Input interpretation
kyanite (mineral) | zircon (mineral) | lizardite (mineral)
Images

Images
General properties
![| kyanite | zircon | lizardite alternate names | cyanite | distene | disthene | rhaeticite | azorite | cyrtolite | orthoantigorite | scyelite formula | Al_2SiO_5=Al[6]Al[6]OSiO_4 | ZrSiO_4 | Mg_3Si_2O_5(OH)_4](../image_source/180a5dc30943f957f895cf4143bcc953.png)
| kyanite | zircon | lizardite alternate names | cyanite | distene | disthene | rhaeticite | azorite | cyrtolite | orthoantigorite | scyelite formula | Al_2SiO_5=Al[6]Al[6]OSiO_4 | ZrSiO_4 | Mg_3Si_2O_5(OH)_4
Basic properties
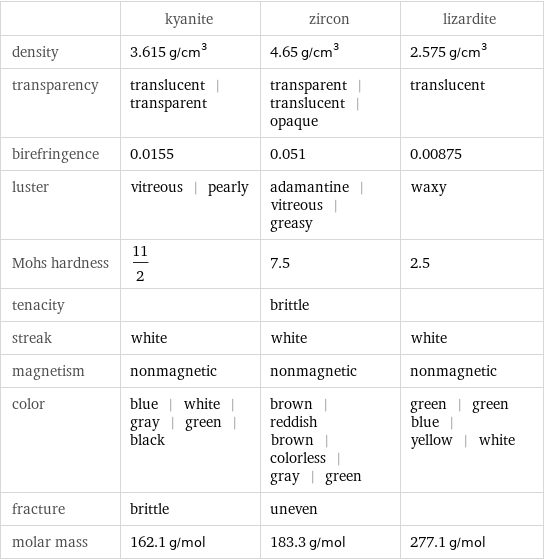
| kyanite | zircon | lizardite density | 3.615 g/cm^3 | 4.65 g/cm^3 | 2.575 g/cm^3 transparency | translucent | transparent | transparent | translucent | opaque | translucent birefringence | 0.0155 | 0.051 | 0.00875 luster | vitreous | pearly | adamantine | vitreous | greasy | waxy Mohs hardness | 11/2 | 7.5 | 2.5 tenacity | | brittle | streak | white | white | white magnetism | nonmagnetic | nonmagnetic | nonmagnetic color | blue | white | gray | green | black | brown | reddish brown | colorless | gray | green | green | green blue | yellow | white fracture | brittle | uneven | molar mass | 162.1 g/mol | 183.3 g/mol | 277.1 g/mol
Units

Mineral identifiers
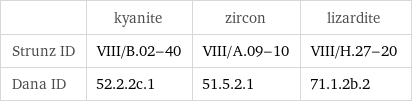
| kyanite | zircon | lizardite Strunz ID | VIII/B.02-40 | VIII/A.09-10 | VIII/H.27-20 Dana ID | 52.2.2c.1 | 51.5.2.1 | 71.1.2b.2
Crystallographic properties
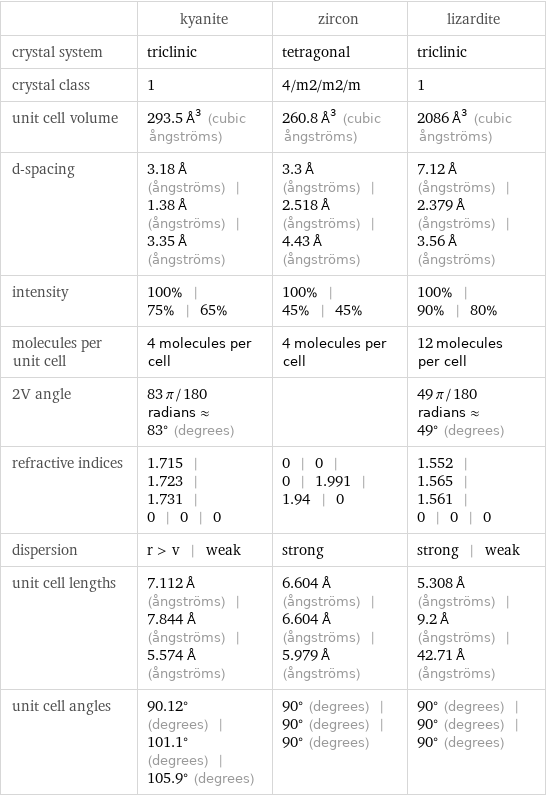
| kyanite | zircon | lizardite crystal system | triclinic | tetragonal | triclinic crystal class | 1 | 4/m2/m2/m | 1 unit cell volume | 293.5 Å^3 (cubic ångströms) | 260.8 Å^3 (cubic ångströms) | 2086 Å^3 (cubic ångströms) d-spacing | 3.18 Å (ångströms) | 1.38 Å (ångströms) | 3.35 Å (ångströms) | 3.3 Å (ångströms) | 2.518 Å (ångströms) | 4.43 Å (ångströms) | 7.12 Å (ångströms) | 2.379 Å (ångströms) | 3.56 Å (ångströms) intensity | 100% | 75% | 65% | 100% | 45% | 45% | 100% | 90% | 80% molecules per unit cell | 4 molecules per cell | 4 molecules per cell | 12 molecules per cell 2V angle | 83 π/180 radians≈83° (degrees) | | 49 π/180 radians≈49° (degrees) refractive indices | 1.715 | 1.723 | 1.731 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.991 | 1.94 | 0 | 1.552 | 1.565 | 1.561 | 0 | 0 | 0 dispersion | r > v | weak | strong | strong | weak unit cell lengths | 7.112 Å (ångströms) | 7.844 Å (ångströms) | 5.574 Å (ångströms) | 6.604 Å (ångströms) | 6.604 Å (ångströms) | 5.979 Å (ångströms) | 5.308 Å (ångströms) | 9.2 Å (ångströms) | 42.71 Å (ångströms) unit cell angles | 90.12° (degrees) | 101.1° (degrees) | 105.9° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees) | 90° (degrees)
Wikipedia summary
Kyanite

Kyanite is typically a blue aluminosilicate mineral, usually found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and/or sedimentary rock. Kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates pressures higher than four kilobars. It is commonly found in quartz. Although potentially stable at lower pressure and low temperature, the activity of water is usually high enough under such conditions that it is replaced by hydrous aluminosilicates such as muscovite, pyrophyllite, or kaolinite. Kyanite is also known as disthene, rhaeticite and cyanite.
Zircon

Zircon is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates. Its chemical name is zirconium silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is ZrSiO_4. A common empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr_(1-y), REE_y)(SiO_4)_(1-x)(OH)_(4x-y). Zircon forms in silicate melts with large proportions of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural colour of zircon varies between colourless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue and green.