Input interpretation

period 4 elements | molar heat capacity
Summary

median | 25.2 J/(mol K) highest | 75.69 J/(mol K) (bromine) lowest | 20.786 J/(mol K) (krypton)
Units

Distribution plots
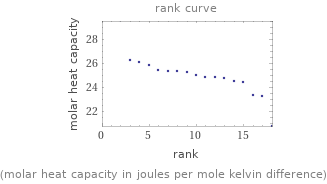
(molar heat capacity in joules per mole kelvin difference)
Molar heat capacity rankings
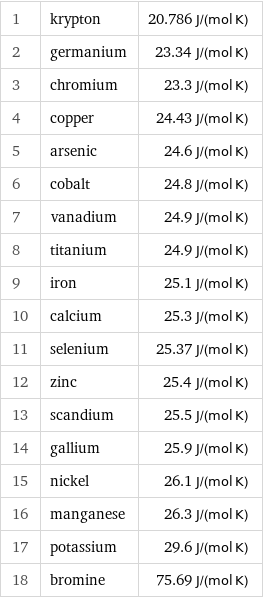
1 | krypton | 20.786 J/(mol K) 2 | germanium | 23.34 J/(mol K) 3 | chromium | 23.3 J/(mol K) 4 | copper | 24.43 J/(mol K) 5 | arsenic | 24.6 J/(mol K) 6 | cobalt | 24.8 J/(mol K) 7 | vanadium | 24.9 J/(mol K) 8 | titanium | 24.9 J/(mol K) 9 | iron | 25.1 J/(mol K) 10 | calcium | 25.3 J/(mol K) 11 | selenium | 25.37 J/(mol K) 12 | zinc | 25.4 J/(mol K) 13 | scandium | 25.5 J/(mol K) 14 | gallium | 25.9 J/(mol K) 15 | nickel | 26.1 J/(mol K) 16 | manganese | 26.3 J/(mol K) 17 | potassium | 29.6 J/(mol K) 18 | bromine | 75.69 J/(mol K)
Unit conversions for median molar heat capacity 25.2 J/(mol K)
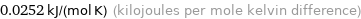
0.0252 kJ/(mol K) (kilojoules per mole kelvin difference)
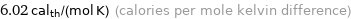
6.02 cal_th/(mol K) (calories per mole kelvin difference)
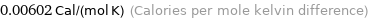
0.00602 Cal/(mol K) (Calories per mole kelvin difference)