Input interpretation
niobium (chemical element) | copper (chemical element) | palladium (chemical element)
Periodic table location
Periodic table location
Images
Images
Basic elemental properties
![| niobium | copper | palladium atomic symbol | Nb | Cu | Pd atomic number | 41 | 29 | 46 short electronic configuration | [Kr]5s^14d^4 | [Ar]4s^13d^10 | [Kr]4d^10 Aufbau diagram | 4d 5s | 3d 4s | 4d block | d | d | d group | 5 | 11 | 10 period | 5 | 4 | 5 atomic mass | 92.90637 u | 63.546 u | 106.42 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | (stable)](../image_source/6d6098e2f8dfd29a52b9199da219ec92.png)
| niobium | copper | palladium atomic symbol | Nb | Cu | Pd atomic number | 41 | 29 | 46 short electronic configuration | [Kr]5s^14d^4 | [Ar]4s^13d^10 | [Kr]4d^10 Aufbau diagram | 4d 5s | 3d 4s | 4d block | d | d | d group | 5 | 11 | 10 period | 5 | 4 | 5 atomic mass | 92.90637 u | 63.546 u | 106.42 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | (stable)
Thermodynamic properties
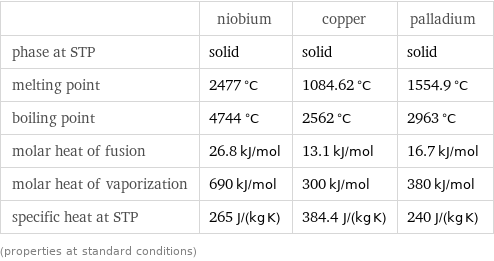
| niobium | copper | palladium phase at STP | solid | solid | solid melting point | 2477 °C | 1084.62 °C | 1554.9 °C boiling point | 4744 °C | 2562 °C | 2963 °C molar heat of fusion | 26.8 kJ/mol | 13.1 kJ/mol | 16.7 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 690 kJ/mol | 300 kJ/mol | 380 kJ/mol specific heat at STP | 265 J/(kg K) | 384.4 J/(kg K) | 240 J/(kg K) (properties at standard conditions)
Material properties
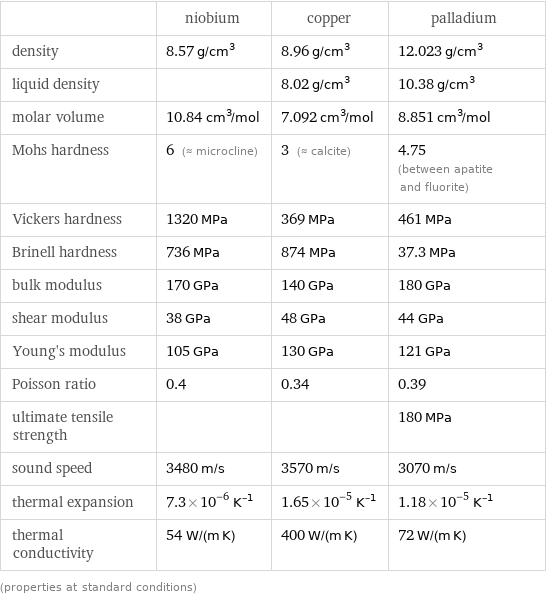
| niobium | copper | palladium density | 8.57 g/cm^3 | 8.96 g/cm^3 | 12.023 g/cm^3 liquid density | | 8.02 g/cm^3 | 10.38 g/cm^3 molar volume | 10.84 cm^3/mol | 7.092 cm^3/mol | 8.851 cm^3/mol Mohs hardness | 6 (≈ microcline) | 3 (≈ calcite) | 4.75 (between apatite and fluorite) Vickers hardness | 1320 MPa | 369 MPa | 461 MPa Brinell hardness | 736 MPa | 874 MPa | 37.3 MPa bulk modulus | 170 GPa | 140 GPa | 180 