Input interpretation
uranotungstite (mineral) | scheelite (mineral)
Images

Images
General properties
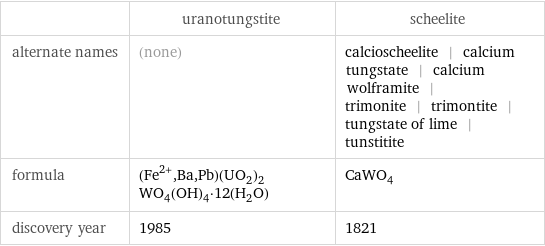
| uranotungstite | scheelite alternate names | (none) | calcioscheelite | calcium tungstate | calcium wolframite | trimonite | trimontite | tungstate of lime | tunstitite formula | (Fe^(2+), Ba, Pb)(UO_2)_2WO_4(OH)_4·12(H_2O) | CaWO_4 discovery year | 1985 | 1821
Basic properties
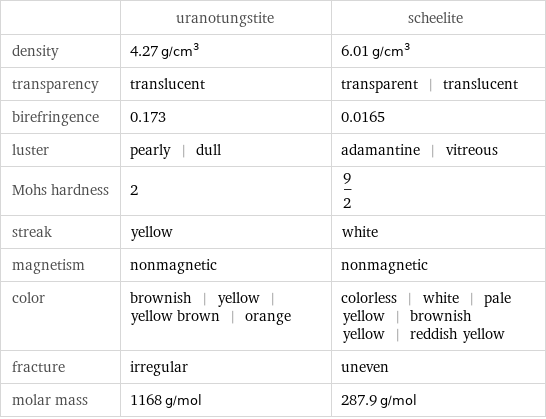
| uranotungstite | scheelite density | 4.27 g/cm^3 | 6.01 g/cm^3 transparency | translucent | transparent | translucent birefringence | 0.173 | 0.0165 luster | pearly | dull | adamantine | vitreous Mohs hardness | 2 | 9/2 streak | yellow | white magnetism | nonmagnetic | nonmagnetic color | brownish | yellow | yellow brown | orange | colorless | white | pale yellow | brownish yellow | reddish yellow fracture | irregular | uneven molar mass | 1168 g/mol | 287.9 g/mol
Units

Mineral identifiers
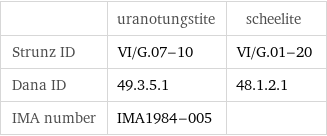
| uranotungstite | scheelite Strunz ID | VI/G.07-10 | VI/G.01-20 Dana ID | 49.3.5.1 | 48.1.2.1 IMA number | IMA1984-005 |
Crystallographic properties
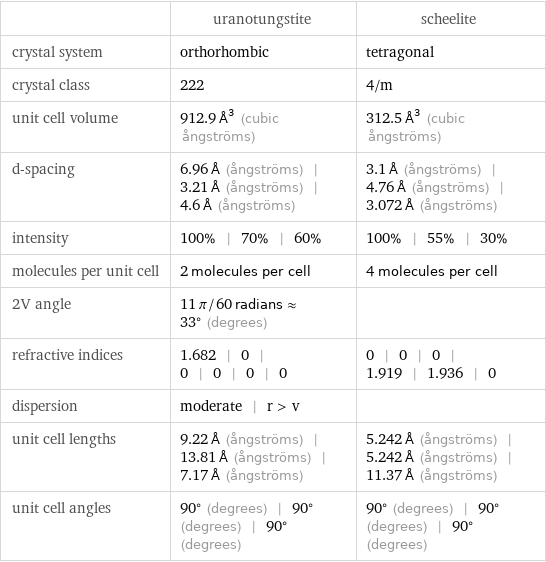
| uranotungstite | scheelite crystal system | orthorhombic | tetragonal crystal class | 222 | 4/m unit cell volume | 912.9 Å^3 (cubic ångströms) | 312.5 Å^3 (cubic ångströms) d-spacing | 6.96 Å (ångströms) | 3.21 Å (ångströms) | 4.6 Å (ångströms) | 3.1 Å (ångströms) | 4.76 Å (ångströms) | 3.072 Å (ångströms) intensity | 100% | 70% | 60% | 100% | 55% | 30% molecules per unit cell | 2 molecules per cell | 4 molecules per cell 2V angle | 11 π/60 radians≈33° (degrees) | refractive indices | 1.682 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.919 | 1.936 | 0 dispersion | moderate | r > v | unit cell lengths | 9.22 Å (ångströms) | 13.81 Å (ångströms) | 7.17 Å (ångströms) | 5.242 Å (ångströms) | 5.242 Å (ångströms) | 11.37 Å (ångströms) unit cell angles | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees)
Wikipedia summary
Scheelite

Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula CaWO_4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895.