Input interpretation

Compton shift
Equation
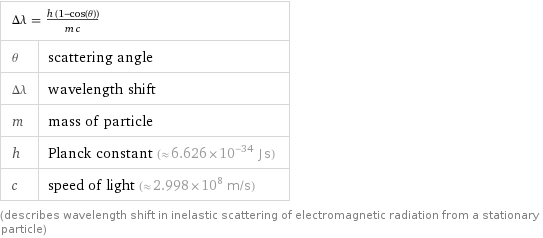
Δλ = (h (1 - cos(θ)))/(m c) | θ | scattering angle Δλ | wavelength shift m | mass of particle h | Planck constant (≈ 6.626×10^-34 J s) c | speed of light (≈ 2.998×10^8 m/s) (describes wavelength shift in inelastic scattering of electromagnetic radiation from a stationary particle)
Units

Input values
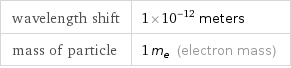
wavelength shift | 1×10^-12 meters mass of particle | 1 m_e (electron mass)
Results

scattering angle | 54° (degrees) = 942.4 mrad (milliradians) = 0.9424 radians = 53 degrees 59 arc minutes 43.1 arc seconds
Possible intermediate steps

Calculate the scattering angle using the following information: known variables | | Δλ | wavelength shift | 1×10^-12 m m | mass of particle | 1 m_e Convert known variables into appropriate units using the following: 1 m_e = 9.11×10^-28 g: known variables | | Δλ | wavelength shift | 1×10^-12 m m | mass of particle | 9.11×10^-28 g The relevant equation that relates scattering angle (θ), wavelength shift (Δλ), and mass of particle (m) is: Δλ = (h (1 - cos(θ)))/(m c) Δλ = ((1 - cos(θ)) h)/(m c) is equivalent to ((1 - cos(θ)) h)/(m c) = Δλ: ((1 - cos(θ)) h)/(m c) = Δλ Divide both sides by h/(c m): 1 - cos(θ) = (m Δλ c)/h Subtract 1 from both sides: -cos(θ) = (m Δλ c)/h - 1 Multiply both sides by -1: cos(θ) = 1 - (m Δλ c)/h Take the inverse cosine of both sides: θ = cos^(-1)(1 - (m Δλ c)/h) Substitute known variables and constants into the equation: known variables | | Δλ | wavelength shift | 1×10^-12 m m | mass of particle | 9.11×10^-28 g constants | | h | Planck constant | 132521403/200000000000000000000000000000000000000 g m^2/s c | speed of light | 3×10^8 m/s | : θ = cos^(-1)(1 - (1×10^-12 m×9.11×10^-28 g×3×10^8 m/s)/(6.63×10^-31 g m^2/s)) Cancel any units in cos^(-1)(1 - (1×10^-12 m×9.11×10^-28 g×3×10^8 m/s)/(6.63×10^-31 g m^2/s)) and add the unit rad for angles: θ = cos^(-1)(1 - (1×10^-12×9.11×10^-28×3×10^8)/(6.63×10^-31)) rad Evaluate cos^(-1)(1 - (1×10^-12×9.11×10^-28×3×10^8)/(6.63×10^-31)): θ = 0.942 rad Convert 0.942 rad into degrees using the following: 1 rad = 57.3°: Answer: | | θ = 54°
Schematic
Schematic