Input interpretation

period 2 elements | thermal conductivity
Summary
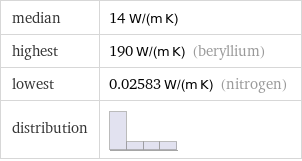
median | 14 W/(m K) highest | 190 W/(m K) (beryllium) lowest | 0.02583 W/(m K) (nitrogen) distribution |
Units

Ranked values
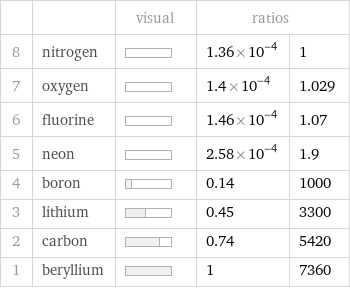
| | visual | ratios | 8 | nitrogen | | 1.36×10^-4 | 1 7 | oxygen | | 1.4×10^-4 | 1.029 6 | fluorine | | 1.46×10^-4 | 1.07 5 | neon | | 2.58×10^-4 | 1.9 4 | boron | | 0.14 | 1000 3 | lithium | | 0.45 | 3300 2 | carbon | | 0.74 | 5420 1 | beryllium | | 1 | 7360
Thermal conductivity rankings
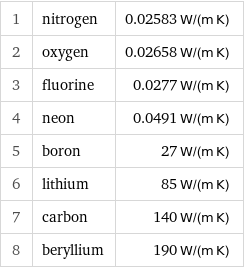
1 | nitrogen | 0.02583 W/(m K) 2 | oxygen | 0.02658 W/(m K) 3 | fluorine | 0.0277 W/(m K) 4 | neon | 0.0491 W/(m K) 5 | boron | 27 W/(m K) 6 | lithium | 85 W/(m K) 7 | carbon | 140 W/(m K) 8 | beryllium | 190 W/(m K)
Unit conversions for median thermal conductivity 14 W/(m K)

14 W/(m °C) (watts per meter degree Celsius difference)
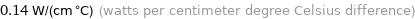
0.14 W/(cm °C) (watts per centimeter degree Celsius difference)

0.14 W/(cm K) (watts per centimeter kelvin difference)

1.4×10^6 erg/(cm K s) (ergs per centimeter kelvin difference second)

0.65 BTU_IT in/(h in^2 °F) (IT British thermal unit inches per hour square inch degree Fahrenheit difference)

7.8 BTU_IT ft/(h ft^2 °F) (IT British thermal unit feet per hour square foot degree Fahrenheit difference)

0.032 cal_th cm/(s cm^2 °C) (thermochemical calorie centimeters per second square centimeter degree Celsius difference)
Comparisons for median thermal conductivity 14 W/(m K)
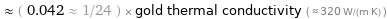
≈ ( 0.042 ≈ 1/24 ) × gold thermal conductivity ( ≈ 320 W/(m K) )

≈ ( 0.097 ≈ 1/10 ) × carbon thermal conductivity ( ≈ 140 W/(m K) )
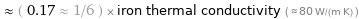
≈ ( 0.17 ≈ 1/6 ) × iron thermal conductivity ( ≈ 80 W/(m K) )