Input interpretation

Sackur-Tetrode equation
Equation
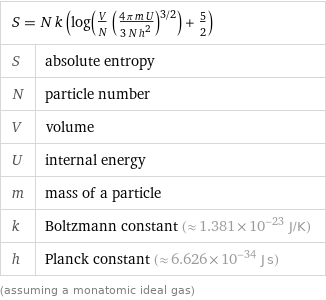
S = N k (log(V/N ((4 π m U)/(3 N h^2))^(3/2)) + 5/2) | S | absolute entropy N | particle number V | volume U | internal energy m | mass of a particle k | Boltzmann constant (≈ 1.381×10^-23 J/K) h | Planck constant (≈ 6.626×10^-34 J s) (assuming a monatomic ideal gas)
Input values
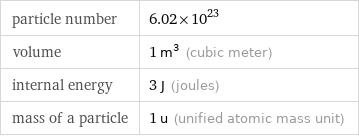
particle number | 6.02×10^23 volume | 1 m^3 (cubic meter) internal energy | 3 J (joules) mass of a particle | 1 u (unified atomic mass unit)
Result

absolute entropy | 50.76 J/K (joules per kelvin) = 3.168×10^20 eV/K (electronvolts per kelvin) = 5.076×10^8 erg/K (ergs per kelvin)