Input interpretation
aspirin
Chemical names and formulas
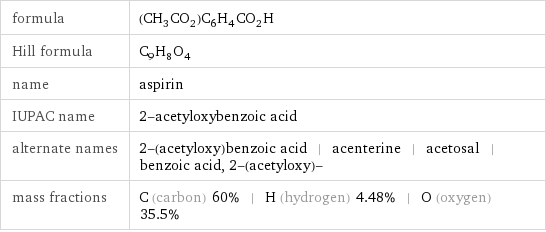
formula | (CH_3CO_2)C_6H_4CO_2H Hill formula | C_9H_8O_4 name | aspirin IUPAC name | 2-acetyloxybenzoic acid alternate names | 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid | acenterine | acetosal | benzoic acid, 2-(acetyloxy)- mass fractions | C (carbon) 60% | H (hydrogen) 4.48% | O (oxygen) 35.5%
Lewis structure
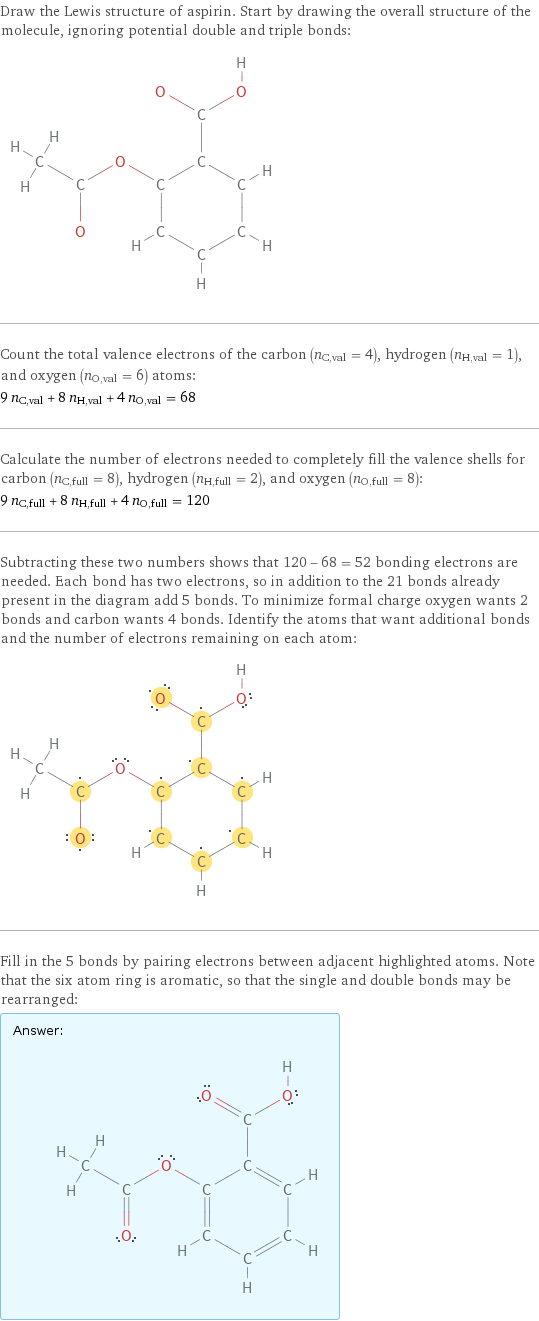
Draw the Lewis structure of aspirin. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 9 n_C, val + 8 n_H, val + 4 n_O, val = 68 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 9 n_C, full + 8 n_H, full + 4 n_O, full = 120 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 120 - 68 = 52 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 21 bonds already present in the diagram add 5 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 5 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom ring is aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
molar mass | 180.16 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 140 °C boiling point | 140 °C density | 1.39 g/cm^3
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 1.4 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 1.43 predicted LogS | -2.09 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -5.06
Drug interactions

acenocoumarol | acetazolamide | acetohexamide | anisindione | betamethasone | chlorpropamide | cortisone acetate | dexamethasone | dichlorphenamide | dicumarol | fludrocortisone | ginkgo biloba | glyburide | gliclazide | glipizide | glisoxepide | glycodiazine | griseofulvin | heparin | hydrocortisone | ... (total: 42)
Basic drug properties
approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent | anticoagulant | cyclooxygenase inhibitor | fibrinolytic agent | platelet aggregation inhibitor | salicylate dosage forms | oral: gum | oral: liquid | oral: powder | oral: solution / drops | rectal: suppository | oral: tablet | oral: tablet, chewable | oral: tablet, coated | oral: tablet, delayed release

brand names | 8-hour bayer | A.S.A. empirin | acenterine | acesal | acetal | aceticyl | acetisal | acetol | acetonyl | acetophen | acetosal | acetosalin | acetylin | acetylsal | acimetten | acisal | acylpyrin | adiro | asagran | asatard | ascoden-30 | aspalon | aspec | aspergum | aspirdrops | aspirine | aspro | asteric | bayer extra strength aspirin for migraine pain | benaspir | Bi-prin | bialpirina | bialpirinia | bufferin | caprin | cemirit | claradin | clariprin | colfarit | contrheuma retard | coricidin | crystar | decaten | delgesic | dolean pH 8 | duramax | ECM | easprin | ecolen | ecotrin | empirin | endydol | entericin | enterophen | enterosarein | enterosarine | entrophen | extren | globentyl | globoid | helicon | idragin | levius | measurin | micristin | neuronika | novid | Nu-seals | Nu-seals aspirin | persistin | pharmacin | pirseal | polopiryna | premaspin | rheumintabletten | rhodine | rhonal | salacetin | salcetogen | saletin | solfrin | solprin | solprin acid | solpyron | spira-dine | St. joseph | St. joseph aspirin for adults | supac | tasprin | temperal | triaminicin | triple-sal | vanquish | xaxa | yasta
Solid properties (at STP)
density | 1.39 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 3×10^-5 mmHg refractive index | 1.5623
Units

Thermodynamic properties
molar heat of vaporization | 106.4 kJ/mol specific heat of vaporization | 0.5906 kJ/g molar heat of combustion | 3927 kJ/mol specific heat of combustion | 21.8 kJ/g molar heat of fusion | 19.3 kJ/mol specific heat of fusion | 0.1071 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 50-78-2 Beilstein number | 779271 PubChem CID number | 2244 PubChem SID number | 4594 SMILES identifier | CC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/C9H8O4/c1-6(10)13-8-5-3-2-4-7(8)9(11)12/h2-5H, 1H3, (H, 11, 12)/f/h11H InChI key | BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-WXRBYKJCCW EU number | 200-064-1 RTECS number | VO0700000 NSC number | 406186
NFPA label

NFPA label
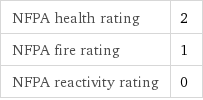
NFPA health rating | 2 NFPA fire rating | 1 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties

flash point | 250 °C
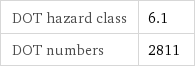
DOT hazard class | 6.1 DOT numbers | 2811
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data