Input interpretation

weak electrolytes | freezing point
Summary
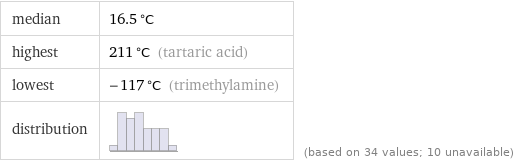
median | 16.5 °C highest | 211 °C (tartaric acid) lowest | -117 °C (trimethylamine) distribution | | (based on 34 values; 10 unavailable)
Entities with missing values

hydroxylamine | nitrous acid | hypochlorous acid | carbonic acid | aluminum hydroxide | sulfurous acid | iron(II) hydroxide | hypobromous acid | arsenious acid | hypoiodous acid (total: 10)
Distribution plots
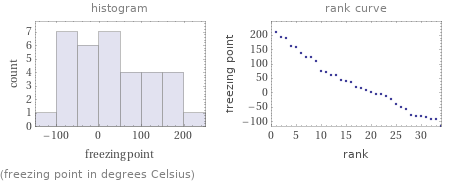
(freezing point in degrees Celsius)
Freezing point rankings
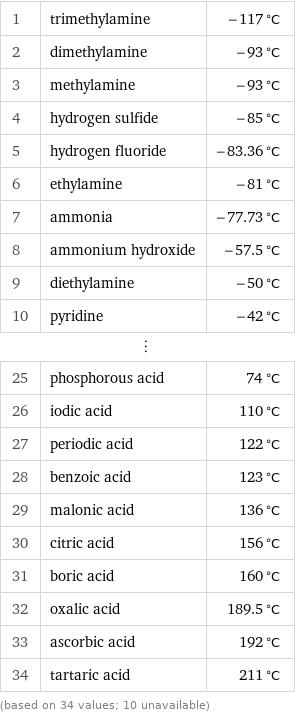
1 | trimethylamine | -117 °C 2 | dimethylamine | -93 °C 3 | methylamine | -93 °C 4 | hydrogen sulfide | -85 °C 5 | hydrogen fluoride | -83.36 °C 6 | ethylamine | -81 °C 7 | ammonia | -77.73 °C 8 | ammonium hydroxide | -57.5 °C 9 | diethylamine | -50 °C 10 | pyridine | -42 °C ⋮ | | 25 | phosphorous acid | 74 °C 26 | iodic acid | 110 °C 27 | periodic acid | 122 °C 28 | benzoic acid | 123 °C 29 | malonic acid | 136 °C 30 | citric acid | 156 °C 31 | boric acid | 160 °C 32 | oxalic acid | 189.5 °C 33 | ascorbic acid | 192 °C 34 | tartaric acid | 211 °C (based on 34 values; 10 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median freezing point 16.5 °C
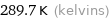
289.7 K (kelvins)

61.7 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
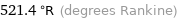
521.4 °R (degrees Rankine)

13.2 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

16.16 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median freezing point 16.5 °C

0.9444 °C above temperature at STP (standard temperature and pressure), using the US customary convention (60 °F)

1.5 °C above temperature at STP (standard temperature and pressure), using the convention of European and South American natural gas companies (15 °C)
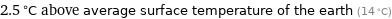
2.5 °C above average surface temperature of the earth (14 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 25 meV (millielectronvolts)
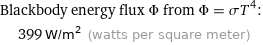
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 399 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 1.8×10^-22 lx (lux)