Input interpretation
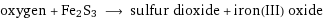
oxygen + Fe2S3 ⟶ sulfur dioxide + iron(III) oxide
Balanced equation

Balance the chemical equation algebraically: + Fe2S3 ⟶ + Add stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, to the reactants and products: c_1 + c_2 Fe2S3 ⟶ c_3 + c_4 Set the number of atoms in the reactants equal to the number of atoms in the products for O, Fe and S: O: | 2 c_1 = 2 c_3 + 3 c_4 Fe: | 2 c_2 = 2 c_4 S: | 3 c_2 = c_3 Since the coefficients are relative quantities and underdetermined, choose a coefficient to set arbitrarily. To keep the coefficients small, the arbitrary value is ordinarily one. For instance, set c_2 = 1 and solve the system of equations for the remaining coefficients: c_1 = 9/2 c_2 = 1 c_3 = 3 c_4 = 1 Multiply by the least common denominator, 2, to eliminate fractional coefficients: c_1 = 9 c_2 = 2 c_3 = 6 c_4 = 2 Substitute the coefficients into the chemical reaction to obtain the balanced equation: Answer: | | 9 + 2 Fe2S3 ⟶ 6 + 2
Structures
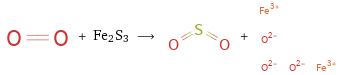
+ Fe2S3 ⟶ +
Names
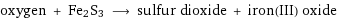
oxygen + Fe2S3 ⟶ sulfur dioxide + iron(III) oxide
Chemical names and formulas
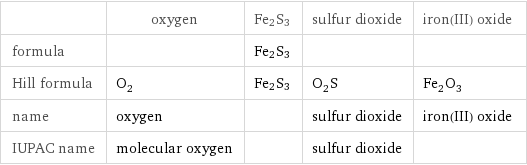
| oxygen | Fe2S3 | sulfur dioxide | iron(III) oxide formula | | Fe2S3 | | Hill formula | O_2 | Fe2S3 | O_2S | Fe_2O_3 name | oxygen | | sulfur dioxide | iron(III) oxide IUPAC name | molecular oxygen | | sulfur dioxide |
Substance properties
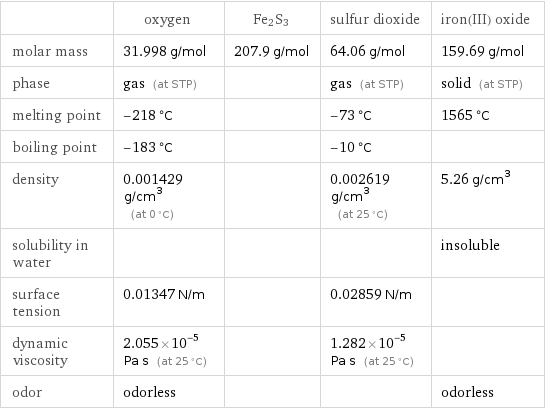
| oxygen | Fe2S3 | sulfur dioxide | iron(III) oxide molar mass | 31.998 g/mol | 207.9 g/mol | 64.06 g/mol | 159.69 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) | | gas (at STP) | solid (at STP) melting point | -218 °C | | -73 °C | 1565 °C boiling point | -183 °C | | -10 °C | density | 0.001429 g/cm^3 (at 0 °C) | | 0.002619 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) | 5.26 g/cm^3 solubility in water | | | | insoluble surface tension | 0.01347 N/m | | 0.02859 N/m | dynamic viscosity | 2.055×10^-5 Pa s (at 25 °C) | | 1.282×10^-5 Pa s (at 25 °C) | odor | odorless | | | odorless
Units
