Input interpretation
carbon (chemical element) | iodine (chemical element) | palladium (chemical element)
Periodic table location
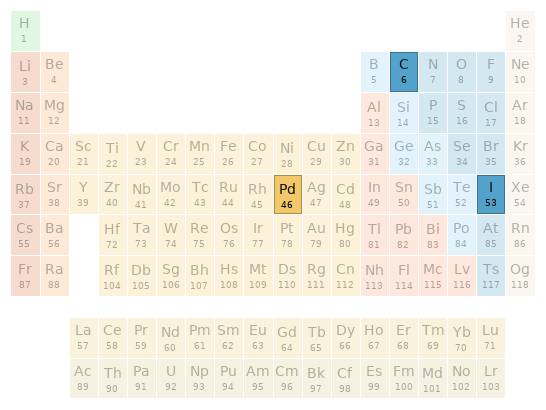
Periodic table location
Images

Images
Basic elemental properties
![| carbon | iodine | palladium atomic symbol | C | I | Pd atomic number | 6 | 53 | 46 short electronic configuration | [He]2s^22p^2 | [Kr]5s^24d^105p^5 | [Kr]4d^10 Aufbau diagram | 2p 2s | 5p 4d 5s | 4d block | p | p | d group | 14 | 17 | 10 period | 2 | 5 | 5 atomic mass | 12.011 u | 126.90447 u | 106.42 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | (stable)](../image_source/ec1ae062769381c4497878464530fbad.png)
| carbon | iodine | palladium atomic symbol | C | I | Pd atomic number | 6 | 53 | 46 short electronic configuration | [He]2s^22p^2 | [Kr]5s^24d^105p^5 | [Kr]4d^10 Aufbau diagram | 2p 2s | 5p 4d 5s | 4d block | p | p | d group | 14 | 17 | 10 period | 2 | 5 | 5 atomic mass | 12.011 u | 126.90447 u | 106.42 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | (stable)
Thermodynamic properties
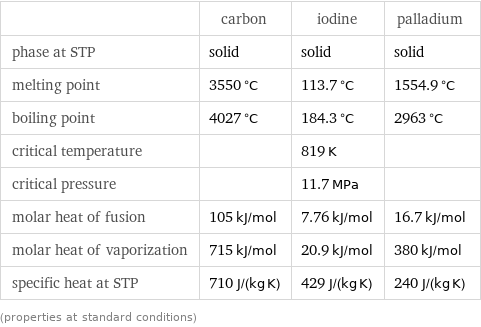
| carbon | iodine | palladium phase at STP | solid | solid | solid melting point | 3550 °C | 113.7 °C | 1554.9 °C boiling point | 4027 °C | 184.3 °C | 2963 °C critical temperature | | 819 K | critical pressure | | 11.7 MPa | molar heat of fusion | 105 kJ/mol | 7.76 kJ/mol | 16.7 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 715 kJ/mol | 20.9 kJ/mol | 380 kJ/mol specific heat at STP | 710 J/(kg K) | 429 J/(kg K) | 240 J/(kg K) (properties at standard conditions)
Material properties
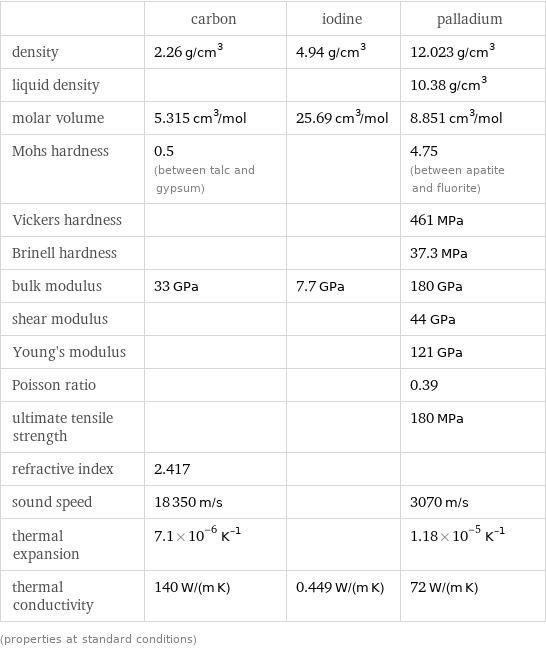
