Input interpretation
2-ethylhexyl methacrylate
Chemical names and formulas
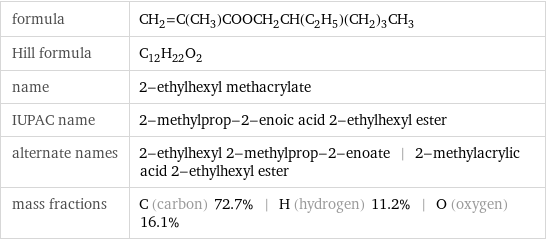
formula | CH_2=C(CH_3)COOCH_2CH(C_2H_5)(CH_2)_3CH_3 Hill formula | C_12H_22O_2 name | 2-ethylhexyl methacrylate IUPAC name | 2-methylprop-2-enoic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester alternate names | 2-ethylhexyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate | 2-methylacrylic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester mass fractions | C (carbon) 72.7% | H (hydrogen) 11.2% | O (oxygen) 16.1%
Lewis structure
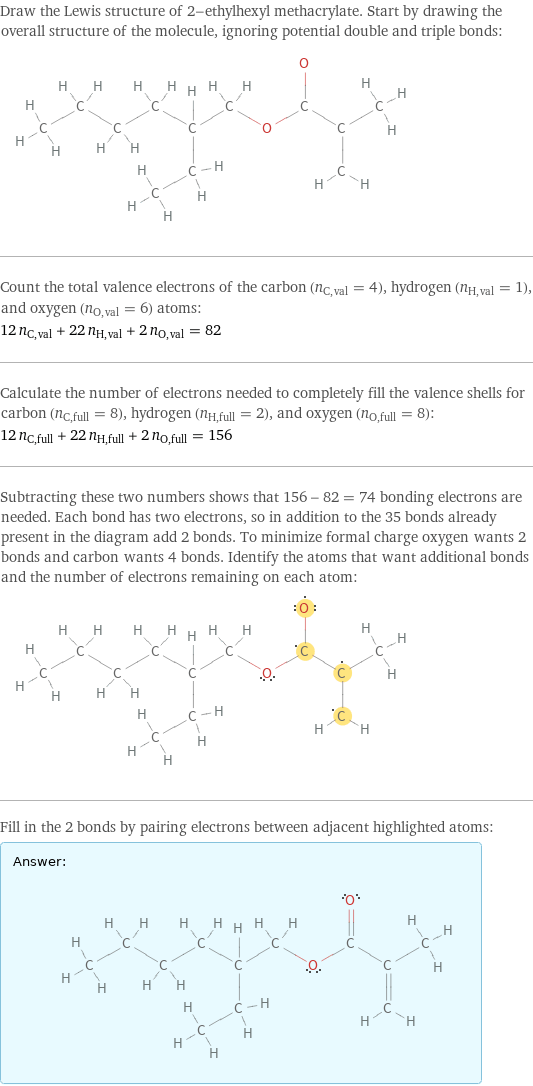
Draw the Lewis structure of 2-ethylhexyl methacrylate. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 12 n_C, val + 22 n_H, val + 2 n_O, val = 82 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 12 n_C, full + 22 n_H, full + 2 n_O, full = 156 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 156 - 82 = 74 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 35 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
molar mass | 198.31 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) boiling point | 120 °C (measured at 2399 Pa) density | 0.885 g/cm^3
Units

Liquid properties (at STP)
density | 0.885 g/cm^3 refractive index | 1.438
Units

Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 688-84-6 Beilstein number | 1769420 PubChem CID number | 12713 PubChem SID number | 24857488 SMILES identifier | CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)C(=C)C InChI identifier | InChI=1/C12H22O2/c1-5-7-8-11(6-2)9-14-12(13)10(3)4/h11H, 3, 5-9H2, 1-2, 4H3 RTECS number | OZ4630000 MDL number | MFCD00009494
Safety properties

flash point | 92.22 °C