Input interpretation

paramagnetic elements | tensile yield strength
Summary

median | 140 MPa highest | 1.29 GPa (technetium) lowest | 60 MPa (4 elements) distribution | | (based on 21 values; 28 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
actinium | aluminum | americium | barium | calcium | cesium | europium | hafnium | iridium | lithium | ... (total: 28)
Distribution plots
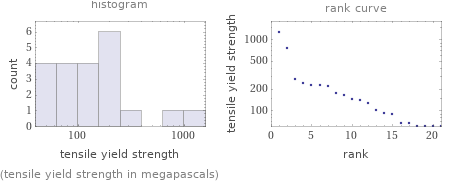
(tensile yield strength in megapascals)
Tensile yield strength rankings
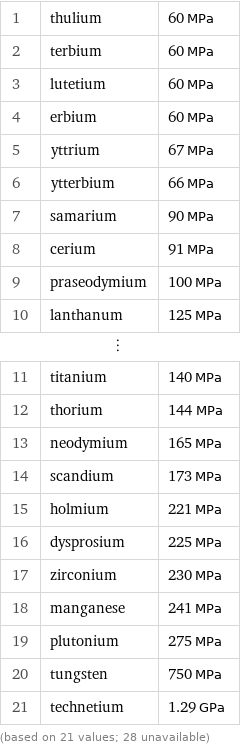
1 | thulium | 60 MPa 2 | terbium | 60 MPa 3 | lutetium | 60 MPa 4 | erbium | 60 MPa 5 | yttrium | 67 MPa 6 | ytterbium | 66 MPa 7 | samarium | 90 MPa 8 | cerium | 91 MPa 9 | praseodymium | 100 MPa 10 | lanthanum | 125 MPa ⋮ | | 11 | titanium | 140 MPa 12 | thorium | 144 MPa 13 | neodymium | 165 MPa 14 | scandium | 173 MPa 15 | holmium | 221 MPa 16 | dysprosium | 225 MPa 17 | zirconium | 230 MPa 18 | manganese | 241 MPa 19 | plutonium | 275 MPa 20 | tungsten | 750 MPa 21 | technetium | 1.29 GPa (based on 21 values; 28 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median tensile yield strength 140 MPa
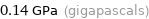
0.14 GPa (gigapascals)
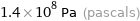
1.4×10^8 Pa (pascals)

1.4×10^8 N/m^2 (newtons per square meter)
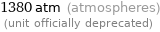
1380 atm (atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)

20300 psi (pounds-force per square inch)
Comparisons for median tensile yield strength 140 MPa
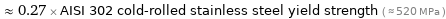
≈ 0.27 × AISI 302 cold-rolled stainless steel yield strength ( ≈ 520 MPa )
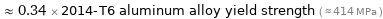
≈ 0.34 × 2014-T6 aluminum alloy yield strength ( ≈ 414 MPa )

≈ 0.56 × ASTM A36 structural steel yield strength ( ≈ 250 MPa )