| carbon | iodine | palladium density | 2.26 g/cm^3 | 4.94 g/cm^3 | 12.023 g/cm^3 liquid density | | | 10.38 g/cm^3 molar volume | 5.315 cm^3/mol | 25.69 cm^3/mol | 8.851 cm^3/mol Mohs hardness | 0.5 (between talc and gypsum) | | 4.75 (between apatite and fluorite) Vickers hardness | | | 461 MPa Brinell hardness | | | 37.3 MPa bulk modulus | 33 GPa | 7.7 GPa | 180 GPa shear modulus | | | 44 GPa Young's modulus | | | 121 GPa Poisson ratio | | | 0.39 ultimate tensile strength | | | 180 MPa refractive index | 2.417 | | sound speed | 18350 m/s | | 3070 m/s thermal expansion | 7.1×10^-6 K^(-1) | | 1.18×10^-5 K^(-1) thermal conductivity | 140 W/(m K) | 0.449 W/(m K) | 72 W/(m K) (properties at standard conditions)
Electromagnetic properties
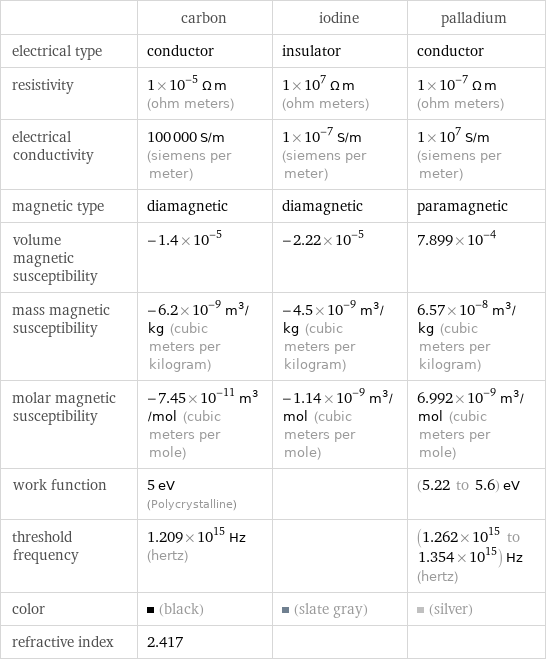
| carbon | iodine | palladium electrical type | conductor | insulator | conductor resistivity | 1×10^-5 Ω m (ohm meters) | 1×10^7 Ω m (ohm meters) | 1×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) electrical conductivity | 100000 S/m (siemens per meter) | 1×10^-7 S/m (siemens per meter) | 1×10^7 S/m (siemens per meter) magnetic type | diamagnetic | diamagnetic | paramagnetic volume magnetic susceptibility | -1.4×10^-5 | -2.22×10^-5 | 7.899×10^-4 mass magnetic susceptibility | -6.2×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | -4.5×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | 6.57×10^-8 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) molar magnetic susceptibility | -7.45×10^-11 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | -1.14×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | 6.992×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) work function | 5 eV (Polycrystalline) | | (5.22 to 5.6) eV threshold frequency | 1.209×10^15 Hz (hertz) | | (1.262×10^15 to 1.354×10^15) Hz (hertz) color | (black) | (slate gray) | (silver) refractive index | 2.417 | |
Reactivity
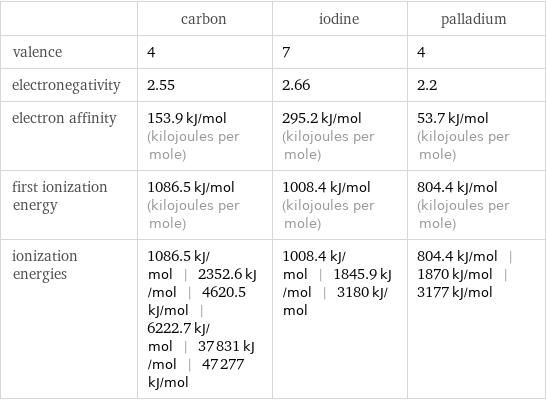
