Input interpretation
3 mol of nitrogen (chemical element)
Basic properties for 3 mol

mass | 42 grams 0.042 kg (kilograms) 1.48 oz (ounces) molar amount | 3 mol (moles) volume | 33.6 L (liters) 0.0336 m^3 (cubic meters) 33600 cm^3 (cubic centimeters) 71 pints 35.5 quarts 8.87 gallons 1.19 ft^3 (cubic feet) equivalents | 3 eq (equivalents) (at STP)
Current commodity price
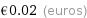
€0.02 (euros)
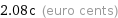
2.08c (euro cents)
Thermodynamic properties for 3 mol
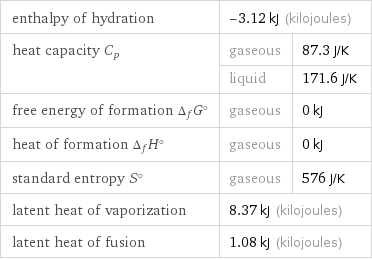
enthalpy of hydration | -3.12 kJ (kilojoules) | heat capacity C_p | gaseous | 87.3 J/K | liquid | 171.6 J/K free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gaseous | 0 kJ heat of formation Δ_fH° | gaseous | 0 kJ standard entropy S° | gaseous | 576 J/K latent heat of vaporization | 8.37 kJ (kilojoules) | latent heat of fusion | 1.08 kJ (kilojoules) |
Units

Phase change energies for 3 mol from 25 °C

energy released from cooling to condensation point | 19.3 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from converting to liquid | 40.3 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from cooling to condensation point and converting to liquid | 27.6 kJ (kilojoules)
Corresponding quantities
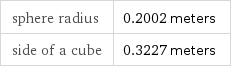
sphere radius | 0.2002 meters side of a cube | 0.3227 meters
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of nitrogen. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the nitrogen (n_N, val = 5) atoms: 2 n_N, val = 10 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for nitrogen (n_N, full = 8): 2 n_N, full = 16 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 16 - 10 = 6 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 1 bond already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
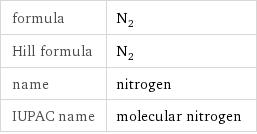
formula | N_2 Hill formula | N_2 name | nitrogen IUPAC name | molecular nitrogen
Substance properties
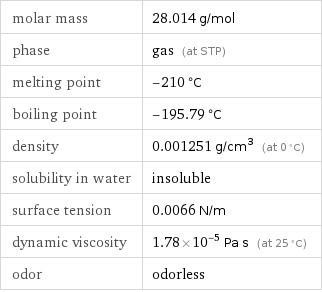
molar mass | 28.014 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -210 °C boiling point | -195.79 °C density | 0.001251 g/cm^3 (at 0 °C) solubility in water | insoluble surface tension | 0.0066 N/m dynamic viscosity | 1.78×10^-5 Pa s (at 25 °C) odor | odorless
Units