GPa shear modulus | 38 GPa | 48 GPa | 44 GPa Young's modulus | 105 GPa | 130 GPa | 121 GPa Poisson ratio | 0.4 | 0.34 | 0.39 ultimate tensile strength | | | 180 MPa sound speed | 3480 m/s | 3570 m/s | 3070 m/s thermal expansion | 7.3×10^-6 K^(-1) | 1.65×10^-5 K^(-1) | 1.18×10^-5 K^(-1) thermal conductivity | 54 W/(m K) | 400 W/(m K) | 72 W/(m K) (properties at standard conditions)
Electromagnetic properties
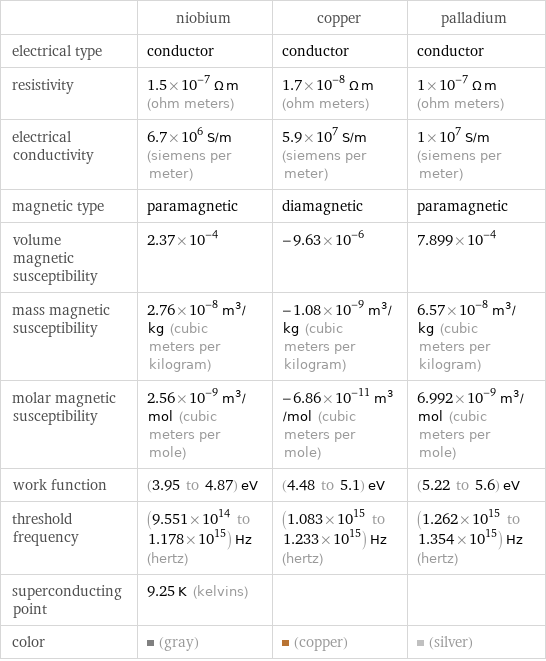
| niobium | copper | palladium electrical type | conductor | conductor | conductor resistivity | 1.5×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) | 1.7×10^-8 Ω m (ohm meters) | 1×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) electrical conductivity | 6.7×10^6 S/m (siemens per meter) | 5.9×10^7 S/m (siemens per meter) | 1×10^7 S/m (siemens per meter) magnetic type | paramagnetic | diamagnetic | paramagnetic volume magnetic susceptibility | 2.37×10^-4 | -9.63×10^-6 | 7.899×10^-4 mass magnetic susceptibility | 2.76×10^-8 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | -1.08×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | 6.57×10^-8 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) molar magnetic susceptibility | 2.56×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | -6.86×10^-11 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | 6.992×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) work function | (3.95 to 4.87) eV | (4.48 to 5.1) eV | (5.22 to 5.6) eV threshold frequency | (9.551×10^14 to 1.178×10^15) Hz (hertz) | (1.083×10^15 to 1.233×10^15) Hz (hertz) | (1.262×10^15 to 1.354×10^15) Hz (hertz) superconducting point | 9.25 K (kelvins) | | color | (gray) | (copper) | (silver)
Reactivity
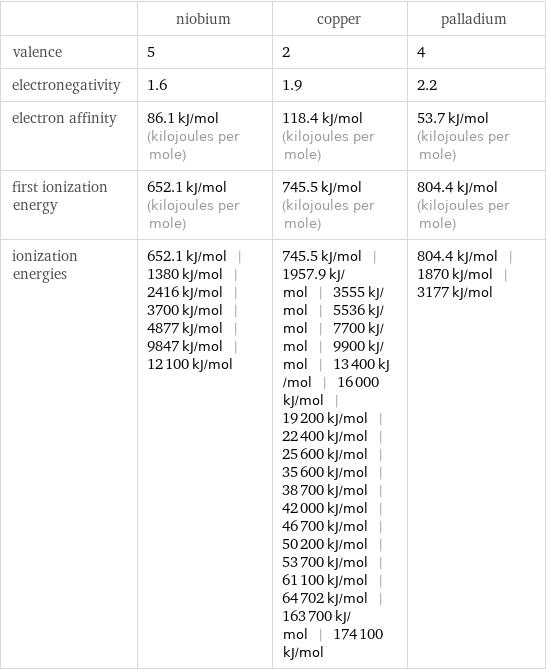
