Input interpretation
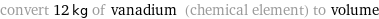
convert 12 kg of vanadium (chemical element) to volume
Results
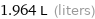
1.964 L (liters)
Possible intermediate steps
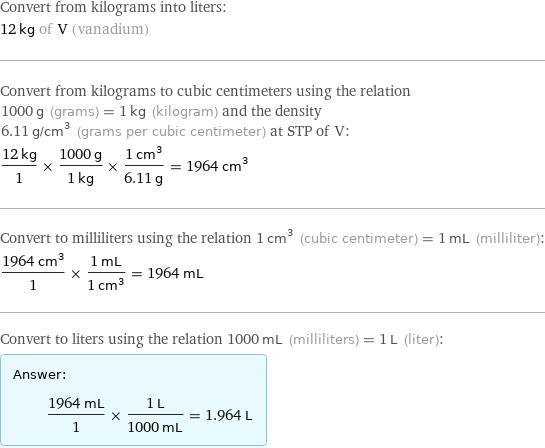
Convert from kilograms into liters: 12 kg of V (vanadium) Convert from kilograms to cubic centimeters using the relation 1000 g (grams) = 1 kg (kilogram) and the density 6.11 g/cm^3 (grams per cubic centimeter) at STP of V: (12 kg)/1 × (1000 g)/(1 kg) × (1 cm^3)/(6.11 g) = 1964 cm^3 Convert to milliliters using the relation 1 cm^3 (cubic centimeter) = 1 mL (milliliter): (1964 cm^3)/1 × (1 mL)/(1 cm^3) = 1964 mL Convert to liters using the relation 1000 mL (milliliters) = 1 L (liter): Answer: | | (1964 mL)/1 × (1 L)/(1000 mL) = 1.964 L
Unit conversions
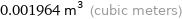
0.001964 m^3 (cubic meters)
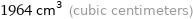
1964 cm^3 (cubic centimeters)
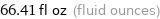
66.41 fl oz (fluid ounces)
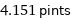
4.151 pints
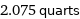
2.075 quarts
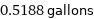
0.5188 gallons
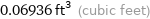
0.06936 ft^3 (cubic feet)
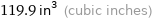
119.9 in^3 (cubic inches)
Comparisons as volume
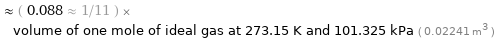
≈ ( 0.088 ≈ 1/11 ) × volume of one mole of ideal gas at 273.15 K and 101.325 kPa ( 0.02241 m^3 )
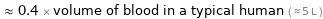
≈ 0.4 × volume of blood in a typical human ( ≈ 5 L )
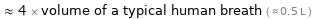
≈ 4 × volume of a typical human breath ( ≈ 0.5 L )
Comparisons as volume of food or beverage

≈ 0.63 × volume of a US size 10 can ( 105 fl oz )
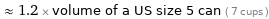
≈ 1.2 × volume of a US size 5 can ( 7 cups )
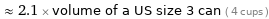
≈ 2.1 × volume of a US size 3 can ( 4 cups )
Interpretations
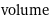
volume
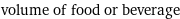
volume of food or beverage
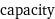
capacity
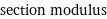
section modulus
Basic unit dimensions
![[length]^3](../image_source/ac705cffd1ff8d6c99bffb5d2d434f22.png)
[length]^3
Corresponding quantities
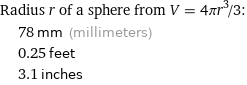
Radius r of a sphere from V = 4πr^3/3: | 78 mm (millimeters) | 0.25 feet | 3.1 inches
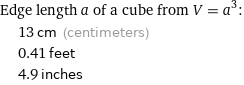
Edge length a of a cube from V = a^3: | 13 cm (centimeters) | 0.41 feet | 4.9 inches
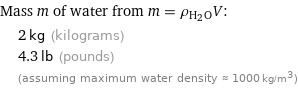
Mass m of water from m = ρ_(H_2O)V: | 2 kg (kilograms) | 4.3 lb (pounds) | (assuming maximum water density ≈ 1000 kg/m^3)
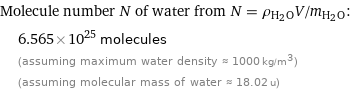
Molecule number N of water from N = ρ_(H_2O)V/m_(H_2O): | 6.565×10^25 molecules | (assuming maximum water density ≈ 1000 kg/m^3) | (assuming molecular mass of water ≈ 18.02 u)