Input interpretation
bromoethane-1, 1-d 2
Chemical names and formulas
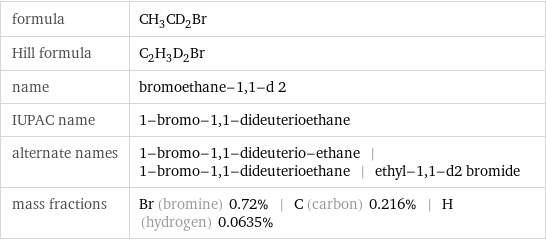
formula | CH_3CD_2Br Hill formula | C_2H_3D_2Br name | bromoethane-1, 1-d 2 IUPAC name | 1-bromo-1, 1-dideuterioethane alternate names | 1-bromo-1, 1-dideuterio-ethane | 1-bromo-1, 1-dideuterioethane | ethyl-1, 1-d2 bromide mass fractions | Br (bromine) 0.72% | C (carbon) 0.216% | H (hydrogen) 0.0635%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of bromoethane-1, 1-d 2. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the bromine (n_Br, val = 7), carbon (n_C, val = 4), and hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: n_Br, val + 2 n_C, val + 5 n_H, val = 20 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for bromine (n_Br, full = 8), carbon (n_C, full = 8), and hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): n_Br, full + 2 n_C, full + 5 n_H, full = 34 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 34 - 20 = 14 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 7 bonds and hence 14 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 20 - 14 = 6 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
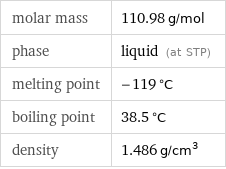
molar mass | 110.98 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | -119 °C boiling point | 38.5 °C density | 1.486 g/cm^3
Units

Liquid properties (at STP)
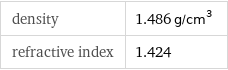
density | 1.486 g/cm^3 refractive index | 1.424
Units

Non-standard atom properties

H-2 | 2
Chemical identifiers
CAS number | 3652-84-4 PubChem CID number | 12112954 PubChem SID number | 24872137 SMILES identifier | CCBr InChI identifier | InChI=1/C2H5Br/c1-2-3/h2H2, 1H3/i2D2 MDL number | MFCD00190387
Safety properties

flash point | -23.33 °C