Input interpretation

N-hexane | orbital hybridization
Result

First draw the structure diagram for N-hexane, and for every non-hydrogen atom, count the σ-bonds. Note that double and triple bonds consist of one σ-bond together with one or two π-bonds: For N-hexane there are no lone pairs, so the steric number is given by the σ-bond count. Consult the following chart to determine the hybridization from the steric number: steric number | hybridization 2 | sp 3 | sp^2 4 | sp^3 5 | dsp^3 6 | d^2sp^3 7 | d^3sp^3 Now assign the hybridization for each atom: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
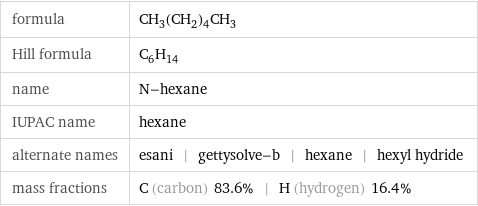
formula | CH_3(CH_2)_4CH_3 Hill formula | C_6H_14 name | N-hexane IUPAC name | hexane alternate names | esani | gettysolve-b | hexane | hexyl hydride mass fractions | C (carbon) 83.6% | H (hydrogen) 16.4%