Input interpretation
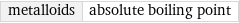
metalloids | absolute boiling point
Summary
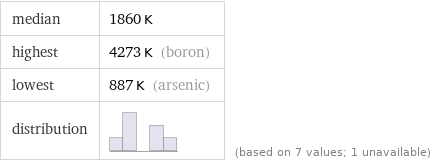
median | 1860 K highest | 4273 K (boron) lowest | 887 K (arsenic) distribution | | (based on 7 values; 1 unavailable)
Entity with missing value
tennessine
Absolute boiling point rankings
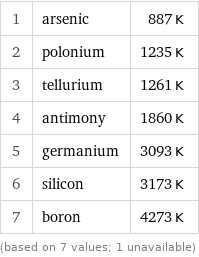
1 | arsenic | 887 K 2 | polonium | 1235 K 3 | tellurium | 1261 K 4 | antimony | 1860 K 5 | germanium | 3093 K 6 | silicon | 3173 K 7 | boron | 4273 K (based on 7 values; 1 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median absolute boiling point 1860 K
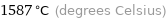
1587 °C (degrees Celsius)

2888 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
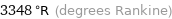
3348 °R (degrees Rankine)

1269 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

840.6 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median absolute boiling point 1860 K
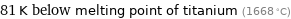
81 K below melting point of titanium (1668 °C)
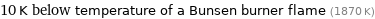
10 K below temperature of a Bunsen burner flame (1870 K)
49 K above melting point of iron (1538 °C)
Blackbody information for median absolute boiling point 1860 K (kelvins)
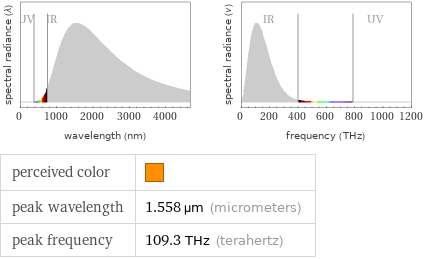
perceived color | peak wavelength | 1.558 µm (micrometers) peak frequency | 109.3 THz (terahertz)
Corresponding quantities
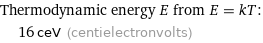
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 16 ceV (centielectronvolts)
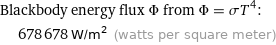
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 678678 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)
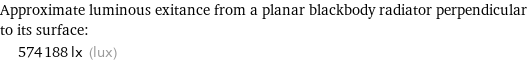
Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 574188 lx (lux)