| carbon | iodine | palladium valence | 4 | 7 | 4 electronegativity | 2.55 | 2.66 | 2.2 electron affinity | 153.9 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 295.2 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 53.7 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) first ionization energy | 1086.5 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 1008.4 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 804.4 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) ionization energies | 1086.5 kJ/mol | 2352.6 kJ/mol | 4620.5 kJ/mol | 6222.7 kJ/mol | 37831 kJ/mol | 47277 kJ/mol | 1008.4 kJ/mol | 1845.9 kJ/mol | 3180 kJ/mol | 804.4 kJ/mol | 1870 kJ/mol | 3177 kJ/mol
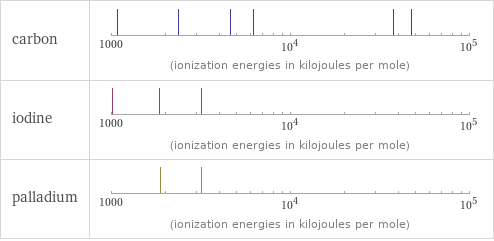
Reactivity
Atomic properties
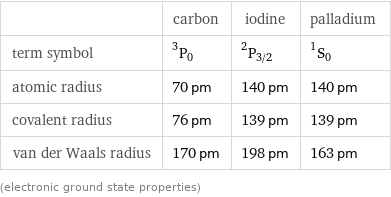
| carbon | iodine | palladium term symbol | ^3P_0 | ^2P_(3/2) | ^1S_0 atomic radius | 70 pm | 140 pm | 140 pm covalent radius | 76 pm | 139 pm | 139 pm van der Waals radius | 170 pm | 198 pm | 163 pm (electronic ground state properties)
Abundances
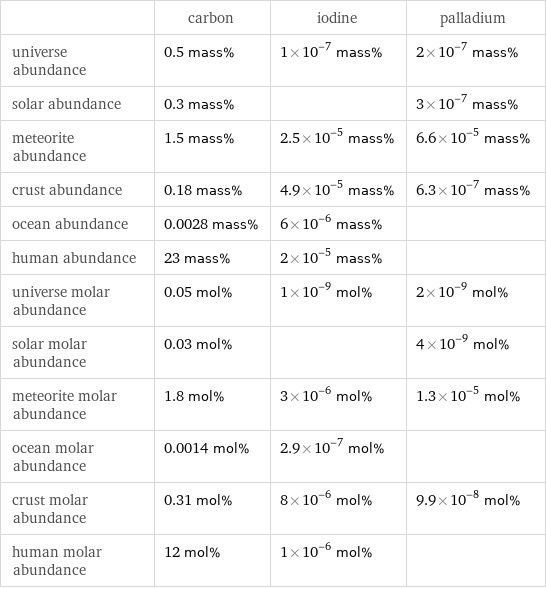
| carbon | iodine | palladium universe abundance | 0.5 mass% | 1×10^-7 mass% | 2×10^-7 mass% solar abundance | 0.3 mass% | | 3×10^-7 mass% meteorite abundance | 1.5 mass% | 2.5×10^-5 mass% | 6.6×10^-5 mass% crust abundance | 0.18 mass% | 4.9×10^-5 mass% | 6.3×10^-7 mass% ocean abundance | 0.0028 mass% | 6×10^-6 mass% | human abundance | 23 mass% | 2×10^-5 mass% | universe molar abundance | 0.05 mol% | 1×10^-9 mol% | 2×10^-9 mol% solar molar abundance | 0.03 mol% | | 4×10^-9 mol% meteorite molar abundance | 1.8 mol% | 3×10^-6 mol% | 1.3×10^-5 mol% ocean molar abundance | 0.0014 mol% | 2.9×10^-7 mol% | crust molar abundance | 0.31 mol% | 8×10^-6 mol% | 9.9×10^-8 mol% human molar abundance | 12 mol% | 1×10^-6 mol% |