Input interpretation
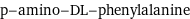
p-amino-DL-phenylalanine
Chemical names and formulas
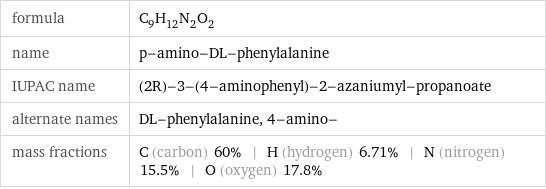
formula | C_9H_12N_2O_2 name | p-amino-DL-phenylalanine IUPAC name | (2R)-3-(4-aminophenyl)-2-azaniumyl-propanoate alternate names | DL-phenylalanine, 4-amino- mass fractions | C (carbon) 60% | H (hydrogen) 6.71% | N (nitrogen) 15.5% | O (oxygen) 17.8%
Lewis structure
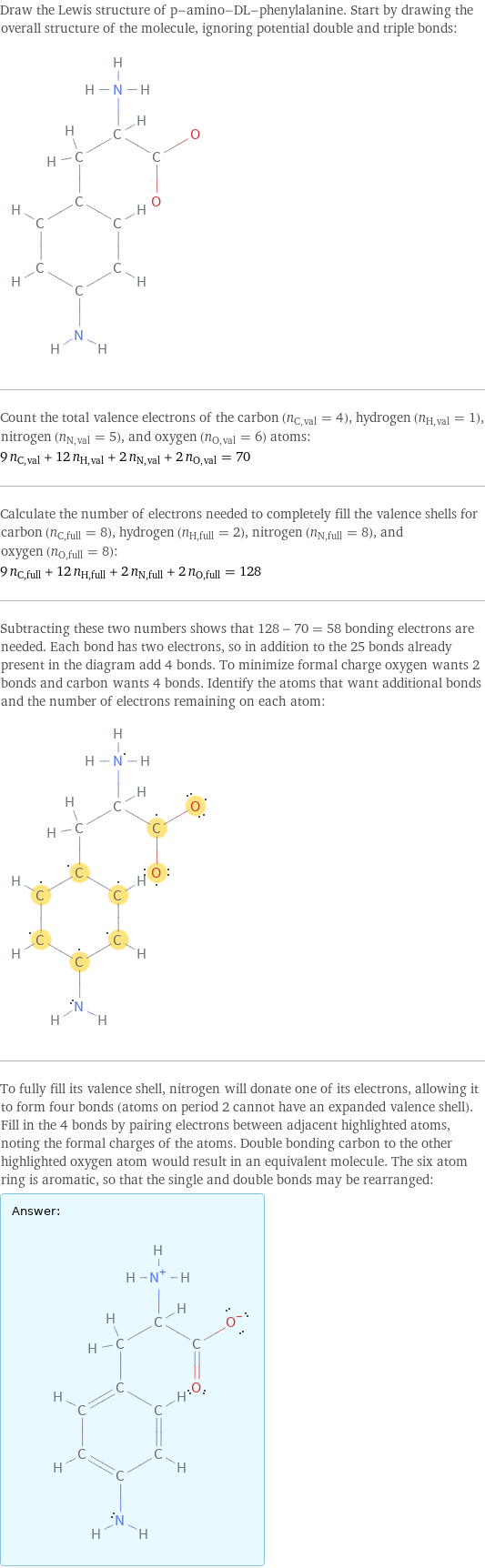
Draw the Lewis structure of p-amino-DL-phenylalanine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 9 n_C, val + 12 n_H, val + 2 n_N, val + 2 n_O, val = 70 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 9 n_C, full + 12 n_H, full + 2 n_N, full + 2 n_O, full = 128 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 128 - 70 = 58 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 25 bonds already present in the diagram add 4 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: To fully fill its valence shell, nitrogen will donate one of its electrons, allowing it to form four bonds (atoms on period 2 cannot have an expanded valence shell). Fill in the 4 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding carbon to the other highlighted oxygen atom would result in an equivalent molecule. The six atom ring is aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
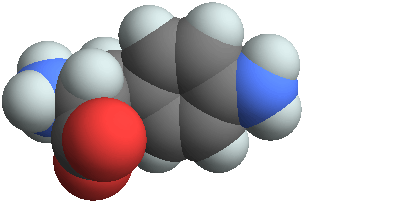
3D structure
Basic properties
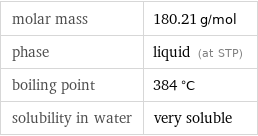
molar mass | 180.21 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) boiling point | 384 °C solubility in water | very soluble
Units

Liquid properties (at STP)
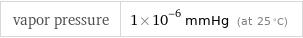
vapor pressure | 1×10^-6 mmHg (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties

molar heat of vaporization | 66.7 kJ/mol specific heat of vaporization | 0.37 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
![CAS number | 2922-41-0 Beilstein number | 2723207 PubChem CID number | 7135682 SMILES identifier | C1=CC(=CC=C1CC(C(=O)[O-])[NH3+])N InChI identifier | InChI=1/C9H12N2O2/c10-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)5-8(11)9(12)13/h1-4, 8H, 5, 10-11H2, (H, 12, 13)/t8-/m1/s1/f/h11H EU number | 220-869-1 NSC number | 29446](../image_source/dcc9c79a31e68039e4f1f737640ddd15.png)
CAS number | 2922-41-0 Beilstein number | 2723207 PubChem CID number | 7135682 SMILES identifier | C1=CC(=CC=C1CC(C(=O)[O-])[NH3+])N InChI identifier | InChI=1/C9H12N2O2/c10-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)5-8(11)9(12)13/h1-4, 8H, 5, 10-11H2, (H, 12, 13)/t8-/m1/s1/f/h11H EU number | 220-869-1 NSC number | 29446
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 1 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties

flash point | 186 °C