Input interpretation
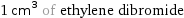
1 cm^3 of ethylene dibromide
Basic properties for 1 cm^3
mass | 2.18 grams 0.00218 kg (kilograms) molar amount | 11.6 mmol (millimoles) 0.0116 mol (moles) volume | 1 mL (milliliter) 1000 µL (microliters) 0.001 L (liters) 1×10^-6 m^3 (cubic meters) 0.203 tsp (teaspoons) 0.00106 quarts equivalents | 0.0116 eq (equivalents) (at STP)
Corresponding quantities
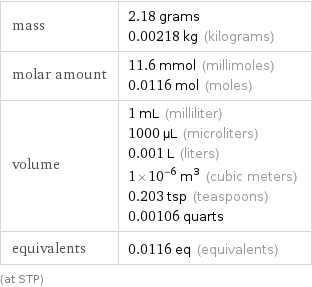
sphere radius | 6.204 mm (millimeters) side of a cube | 10 mm (millimeters)
Thermodynamic properties for 1 cm^3
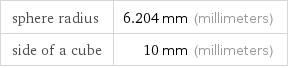
latent heat of vaporization | 0.42 kJ (kilojoules) latent heat of fusion | 0.126 kJ (kilojoules)
Phase change energies for 1 cm^3 from 25 °C

energy required to convert to vapor | 0.42 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from converting to solid | 0.126 kJ (kilojoules)
Mass composition for 1 cm^3
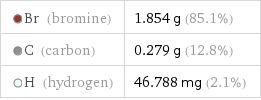
Br (bromine) | 1.854 g (85.1%) C (carbon) | 0.279 g (12.8%) H (hydrogen) | 46.788 mg (2.1%)
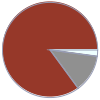
Mass composition for 1 cm^3
Lewis structure
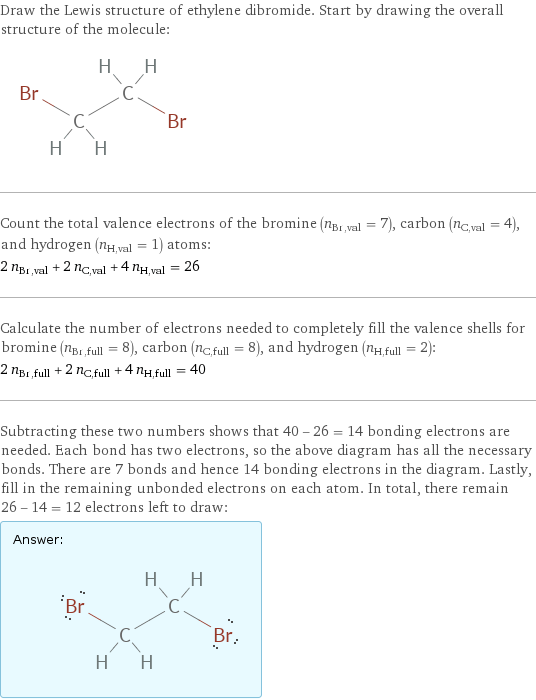
Draw the Lewis structure of ethylene dibromide. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the bromine (n_Br, val = 7), carbon (n_C, val = 4), and hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: 2 n_Br, val + 2 n_C, val + 4 n_H, val = 26 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for bromine (n_Br, full = 8), carbon (n_C, full = 8), and hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): 2 n_Br, full + 2 n_C, full + 4 n_H, full = 40 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 40 - 26 = 14 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 7 bonds and hence 14 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 26 - 14 = 12 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
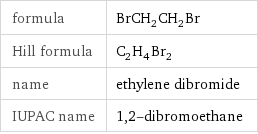
formula | BrCH_2CH_2Br Hill formula | C_2H_4Br_2 name | ethylene dibromide IUPAC name | 1, 2-dibromoethane
Substance properties
molar mass | 187.86 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | 9.5 °C boiling point | 131.5 °C density | 2.18 g/cm^3 surface tension | 0.03875 N/m dynamic viscosity | 0.001595 Pa s (at 25 °C)
Units
