Input interpretation
silicon monosulfide
Chemical names and formulas

formula | SiS Hill formula | SSi name | silicon monosulfide mass fractions | S (sulfur) 53.3% | Si (silicon) 46.7%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of silicon monosulfide. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the sulfur (n_S, val = 6) and silicon (n_Si, val = 4) atoms: n_S, val + n_Si, val = 10 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for sulfur (n_S, full = 8) and silicon (n_Si, full = 8): n_S, full + n_Si, full = 16 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 16 - 10 = 6 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 1 bond already present in the diagram we expect to add 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Because the bonds cannot all fit and period 2 elements cannot expand their valence, the central silicon atom will have a deficient valence. Therefore we add a total of 1 bond to the diagram: Answer: | |
Basic properties
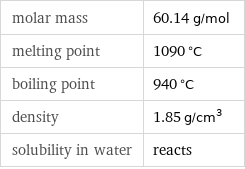
molar mass | 60.14 g/mol melting point | 1090 °C boiling point | 940 °C density | 1.85 g/cm^3 solubility in water | reacts
Units

Chemical identifiers
![CAS number | 12504-41-5 SMILES identifier | S=[Si]](../image_source/fd26771ffa84f6d4f0ef0a60a57bbbbf.png)
CAS number | 12504-41-5 SMILES identifier | S=[Si]