Input interpretation

selenium tetrachloride
Chemical names and formulas
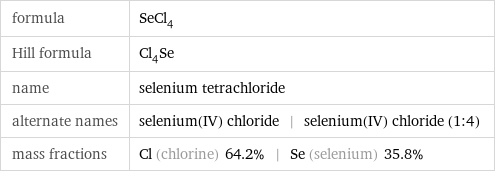
formula | SeCl_4 Hill formula | Cl_4Se name | selenium tetrachloride alternate names | selenium(IV) chloride | selenium(IV) chloride (1:4) mass fractions | Cl (chlorine) 64.2% | Se (selenium) 35.8%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of selenium tetrachloride. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the chlorine (n_Cl, val = 7) and selenium (n_Se, val = 6) atoms: 4 n_Cl, val + n_Se, val = 34 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for chlorine (n_Cl, full = 8) and selenium (n_Se, full = 8): 4 n_Cl, full + n_Se, full = 40 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 40 - 34 = 6 bonding electrons are needed, which are already accounted for in the structure. Note that the valence shell of selenium has been expanded. After accounting for the expanded valence, there are 4 bonds and hence 8 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 34 - 8 = 26 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
Basic properties
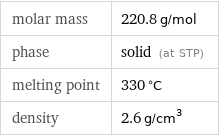
molar mass | 220.8 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 330 °C density | 2.6 g/cm^3
Units

Solid properties (at STP)
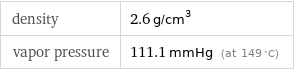
density | 2.6 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 111.1 mmHg (at 149 °C)
Units

Chemical identifiers
(Cl)Cl InChI identifier | InChI=1/Cl4Se/c1-5(2, 3)4 RTECS number | VS7875000 MDL number | MFCD00011225](../image_source/22d9665f9676af95a4bd7fd4c76b756e.png)
CAS number | 10026-03-6 PubChem CID number | 66205 PubChem SID number | 24859372 SMILES identifier | Cl[Se](Cl)(Cl)Cl InChI identifier | InChI=1/Cl4Se/c1-5(2, 3)4 RTECS number | VS7875000 MDL number | MFCD00011225
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 2 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | other