Input interpretation

niobium pentoxide | freezing point
Result
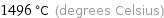
1496 °C (degrees Celsius)
Unit conversions
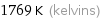
1769 K (kelvins)
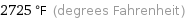
2725 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
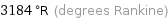
3184 °R (degrees Rankine)
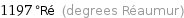
1197 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
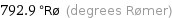
792.9 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature
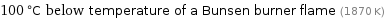
100 °C below temperature of a Bunsen burner flame (1870 K)
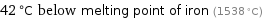
42 °C below melting point of iron (1538 °C)
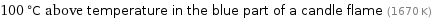
100 °C above temperature in the blue part of a candle flame (1670 K)
Blackbody information
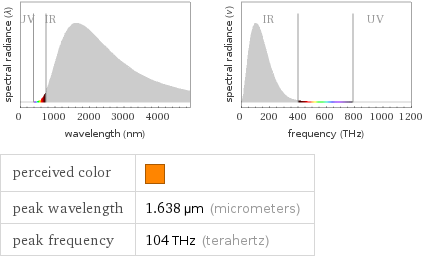
perceived color | peak wavelength | 1.638 µm (micrometers) peak frequency | 104 THz (terahertz)
Corresponding quantities
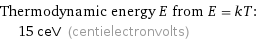
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 15 ceV (centielectronvolts)
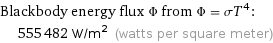
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 555482 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)
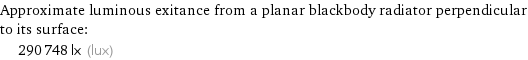
Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 290748 lx (lux)