Input interpretation
scopolamine
Chemical names and formulas

formula | C_17H_21NO_4 name | scopolamine alternate names | 6, 7-epoxytropine tropate | atrochin | atroquin | hyoscine mass fractions | C (carbon) 67.3% | H (hydrogen) 6.98% | N (nitrogen) 4.62% | O (oxygen) 21.1%
Lewis structure
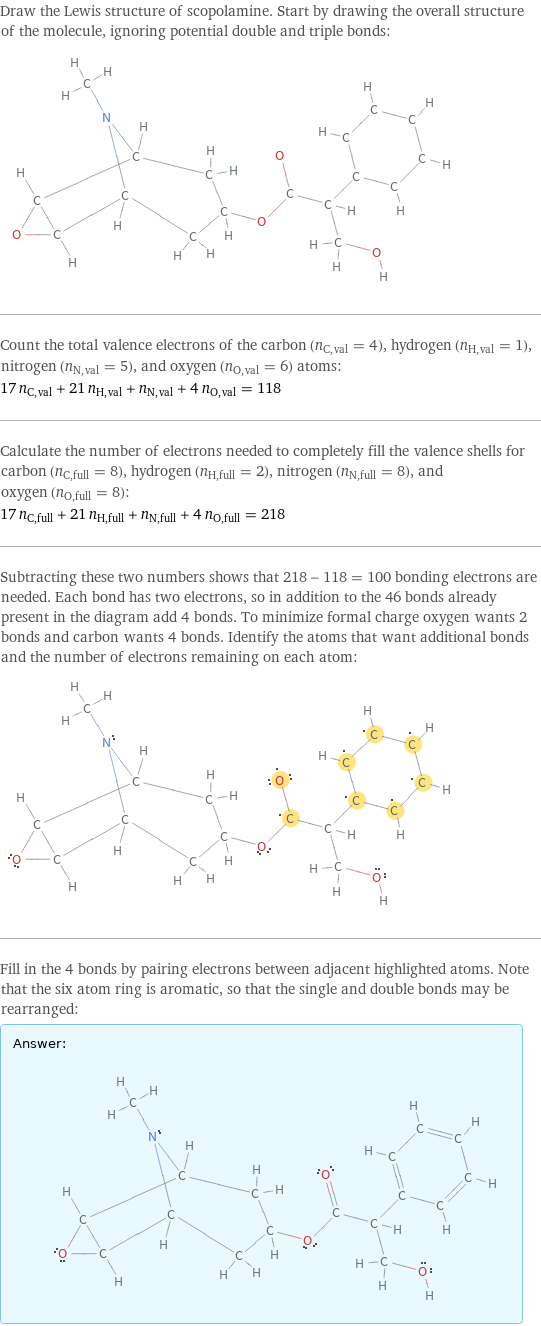
Draw the Lewis structure of scopolamine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 17 n_C, val + 21 n_H, val + n_N, val + 4 n_O, val = 118 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 17 n_C, full + 21 n_H, full + n_N, full + 4 n_O, full = 218 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 218 - 118 = 100 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 46 bonds already present in the diagram add 4 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 4 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom ring is aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
Basic properties
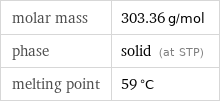
molar mass | 303.36 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 59 °C
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties
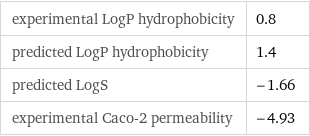
experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 0.8 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 1.4 predicted LogS | -1.66 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -4.93
Basic drug properties

approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | adjuvant | anesthesia adjuvant | antimuscarinic | antispasmodic | cholinergic antagonist | muscarinic antagonist | mydriatic dosage forms | transdermal: disc | intravenous: liquid | intramuscular: solution | intravenous: solution | oral: tablet

brand names | atrochin | atroquin | atroscine hydrobromide | beldavrin | buscopan | epoxytropine tropate | euscopol | hydroscine hydrobromide | hyocine F hydrobromide | hyosceine | hyoscine | hyoscine bromide | hyoscine hydrobromide | hyoscyine hydrobromide | hyosol | hysco | isopto hyoscine | isoscopil | kwells | L-hyoscine hydrobromide | L-scopolamine | methscopolamine bromide | oscine | SEE | scop | scopamin | scopine tropate | scopoderm-tts | scopolamine bromide | scopolamine hydrobromide | scopolamine hydrobromide trihydrate | scopolamine hyoscine | scopolaminhydrobromid | scopolaminium bromide | scopolammonium bromide | scopos | sereen | skopolamin | tranaxine | transcop | transderm-scop | transderm-V | triptone | tropic acid, ester with scopine
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 51-34-3 Beilstein number | 91903 PubChem CID number | 5809 PubChem SID number | 548858 SMILES identifier | CN1C2CC(CC1C3C2O3)OC(=O)C(CO)C4=CC=CC=C4 InChI identifier | InChI=1/C17H21NO4/c1-18-13-7-11(8-14(18)16-15(13)22-16)21-17(20)12(9-19)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-6, 11-16, 19H, 7-9H2, 1H3/t11?, 12u, 13-, 14-, 15-, 16+/m0/s1 InChI key | STECJAGHUSJQJN-UHFFFAOYAH EU number | 200-090-3 RTECS number | VR3675000
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data