Input interpretation
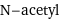
N-acetyl
Stability under oxidizing conditions
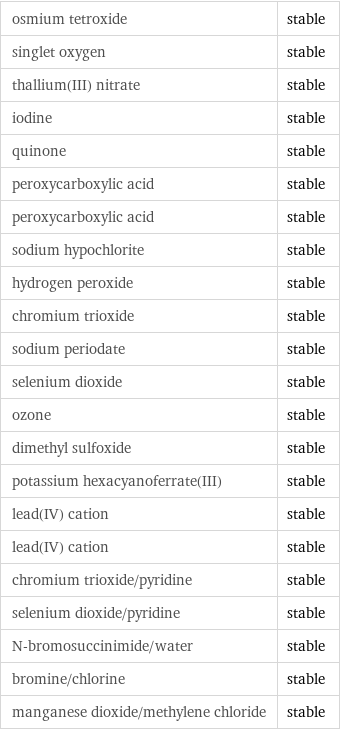
osmium tetroxide | stable singlet oxygen | stable thallium(III) nitrate | stable iodine | stable quinone | stable peroxycarboxylic acid | stable peroxycarboxylic acid | stable sodium hypochlorite | stable hydrogen peroxide | stable chromium trioxide | stable sodium periodate | stable selenium dioxide | stable ozone | stable dimethyl sulfoxide | stable potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) | stable lead(IV) cation | stable lead(IV) cation | stable chromium trioxide/pyridine | stable selenium dioxide/pyridine | stable N-bromosuccinimide/water | stable bromine/chlorine | stable manganese dioxide/methylene chloride | stable
Stability under reducing conditions
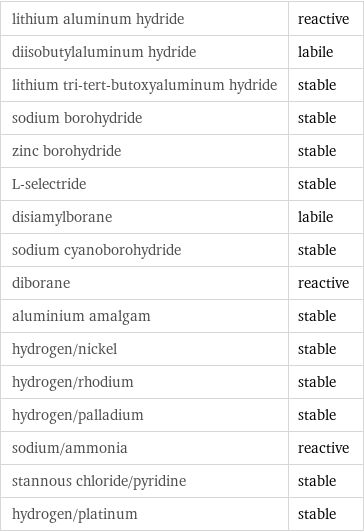
lithium aluminum hydride | reactive diisobutylaluminum hydride | labile lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride | stable sodium borohydride | stable zinc borohydride | stable L-selectride | stable disiamylborane | labile sodium cyanoborohydride | stable diborane | reactive aluminium amalgam | stable hydrogen/nickel | stable hydrogen/rhodium | stable hydrogen/palladium | stable sodium/ammonia | reactive stannous chloride/pyridine | stable hydrogen/platinum | stable
Stability under nucleophilic conditions
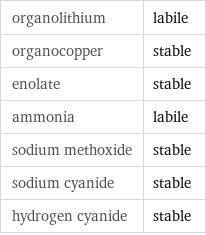
organolithium | labile organocopper | stable enolate | stable ammonia | labile sodium methoxide | stable sodium cyanide | stable hydrogen cyanide | stable
Stability under basic conditions
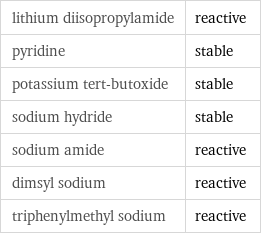
lithium diisopropylamide | reactive pyridine | stable potassium tert-butoxide | stable sodium hydride | stable sodium amide | reactive dimsyl sodium | reactive triphenylmethyl sodium | reactive
Stability under acidic conditions

lithium perchlorate/magnesium bromide | stable stannic chloride/boron trifluoride | stable copper(II) cation/pyridine | stable silver(I) cation | stable mercury(II) cation | stable
Stability under other conditions

dicyclohexylcarbodiimide | stable thionyl chloride | stable nickel carbonyl | stable diazomethane | stable trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate(1-) | reactive methyl iodide | stable
Stability under aqueous conditions
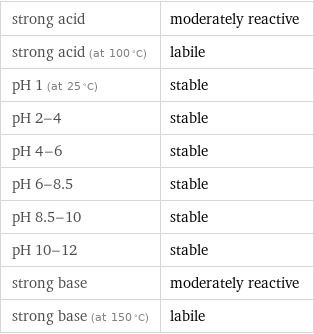
strong acid | moderately reactive strong acid (at 100 °C) | labile pH 1 (at 25 °C) | stable pH 2-4 | stable pH 4-6 | stable pH 6-8.5 | stable pH 8.5-10 | stable pH 10-12 | stable strong base | moderately reactive strong base (at 150 °C) | labile
Stability under thermal conditions
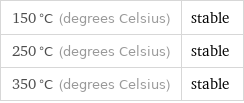
150 °C (degrees Celsius) | stable 250 °C (degrees Celsius) | stable 350 °C (degrees Celsius) | stable
Stability under organometallic conditions
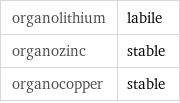
organolithium | labile organozinc | stable organocopper | stable