Input interpretation
perfluorobutane
Chemical names and formulas
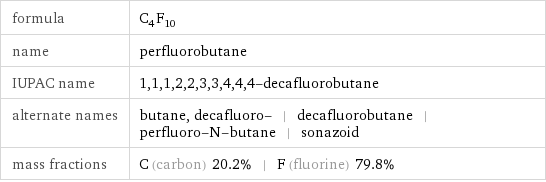
formula | C_4F_10 name | perfluorobutane IUPAC name | 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4-decafluorobutane alternate names | butane, decafluoro- | decafluorobutane | perfluoro-N-butane | sonazoid mass fractions | C (carbon) 20.2% | F (fluorine) 79.8%
Lewis structure
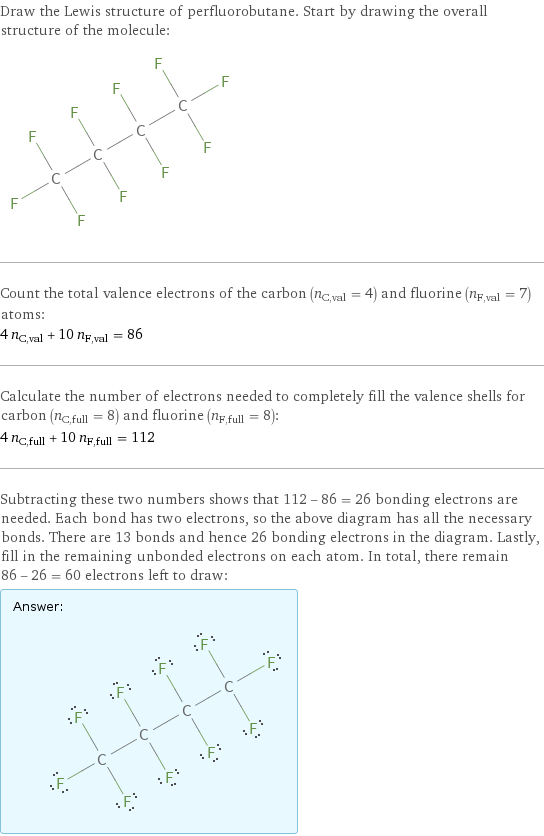
Draw the Lewis structure of perfluorobutane. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4) and fluorine (n_F, val = 7) atoms: 4 n_C, val + 10 n_F, val = 86 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8) and fluorine (n_F, full = 8): 4 n_C, full + 10 n_F, full = 112 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 112 - 86 = 26 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 13 bonds and hence 26 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 86 - 26 = 60 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
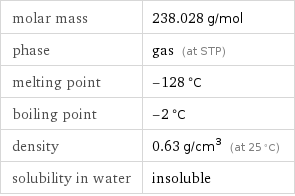
molar mass | 238.028 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -128 °C boiling point | -2 °C density | 0.63 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) solubility in water | insoluble
Units

Gas properties (at STP)
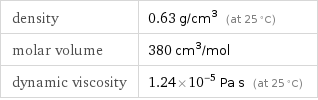
density | 0.63 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) molar volume | 380 cm^3/mol dynamic viscosity | 1.24×10^-5 Pa s (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties
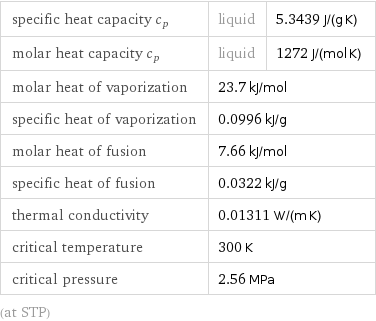
specific heat capacity c_p | liquid | 5.3439 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | liquid | 1272 J/(mol K) molar heat of vaporization | 23.7 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.0996 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 7.66 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.0322 kJ/g | thermal conductivity | 0.01311 W/(m K) | critical temperature | 300 K | critical pressure | 2.56 MPa | (at STP)
Phase diagram
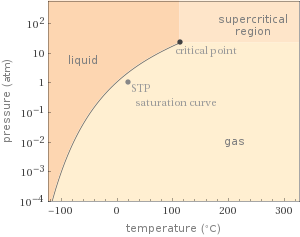
Phase diagram
Units

Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 355-25-9 PubChem CID number | 9638 SMILES identifier | C(C(C(F)(F)F)(F)F)(C(F)(F)F)(F)F InChI identifier | InChI=1/C4F10/c5-1(6, 3(9, 10)11)2(7, 8)4(12, 13)14 EU number | 206-580-3
NFPA label

NFPA label
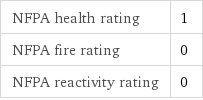
NFPA health rating | 1 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0