| niobium | copper | palladium valence | 5 | 2 | 4 electronegativity | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.2 electron affinity | 86.1 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 118.4 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 53.7 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) first ionization energy | 652.1 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 745.5 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 804.4 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) ionization energies | 652.1 kJ/mol | 1380 kJ/mol | 2416 kJ/mol | 3700 kJ/mol | 4877 kJ/mol | 9847 kJ/mol | 12100 kJ/mol | 745.5 kJ/mol | 1957.9 kJ/mol | 3555 kJ/mol | 5536 kJ/mol | 7700 kJ/mol | 9900 kJ/mol | 13400 kJ/mol | 16000 kJ/mol | 19200 kJ/mol | 22400 kJ/mol | 25600 kJ/mol | 35600 kJ/mol | 38700 kJ/mol | 42000 kJ/mol | 46700 kJ/mol | 50200 kJ/mol | 53700 kJ/mol | 61100 kJ/mol | 64702 kJ/mol | 163700 kJ/mol | 174100 kJ/mol | 804.4 kJ/mol | 1870 kJ/mol | 3177 kJ/mol
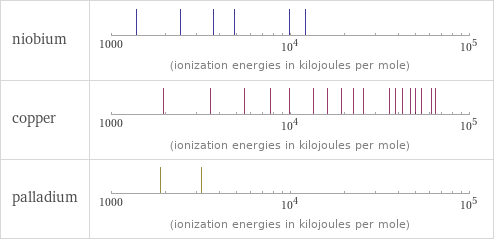
Reactivity
Atomic properties

| niobium | copper | palladium term symbol | ^6D_(1/2) | ^2S_(1/2) | ^1S_0 atomic radius | 145 pm | 135 pm | 140 pm covalent radius | 164 pm | 132 pm | 139 pm van der Waals radius | | 140 pm | 163 pm (electronic ground state properties)
Abundances
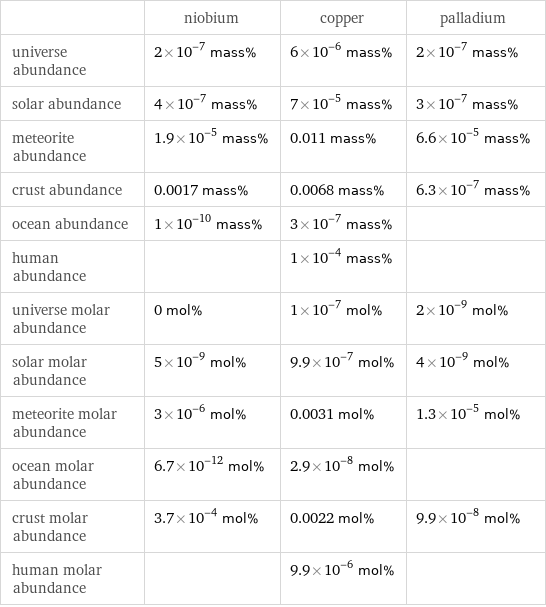
| niobium | copper | palladium universe abundance | 2×10^-7 mass% | 6×10^-6 mass% | 2×10^-7 mass% solar abundance | 4×10^-7 mass% | 7×10^-5 mass% | 3×10^-7 mass% meteorite abundance | 1.9×10^-5 mass% | 0.011 mass% | 6.6×10^-5 mass% crust abundance | 0.0017 mass% | 0.0068 mass% | 6.3×10^-7 mass% ocean abundance | 1×10^-10 mass% | 3×10^-7 mass% | human abundance | | 1×10^-4 mass% | universe molar abundance | 0 mol% | 1×10^-7 mol% | 2×10^-9 mol% solar molar abundance | 5×10^-9 mol% | 9.9×10^-7 mol% | 4×10^-9 mol% meteorite molar abundance | 3×10^-6 mol% | 0.0031 mol% | 1.3×10^-5 mol% ocean molar abundance | 6.7×10^-12 mol% | 2.9×10^-8 mol% | crust molar abundance | 3.7×10^-4 mol% | 0.0022 mol% | 9.9×10^-8 mol% human molar abundance | | 9.9×10^-6 mol% |