Input interpretation
thiocyanate anion
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of thiocyanate anion. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and sulfur (n_S, val = 6) atoms, including the net charge: n_C, val + n_N, val + n_S, val - n_charge = 16 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and sulfur (n_S, full = 8): n_C, full + n_N, full + n_S, full = 24 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 24 - 16 = 8 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 2 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge sulfur wants 2 bonds, nitrogen wants 3 bonds, and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom. The net charge has been given to the most electronegative atom, sulfur: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms, noting the formal charges of the atoms: Answer: | |
General properties
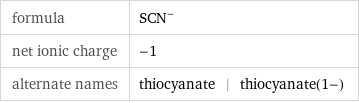
formula | (SCN)^- net ionic charge | -1 alternate names | thiocyanate | thiocyanate(1-)
Other properties

ion class | anions | polyatomic ions common sources of ion | tetrabutylammonium thiocyanate (1 eq) | sodium thiocyanate (1 eq) | lithium thiocyanate hydrate (1 eq) | cobalt dithiocyanate (2 eq) | calcium thiocyanate tetrahydrate (2 eq) | barium thiocyanate hydrate (2 eq)
Thermodynamic properties
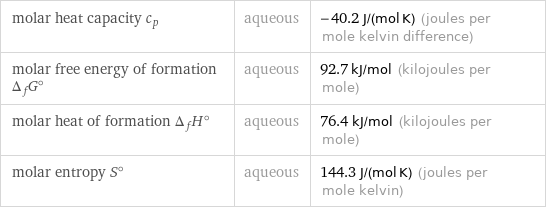
molar heat capacity c_p | aqueous | -40.2 J/(mol K) (joules per mole kelvin difference) molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | aqueous | 92.7 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | aqueous | 76.4 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) molar entropy S° | aqueous | 144.3 J/(mol K) (joules per mole kelvin)