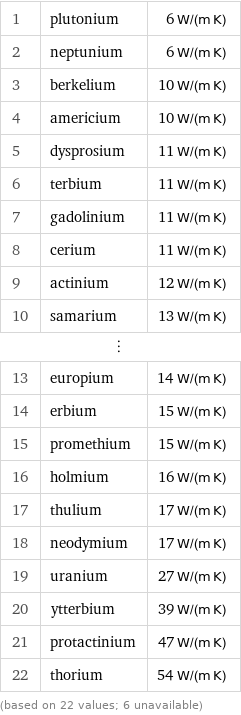
1 | plutonium | 6 W/(m K) 2 | neptunium | 6 W/(m K) 3 | berkelium | 10 W/(m K) 4 | americium | 10 W/(m K) 5 | dysprosium | 11 W/(m K) 6 | terbium | 11 W/(m K) 7 | gadolinium | 11 W/(m K) 8 | cerium | 11 W/(m K) 9 | actinium | 12 W/(m K) 10 | samarium | 13 W/(m K) ⋮ | | 13 | europium | 14 W/(m K) 14 | erbium | 15 W/(m K) 15 | promethium | 15 W/(m K) 16 | holmium | 16 W/(m K) 17 | thulium | 17 W/(m K) 18 | neodymium | 17 W/(m K) 19 | uranium | 27 W/(m K) 20 | ytterbium | 39 W/(m K) 21 | protactinium | 47 W/(m K) 22 | thorium | 54 W/(m K) (based on 22 values; 6 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median thermal conductivity 13 W/(m K)

13 W/(m °C) (watts per meter degree Celsius difference)
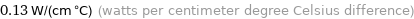
0.13 W/(cm °C) (watts per centimeter degree Celsius difference)

0.13 W/(cm K) (watts per centimeter kelvin difference)

1.3×10^6 erg/(cm K s) (ergs per centimeter kelvin difference second)

0.63 BTU_IT in/(h in^2 °F) (IT British thermal unit inches per hour square inch degree Fahrenheit difference)

7.5 BTU_IT ft/(h ft^2 °F) (IT British thermal unit feet per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit difference)

0.031 cal_th cm/(s cm^2 °C) (thermochemical calorie centimeters per second square centimeter degree Celsius difference)
Comparisons for median thermal conductivity 13 W/(m K)
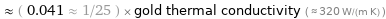
≈ ( 0.041 ≈ 1/25 ) × gold thermal conductivity ( ≈ 320 W/(m K) )

≈ ( 0.093 ≈ 1/11 ) × carbon thermal conductivity ( ≈ 140 W/(m K) )
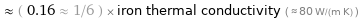
≈ ( 0.16 ≈ 1/6 ) × iron thermal conductivity ( ≈ 80 W/(m K) )