Input interpretation
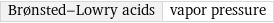
Brønsted-Lowry acids | vapor pressure
Summary

median | 1293 Pa highest | 1.737×10^6 Pa (hydrogen sulfide) lowest | 0.008 Pa (sulfuric acid) | (based on 8 values; 2 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
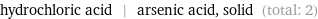
hydrochloric acid | arsenic acid, solid (total: 2)
Vapor pressure rankings
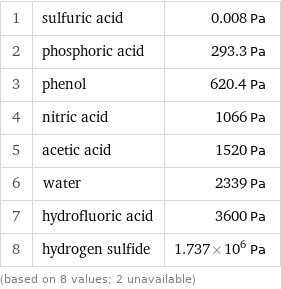
1 | sulfuric acid | 0.008 Pa 2 | phosphoric acid | 293.3 Pa 3 | phenol | 620.4 Pa 4 | nitric acid | 1066 Pa 5 | acetic acid | 1520 Pa 6 | water | 2339 Pa 7 | hydrofluoric acid | 3600 Pa 8 | hydrogen sulfide | 1.737×10^6 Pa (based on 8 values; 2 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median vapor pressure 1293 Pa
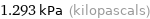
1.293 kPa (kilopascals)

1293 N/m^2 (newtons per square meter)
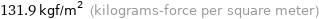
131.9 kgf/m^2 (kilograms-force per square meter)
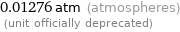
0.01276 atm (atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)

0.01319 at (technical atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)
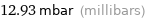
12.93 mbar (millibars)
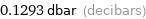
0.1293 dbar (decibars)
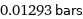
0.01293 bars
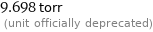
9.698 torr (unit officially deprecated)
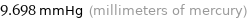
9.698 mmHg (millimeters of mercury)

0.3818 inHg (inches of mercury)

13.19 cm WC (centimeters of water column)

131.9 mm WC (millimeters of water column)

0.1319 m WC (meters of water column)

5.191 in WC (inches of water column (conventional))

0.1875 psi (pounds-force per square inch)
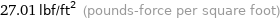
27.01 lbf/ft^2 (pounds-force per square foot)
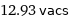
12.93 vacs
Comparisons for median vapor pressure 1293 Pa

≈ 0.43 × typical pressure inside a domestic LPG cylinder with 70% propane and 30% butane at 20 degrees Celsius ( 3 kPa )

≈ (0.1 to 1.3) × approximate explosion peak overpressure needed to break a glass window ( 1000 to 10000 Pa )
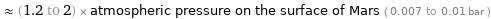
≈ (1.2 to 2) × atmospheric pressure on the surface of Mars ( 0.007 to 0.01 bar )
Corresponding quantities
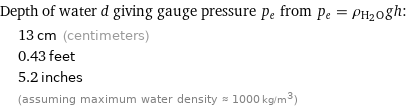
Depth of water d giving gauge pressure p_e from p_e = ρ_(H_2O)gh: | 13 cm (centimeters) | 0.43 feet | 5.2 inches | (assuming maximum water density ≈ 1000 kg/m^3)

Standard Atmosphere altitude: | 29 km (kilometers) | 18 miles | (based on 1976 US Standard Atmosphere)